The classic and trusted book "Fifty Common Trees of Indiana" by T.E. Shaw was published in 1956 as a user-friendly guide to local species. Nearly 70 years later, the publication has been updated through a joint effort by the Purdue Department of Forestry and Natural Resources, Indiana 4-H, and the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, and reintroduced as "An Introduction to Trees of Indiana."
A printed copy of the full publication is available for purchase for $7 in the Purdue Extension Education Store. The field guide helps identify common Indiana woodlot trees.
Each week, the Intro to Trees of Indiana web series will offer a sneak peek at one species from the book, paired with an ID That Tree video from Purdue Extension forester Lenny Farlee to help visualize each species as it stands in the woods. Threats to species health as well as also insight into the wood provided by the species, will be provided through additional resources as well as the Hardwoods of the Central Midwest exhibit of the Purdue Arboretum, if available.
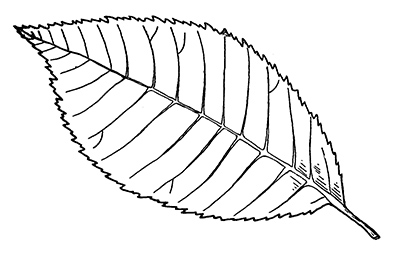 This week, we introduce the slippery elm or Ulmus rubra.
This week, we introduce the slippery elm or Ulmus rubra.
The slippery elm, also called red elm, is easily identified by its doubly-serrated simple leaves on short leaf stems, with a sandpapery upper surface. The bark features strong vertical ridges, which when sliced open feature alternating layers of tan and dark brown. The inner bark is slick, which gives the tree its name. The species also is called red elm due to its reddish heartwood.
Slippery elm has slightly larger leaves than its relative, the American elm, as well as a sandpapery texture on the leaves and twigs. The slippery elm is typically found more in upland areas, while the American elm is found in moist soil conditions such as valleys as well as river and creek bottoms.
Slippery elm can be found throughout much of the eastern and central United States, from Minnesota south into central Texas and as far west as central Kansas and Nebraska. Its range extends from northern Florida to Vermont along the east coast.
Like the American elm, which used to be a common street tree in Indiana, the number of slippery elms has dwindled due to Dutch elm disease, a fungal diseased which ravaged the species in the second half of the 20th century. Another disease called Elm Yellows (formerly phloem necrosis) also seriously affected slippery elms.
According to Morton Arboretum, the slippery elm grows to between 40 and 60 feet tall.
In contrast to slippery elm, the American elm has spongy bark, with strong crisscrossing ridges, which when sliced open show distinct reddish brown and light tan/white colored layers inside the bark.
According to the Wood Database, elm is commonly used to make boxes, baskets, furniture, hockey sticks, veneer, wood pulp and in papermaking. Elm is rated as one of the better woods for steam bending and is  rated intermediate in strength with 12 percent moisture content and an average weight of 36 pounds per cubic foot.
rated intermediate in strength with 12 percent moisture content and an average weight of 36 pounds per cubic foot.
Lumber from slippery elm is distinct from American and rock elm due its darker red/brown color.
Boards 4 and 6 of the wood panels shown at right are red elm. Boards 2, 3 and 5 are American elm. Board 1 is a heavy rock elm. Boards 1 and 3 are high quality examples of wood panels from the elm species.
Other Resources:
Elm in the Hardwood Lumber and Veneer Series
Fifty Trees of the Midwest app for the iPhone
Native Trees of the Midwest
Shrubs and Woody Vines of Indiana and the Midwest
ID That Tree YouTube playlist
Woodland Management Moment YouTube playlist
Investing in Indiana Woodlands
Forest Improvement Handbook