Agrivoltaics
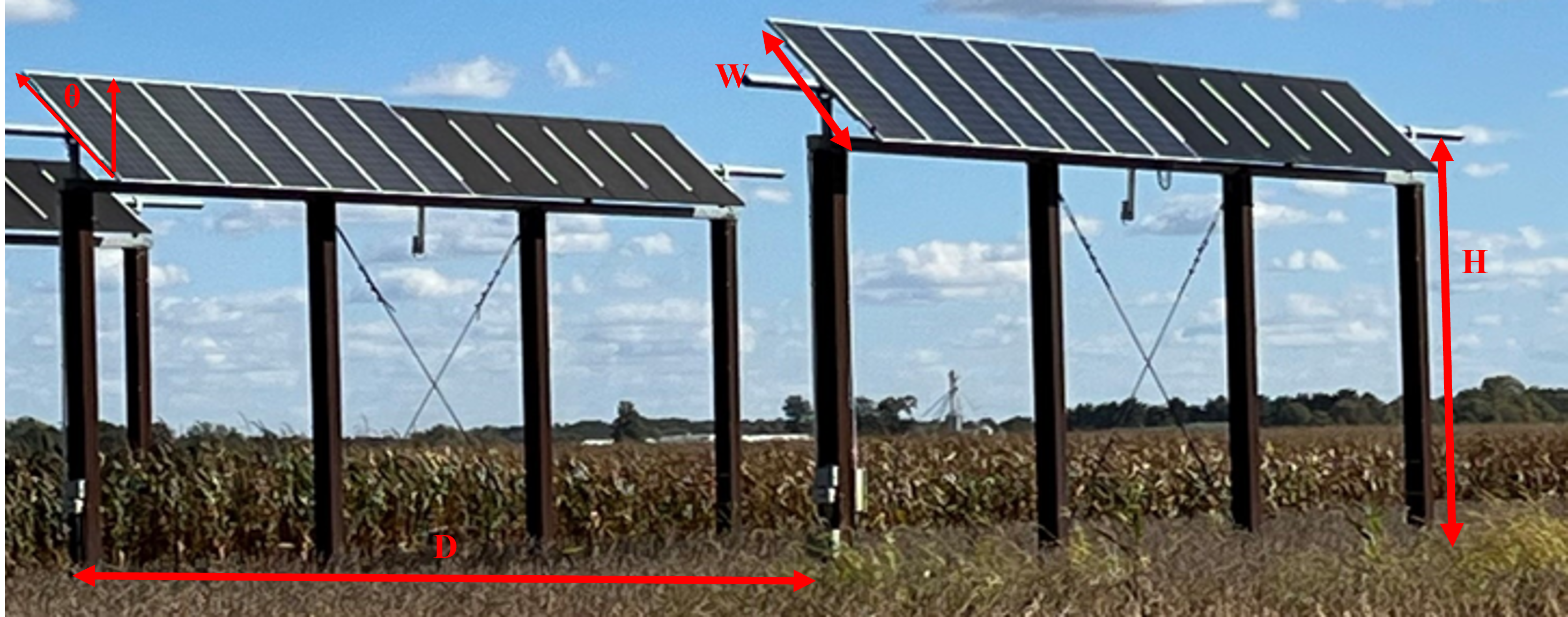
AGRIVOLTAICS RESEARCH PLATFORM (AgPV)
The Purdue AgPV research platform was built in 2019 with support from the National Science Foundation (NSF) under grants #1735282-NRT/10001536 and Purdue University.
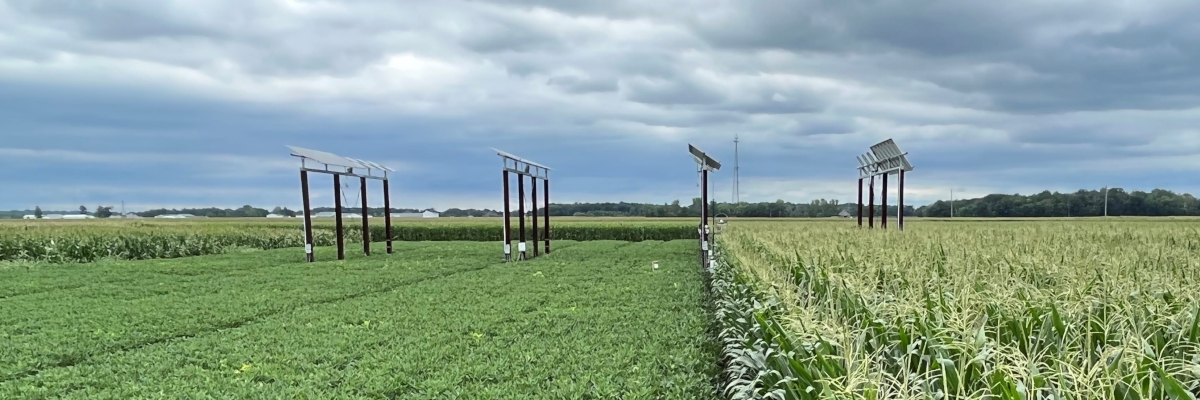

