The classic and trusted book "Fifty Common Trees of Indiana" by T.E. Shaw was published in 1956 as a user-friendly guide to local species. Nearly 70 years later, the publication has been updated through a joint effort by the Purdue Department of Forestry and Natural Resources, Indiana 4-H, and the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, and reintroduced as "An Introduction to Trees of Indiana."
A printed copy of the full publication is available for purchase for $7 in the Purdue Extension Education Store. The field guide helps identify common Indiana woodlot trees.
Each week, the Intro to Trees of Indiana web series will offer a sneak peek at one species from the book, paired with an ID That Tree video from Purdue Extension forester Lenny Farlee to help visualize each species as it stands in the woods. Threats to species health as well as also insight into the wood provided by the species, will be provided through additional resources as well as the Hardwoods of the Central Midwest exhibit of the Purdue Arboretum, if available.
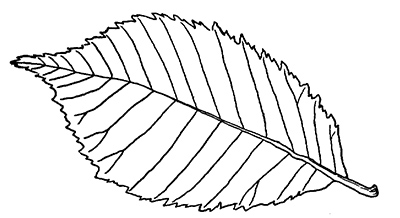 This week, we introduce the American elm or Ulmus americana.
This week, we introduce the American elm or Ulmus americana.
The American elm, also called white elm, is easily identified by its simple doubly-serrated oval leaves, which feature a large tooth with small teeth like edges on top that. The leaves are held on fine twigs, which turn a medium brown over the summer. The bark of the American elm is spongy, with strong crisscrossing ridges. When sliced open, these ridges show distinct reddish brown and light tan/white colored layers inside the bark. This is different from the dark brown and reddish-brown layers found in the bark of red elm or slippery elm.
The American elm features an open, spreading crown and drooping limbs that form a vase shape.
American elm is a common tree in many riparian forest areas or moist soil forest areas. The species used to be a common street tree in Indiana, but that number has dwindled due to Dutch elm disease, a fungal diseased which ravaged the species in the second half of the 20th century.
American elm can be found throughout the northeastern United States south to central Florida and west to central Texas and north to southeastern Saskatchewan.
According to Morton Arboretum, the American elm grows to more than 40 feet tall.
At one time, elm was a very important lumber species, and was used for barrel staves and hoops, but it has since been replaced by other materials. It was also used in children’s wagons and sleds because it did not easily splinter. It was also used for bent chair parts and the wood trim on old time steamer trunks due to its  ability to bend.
ability to bend.
According to the Wood Database, American elm is commonly used to make boxes, baskets, furniture, hockey sticks, veneer, wood pulp and in papermaking.
Boards 2, 3 and 5 of the wood panels shown at right are American elm. Board 1 is a heavy rock elm. Boards 1 and 3 are high quality examples of wood panels from the elm species. Boards 4 and 6 are red elm.
Other Resources:
American Elm in the Hardwoods of the Central Midwest database
Elm in the Hardwood Lumber and Veneer Series
Fifty Trees of the Midwest app for the iPhone
Native Trees of the Midwest
Shrubs and Woody Vines of Indiana and the Midwest
ID That Tree YouTube playlist
Woodland Management Moment YouTube playlist
Investing in Indiana Woodlands
Forest Improvement Handbook