Featured Stories
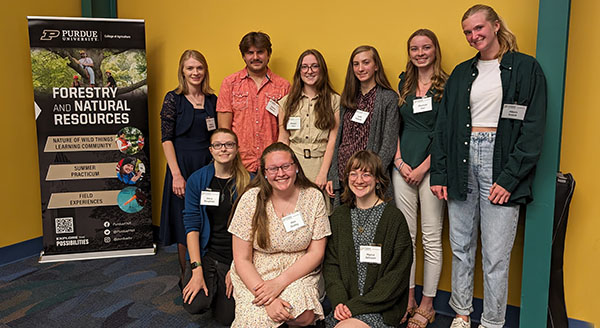
FNR Celebrates Students at Annual Awards, Scholarship Ceremony
Purdue Forestry and Natural Resources recognized the department’s student award and...

For the love of the land
2016 was the first time that Jalyn Gearries, a Natural Resources and Environmental Science (NRES)...

Purdue Agriculture’s Sloan Scholars
The Sloan Indigenous Graduate Partnership (SIGP) is an organization of 11 universities funded by...

Purdue agriculture professors named AAAS Fellows
Purdue College of Agriculture professors Songlin Fei and Tesfaye Mengiste have been named fellows...
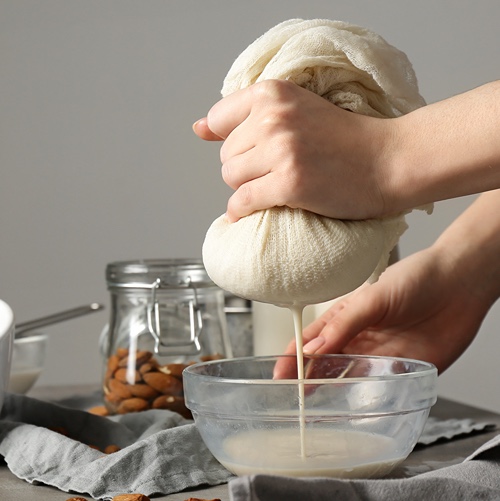

Homemade nut-based dairy analogs raise questions about bacterial risks
Many consumers know the food safety risks of dairy products, eggs and raw meat. But they are less...
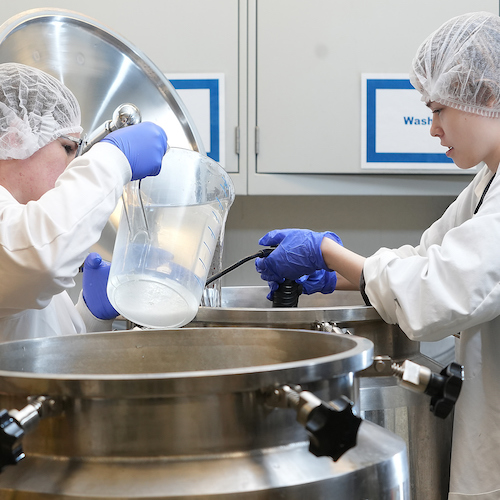

CH4 Global partners with Food Entrepreneurship and Manufacturing Institute to combat methane emissions in the cattle industry
The Food Entrepreneurship and Manufacturing Institute (FEMI), housed within Purdue...