The Purdue AgPV site was divided into 5 blocks of 12 field rows per block managed as a corn-soybean rotation.
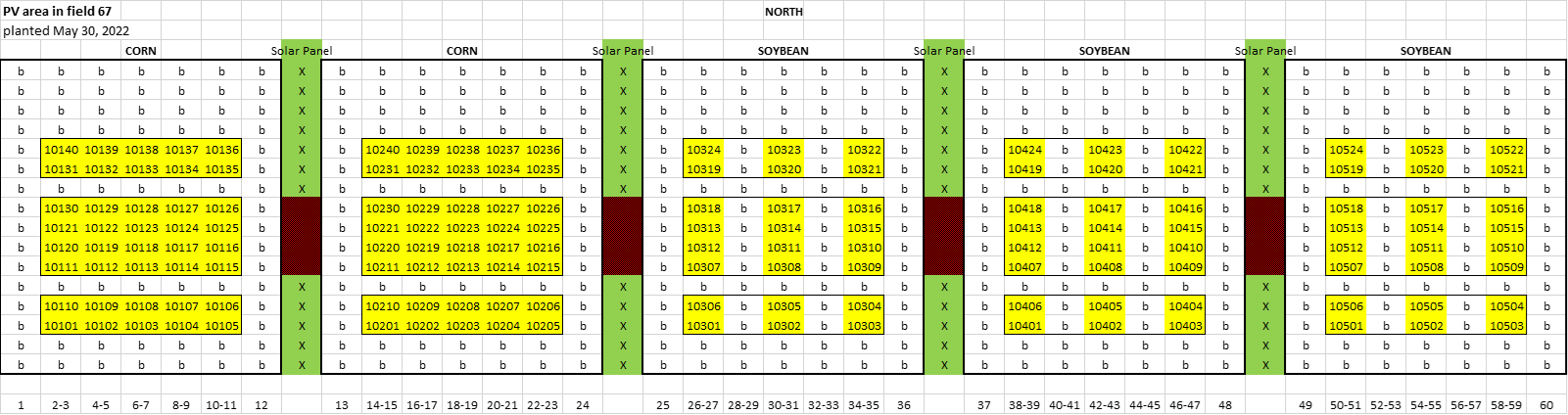
Red boxes represent solar panels
Light & Shadow
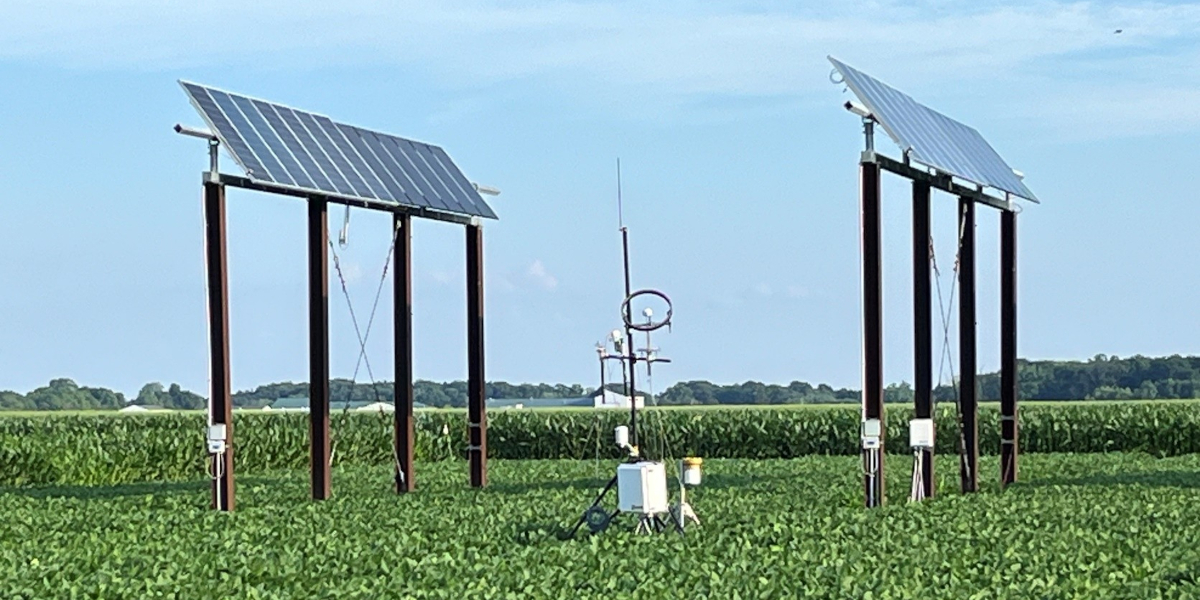
The impacts of AgPV systems on local microclimate are monitored using environmental sensors. Pyranometers and shadow-ring assemblies are used to measure direct and diffused light intensitites at plant height levels.
Direct and diffused light are measure at various locations to quantify and valuate shadow prediction models.

