COVID-19 guarantees that the Summer of 2020 will be like none we have experienced. We will be exploring what that means in Indiana by telling the stories of Purdue Agriculture’s and Purdue Extension’s interactions with communities throughout the state. We invite you to follow our series on this Season of Change.
Farmers markets in Indiana are organized at the local level, subject to county health authorities and regulations. Under normal circumstances, these rules don’t differ much from town to town, Tamara Benjamin, assistant program leader for diversified farming and food systems for Purdue Extension, said.
In the era of COVID-19, however, the regulations dictating safety standards to vendors and visitors can vary drastically.
“In Indiana. you don’t have one guide for the entire state. Everyone wants to have local control, but that does create a lot of challenges for vendors who sell across county lines,” she continued. “One county that has had few COVID-19 instances may have different regulations in place than a county where cases are on the rise.”
While local control can complicate business operations for farmers, it also allowed many farmers markets around the state to open up, even before the state began reopening. Many markets have instituted drastic changes for the vendors, including no longer having places to sit and eat, no music, and vendors are encouraged to wear masks.
Martin Schap, market master for the Lafayette, Ind., farmers market, said they began working with the Tippecanoe County health department in March to ensure a safe opening in May.
“Initially, based on guidance from the health department, we weren’t allowed to have any vendors that sell health and beauty products, no bakeries or cut flowers. It was pretty much just produce, meat, eggs and seedlings, the strictest definition of a farmers market,” he explained.
Those guidelines were eventually relaxed as the state began to open back up, but Schap said organizers are still capping the number of people allowed in to the market at 100 and mandating vendors have hand washing stations that they use every 30 minutes.
The atmosphere of the farmers market has certainly changed, Schap added. No one lingers or socializes. It’s now more like another errand than an outing.
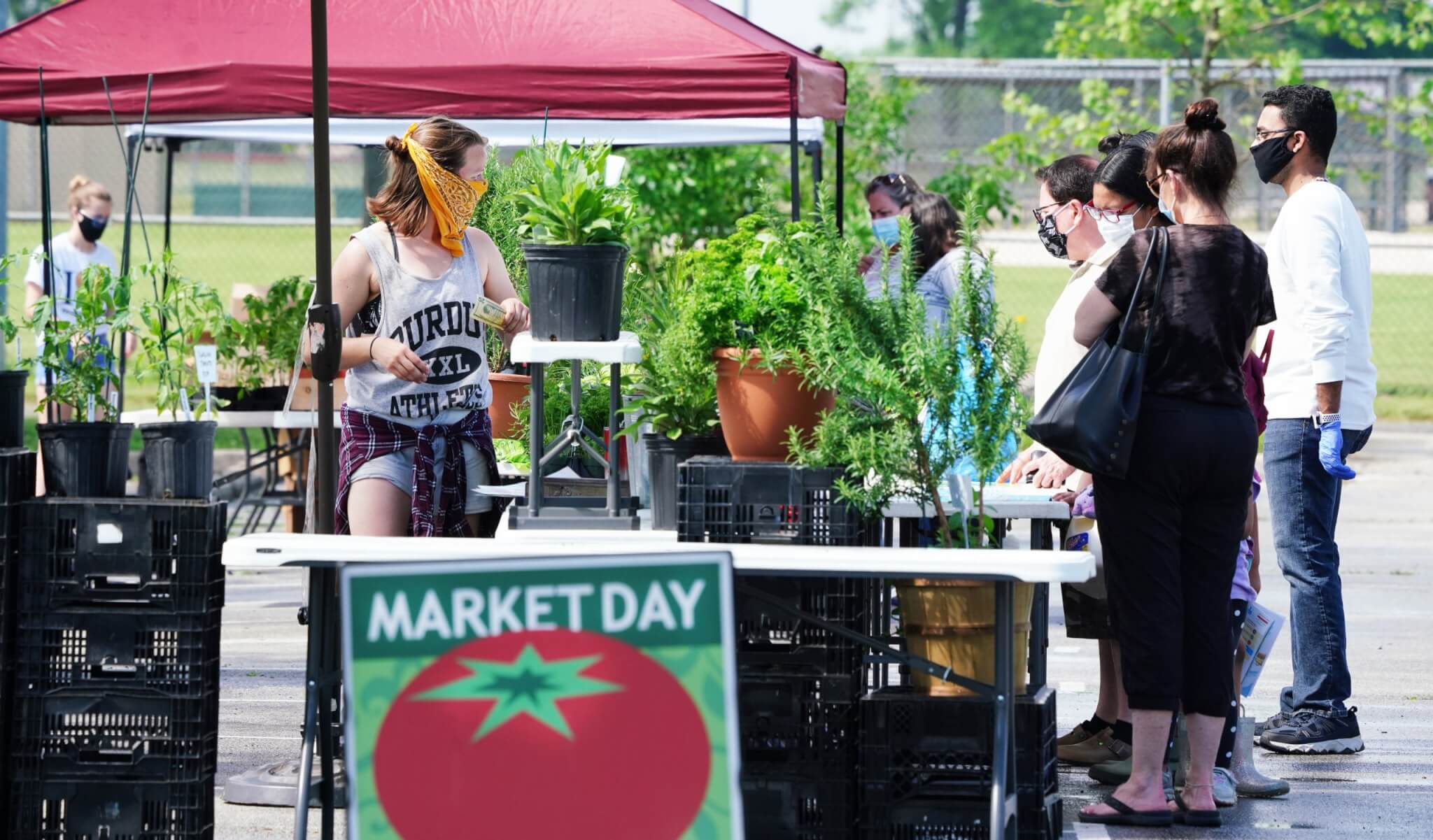

While that idea is somewhat antithetical to farmers markets, Benjamin explained, it’s a necessary adjustment during a pandemic. Farmers markets were originally conceived as a community event where locals could get to know farmers and where their food was coming from while enjoying entertainment and socializing. Now, the market environment is “get in, get your food and get out,” Benjamin observed.
Despite the challenges, keeping farmers markets open is essential for both consumers and small to medium sized farms.
“When COVID came it challenged a lot about our food supply chain,” Ariana Torres, horticulture and landscape architecture and agricultural economics assistant professor, said. “Farmers have had to pour out milk and are throwing away crops if they don’t have an outlet to sell.”
For farmers that rely on income from markets, Benjamin said they are grateful to have a place to sell but feel increasingly burdened by the mosaic of regulations they are required to follow.
“I know numerous farmers who are seriously considering getting out of farming because of all these regulations,” Benjamin said.
Schap asserts the safety of the farmers market model.
“For starters, we only do point and pick. No customer is touching any of the product before buying it. If I’m going to a large grocery store, that’s not necessarily the case,” Schap said. “We are able to have a little more control in terms of safety measures.”
Benjamin said she thinks farmers markets will adhere to stringent guidelines, but, of course, that will continue to look different for every county and town.
“It’s going to continue to morph as we get more information from the state and about the virus,” Benjamin said. “No one likes that answer, but it’s the reality.”
Friday Photo: 05/13/2022
The assignment for Purdue Natural Resources and Environmental Sciences professor Laura Bowling’s last field trip of the semester, was to collect and count invertebrates in a section of Burnett’s Creek, just north of campus. Note the reaction of students (left to right) Avery Fess, Ireland Beebe and Eva Curtis when the inch-long cranefly larvae show a little more mobility than expected.
Read Full Story >>>

