Most Prevalent Diseases
Common Diseases
- Gray mold
- Leaf spots
- Fusarium head blight
Root Diseases
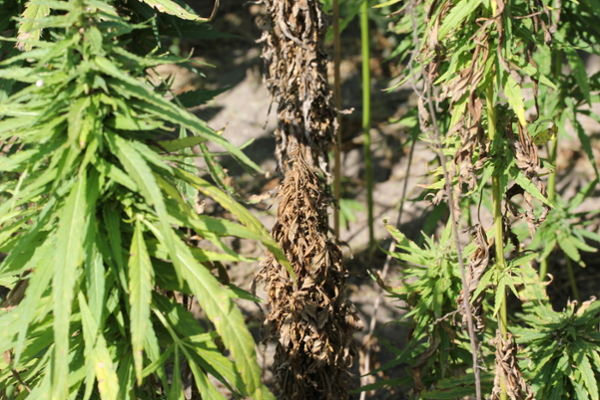
Fusarium wilt and Fusarium root rot
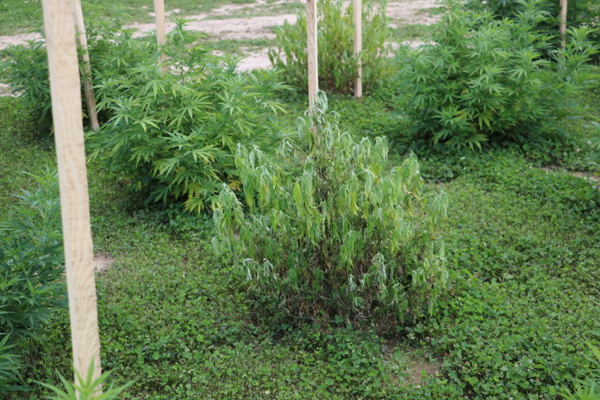
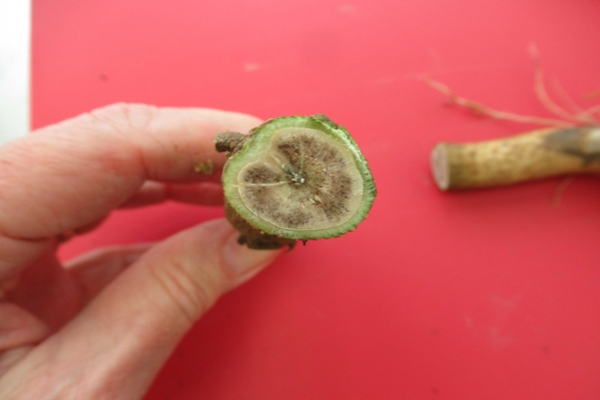
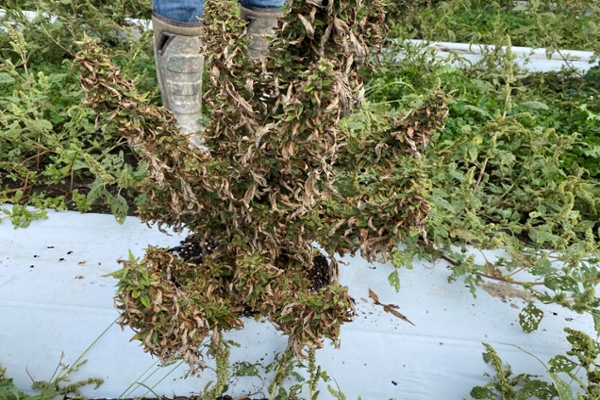
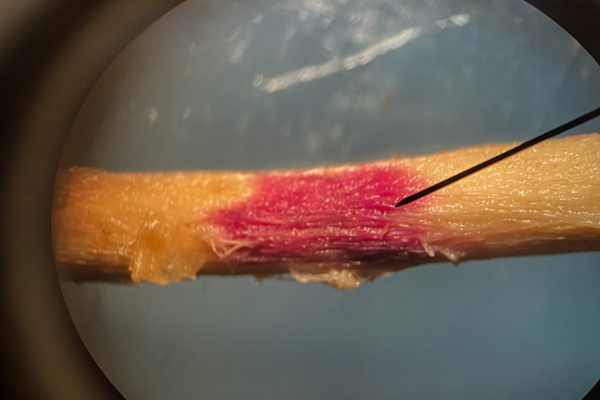
Fusarium wilt is most commonly caused by Fusarium oxysporum in the soil. Fusarium root rots are caused by many species within the genus Fusarium and are widespread in the soil. Yellow leaves are often observed first as the vascular tissue is damaged, followed by more severe wilting. Dark and sunken cankers may be visible on the stem at the soil line. Infected roots may appear pink to brown and have internal staining when cut crosswise. Warm soils with poor drainage are conducive to disease, with damaged roots and girdled roots being more prone to infection.
Pythium
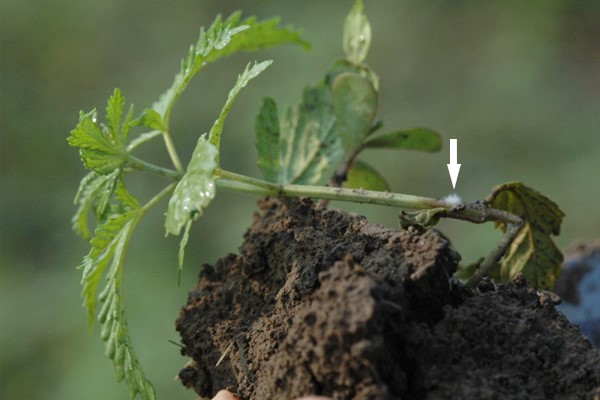
Multiple Pythium species can infect hemp. Infected plants will be stunted, yellow, and eventually wilt. Brown lesions on the stem may be visible. White, cottony mycelium growing from the plants may also be observed. Excessive rainfall and poorly drained fields are conducive to disease.