AgPV Systems for Agronomic Crops
Corn and soybean crops have been produced under the system since 2019 with measurements of crop production, environmental attributes, and PV performance each year.
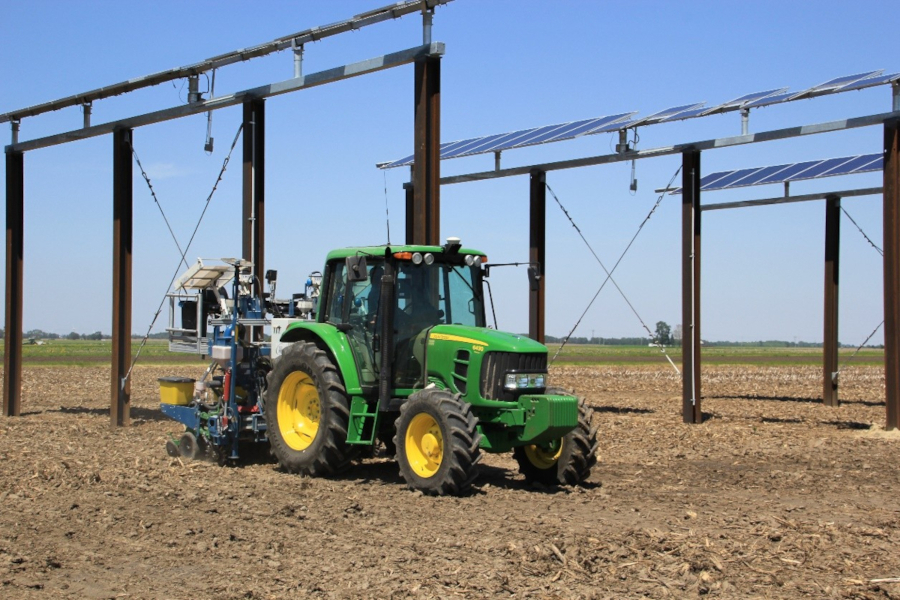

