The Empire State Building, the Pentagon, the National Cathedral and Yankee Stadium: these historic landmarks were all constructed with limestone from Monroe and Lawrence counties in Indiana. The consistent and chemically pure sedimentary rock helped Bedford earn its reputation as “The Limestone Capital of the World.” However, humans are not the only creatures that enjoy structures created from Southern Indiana’s limestone.
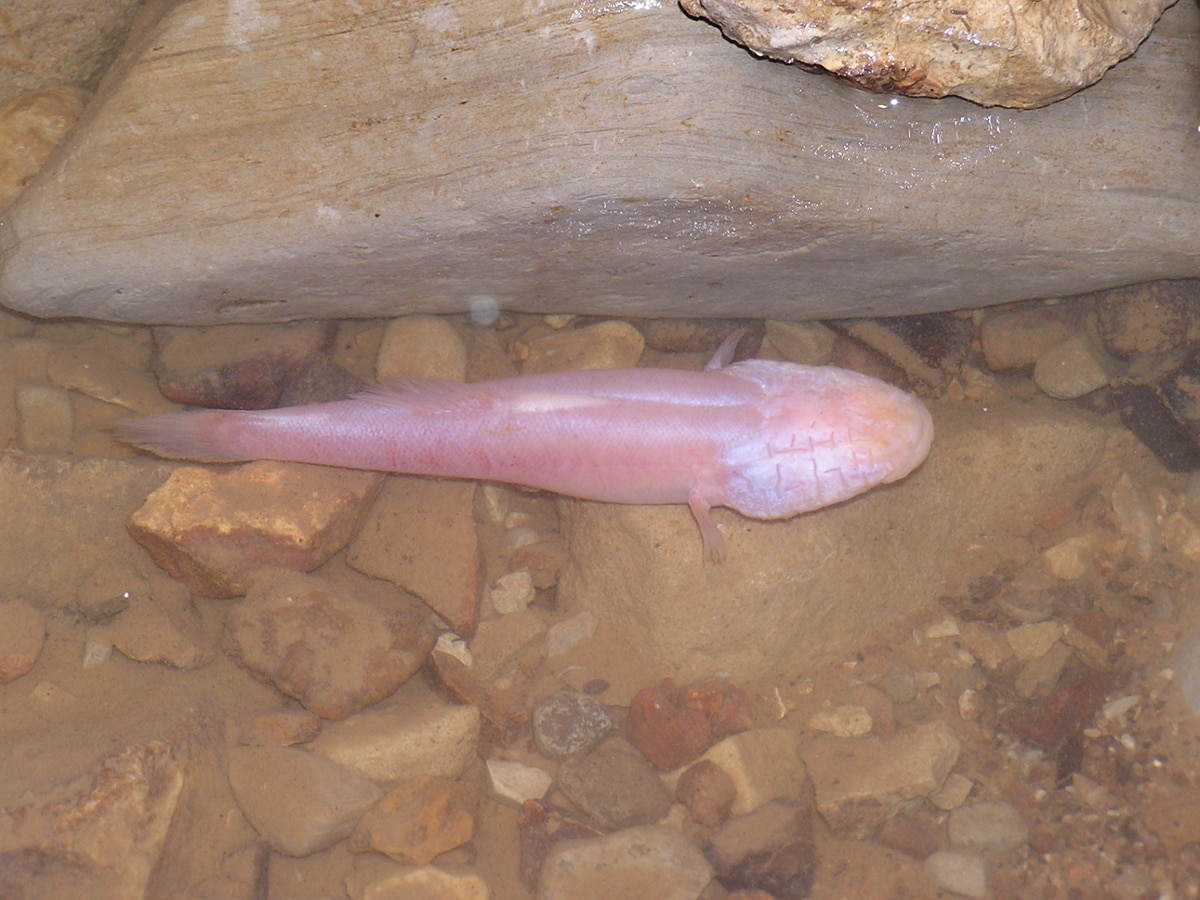
Bedford’s Bluespring Caverns house more than 20 different animal species, a rare level of subterranean biodiversity. The area’s limestone caves also host the longest navigable underground river in the United States. A new and endangered species, the Hoosier cavefish (Amblyopsis hoosieri), lives in the river and its tributaries.
“Hoosier cavefish have a lifespan of 15-to-20 years,” shared Lawrence County Extension educator Ophelia Davis. “To live that long underground with no sunlight, they had to make some significant adaptations.”
Without sunlight, cavefish have no need for pigmentation. When exposed to light, their blood’s hemoglobin gives them a light pink color. Also, like most other cavefish, Hoosier cavefish lack developed eyes.
“The other senses of cavefish are heightened to help them since they can’t see, similar to when a human loses a sense,” explained Davis.
Cavefish compensate for their lack of sight with increased sensitivity to vibrations. Their bumpy rows of sensory papillae help them navigate through the darkness.
Because the temperature of a cave rarely fluctuates more than a degree, cavefish do not need to adjust to variations in heat.
Food scarcity can be problematic for cavefish so they have developed a low metabolic rate. If needed, their fat reserves can sustain them for long periods between meals. Despite only averaging a few inches in length, Hoosier cavefish are the apex predator in their subterranean food chain. They mainly eat small crustaceans.
The Hoosier cavefish was first described in 2014, making it the first new species of amblyopsid cavefish discovered in 40 years. Until then, Hoosier cavefish were thought to be the same as the Northern cavefish (Amblyopsis spelaea) found in Kentucky’s caves. Recent research proved that Hoosier cavefish above the Ohio River are different than their neighbors to the south. Though they look similar, studies showed there are genetic differences between the two and that Hoosier cavefish tend to have more robust bodies.
“You don’t often think about the miles of caves right below your feet when you are in Lawrence County, but there is a whole ecosystem full of living organisms,” said Davis. “There is a whole world to learn about and explore.”Food scarcity can be problematic for cavefish so they have developed a low metabolic rate. If needed, their fat reserves can sustain them for long periods between meals. Despite only averaging a few inches in length, Hoosier cavefish are the apex predator in their subterranean food chain. They mainly eat small crustaceans.
The Hoosier cavefish was first described in 2014, making it the first new species of amblyopsid cavefish discovered in 40 years. Until then, Hoosier cavefish were thought to be the same as the Northern cavefish (Amblyopsis spelaea) found in Kentucky’s caves. Recent research proved that Hoosier cavefish above the Ohio River are different than their neighbors to the south. Though they look similar, studies showed there are genetic differences between the two and that Hoosier cavefish tend to have more robust bodies.
“You don’t often think about the miles of caves right below your feet when you are in Lawrence County, but there is a whole ecosystem full of living organisms,” said Davis. “There is a whole world to learn about and explore.”