Planting with 4-row precision planter
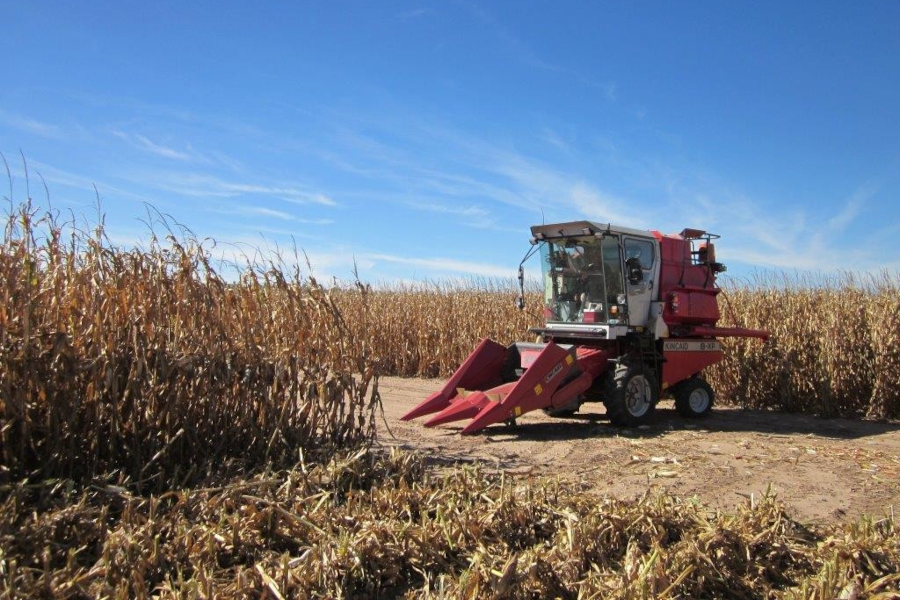

Harvesting with 2-row combine harvester
Crop Phenology Impacts
The impact of AgPV systems on crop phenology was determined by measuring anthesis and silking dates as well as plant and ear height.
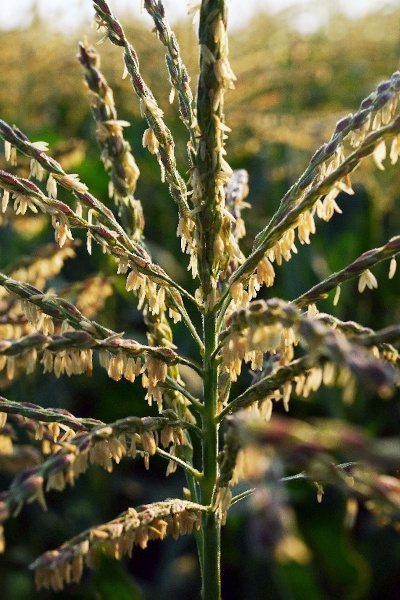

Anthesis dates
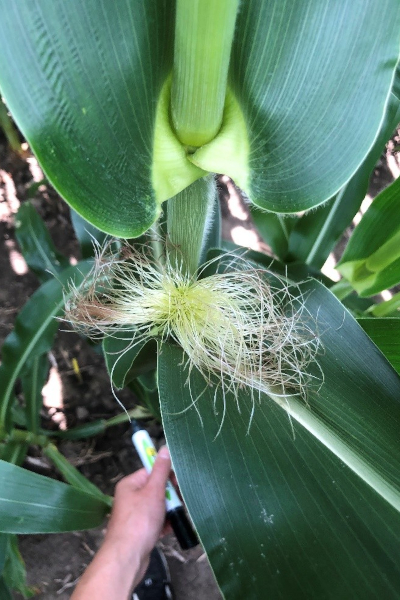

Silking dates
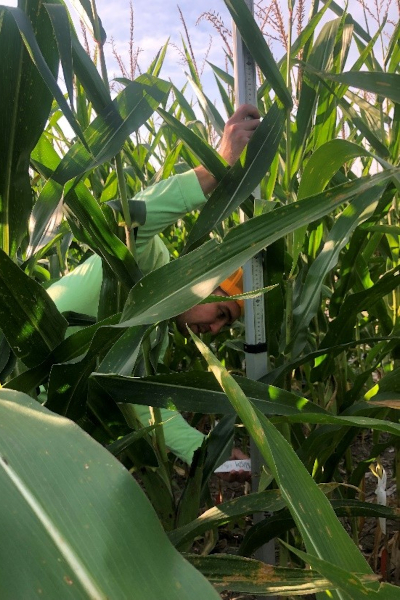

Plant and ear height
Crop Yield & Component Impacts
The impacts of AgPV systems on crop yields and yield components are determined by ear photometry.
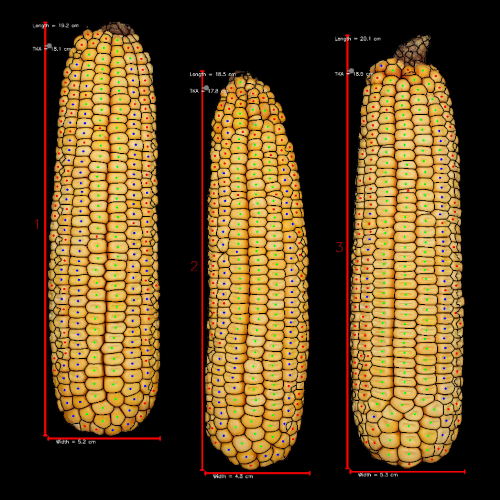


Predictions for yield, kernels per ear, kernel fill, ear length and width, ear fill
Varying Irradiance & Crop Yield
Measurements and simulations of cumulative irradiance distribution at ground level show that each plot is subject to a time varying irradiance profile, resulting in a separate profile for each plot.
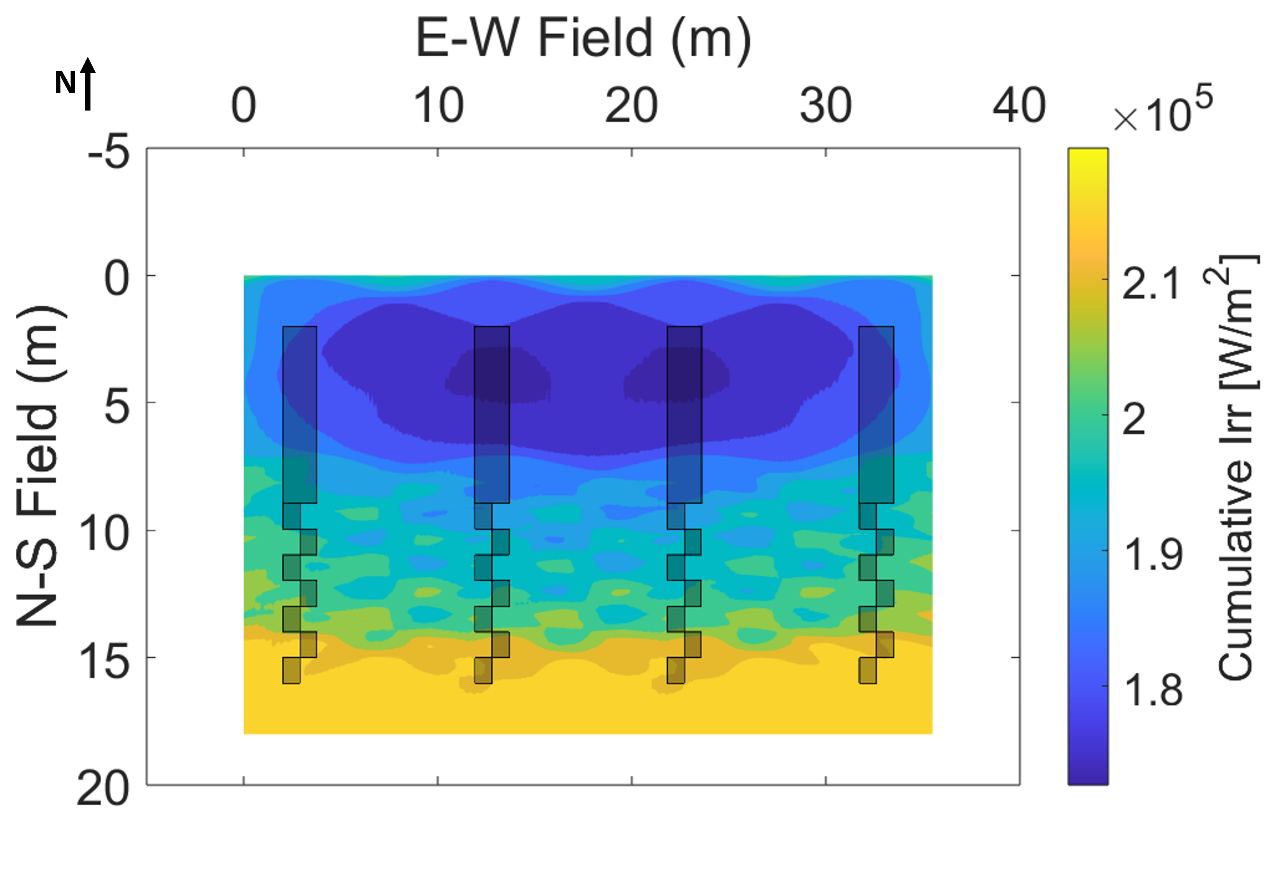
Comparison of spatial irradiance distribution at ground level.
- Analyses of corn grain yields show that soil moisture and irradiance have a significant impact on corn crop performance.
- The average drop in grain yield of corn in the fully shaded area across four years was 7.7% whiile the average shading in the same location was approximately 20%.
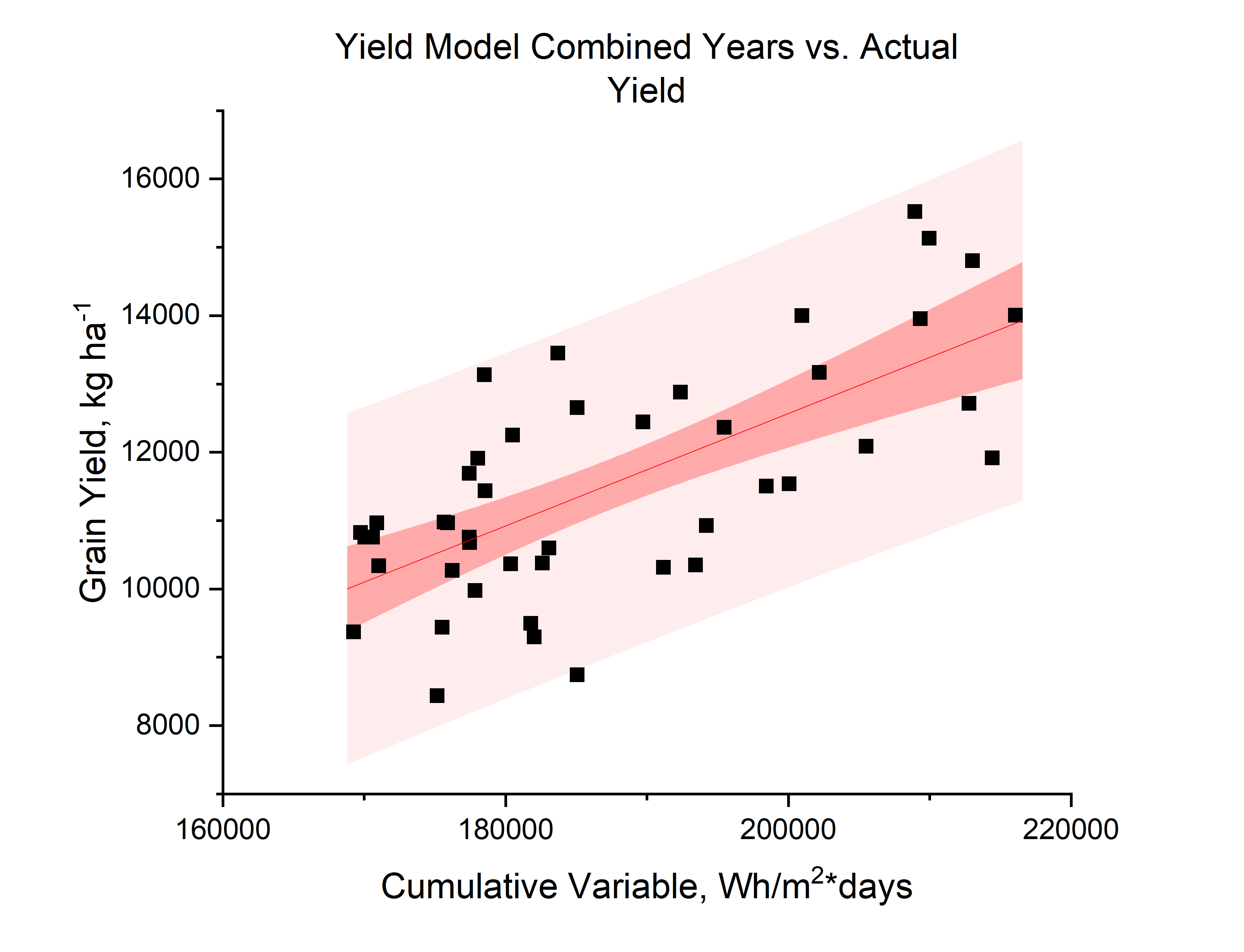
Cumulative Variable is an environmental index that integrates soil moisture and irradiance (r2 = 0.48)
Sanchez et al. Multi-Year Study of Maize Under Elevated Tracking Agrivoltaic System and Simplified Yield Modelling. Available at SSRN 4807752.
Optimizing AgPV System Performance
AgPV systems can be optimized for food or energy production through manipulation of solar tracking and anti-tracking.
Performance chart with energy generation and crop yields under various AgPV layouts:
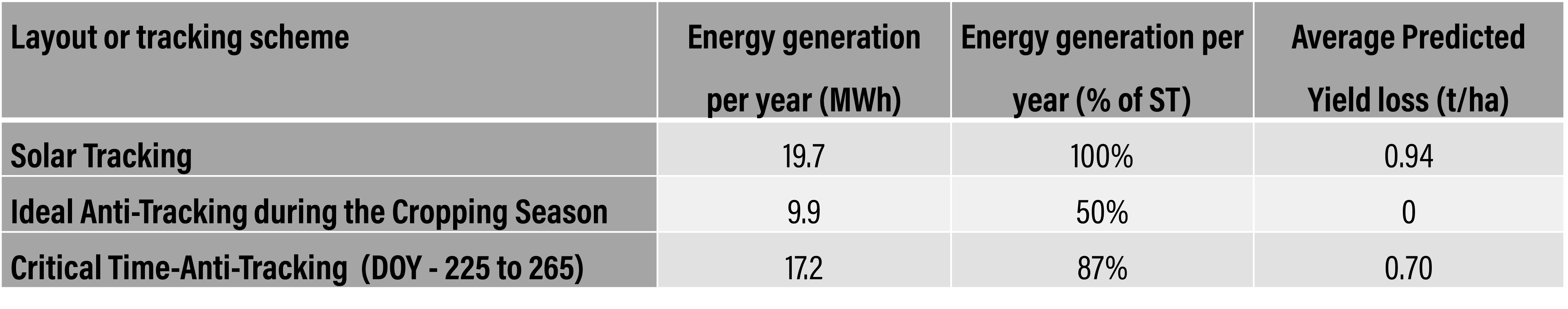
Integration of crop, shadow, and micrometeorological models have identified opportunities for near-neutral coproduction of food and energy leveraging already existing hardware for a viable pathway for widespread solar implementation throughout the contiguous United States.
Grubbs et al. (2024). Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 191, p.114018.
CONCLUSIONS
Integration of PV shadow models, micrometeorological condition analyses, and experimentally validated ray-tracing and irradiance modeling with empirical cropping system research and biophysical crop models can predict crop and energy production in AgPV systems.
Agrivoltaics Research Team

Rakesh Agrawal

Peter Bermel

Sylvie Brouder

Margaret Gitau

Juan Sesmero