Foliar Diseases
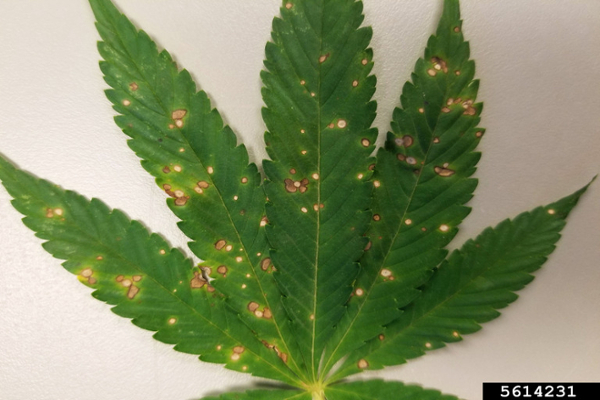
Cercospora leaf spot
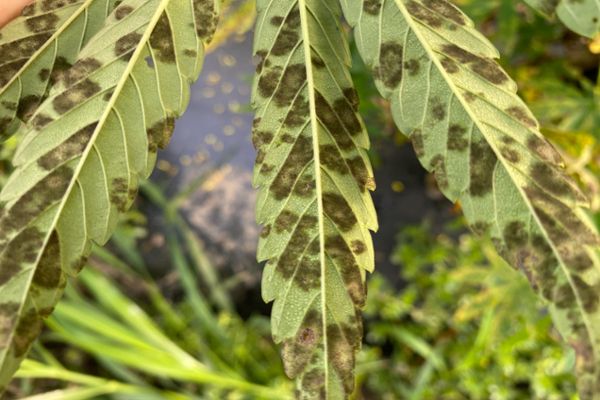
Cercospora leaf spot is caused by Cercospora cannabis and possibly other species. Lesions begin as small yellow spots that become tan to brown with a dark margin. Lesions may merge and cause larger spots. It is sometimes confused with other leaf spots. Humid and warm weather are conducive to disease.
Downy mildew
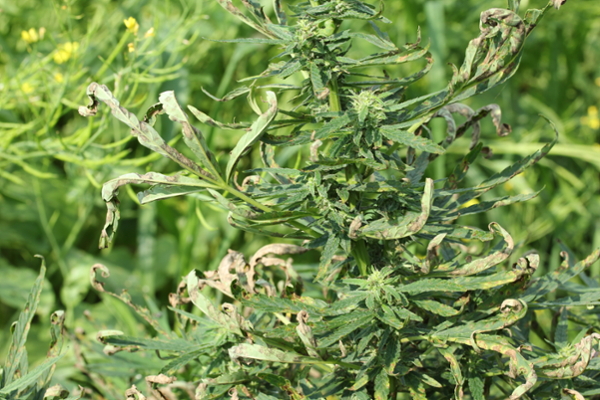
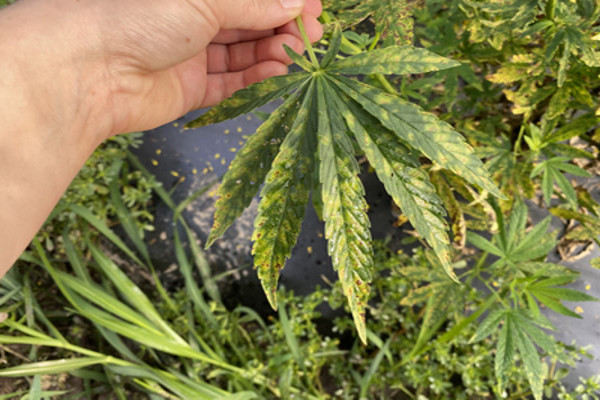
Downy mildew in hemp is caused by the pathogen Pseudoperonospora cannabina. Lesions first appear as yellow-green spots on the upper leaf surface. As lesions progress, they become angular and brown. Leaves with many lesions can become distorted and plants may defoliate. Lesions may look like chemical damage or other types of leaf spots. However, the underside of the leaves can provide a crucial sign of downy mildew. During wet periods, gray to black down-like fuzz can be observed. High humidity and free water on the leaves are conducive to disease.
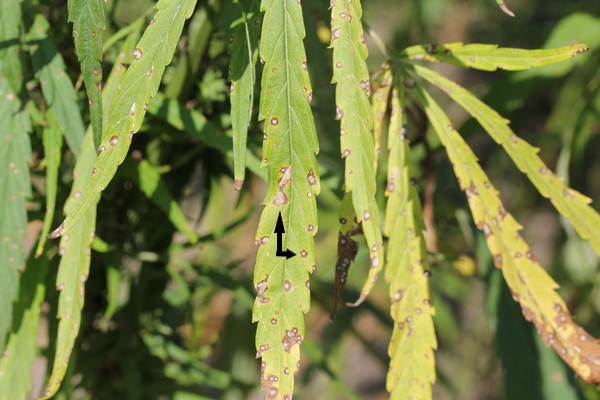
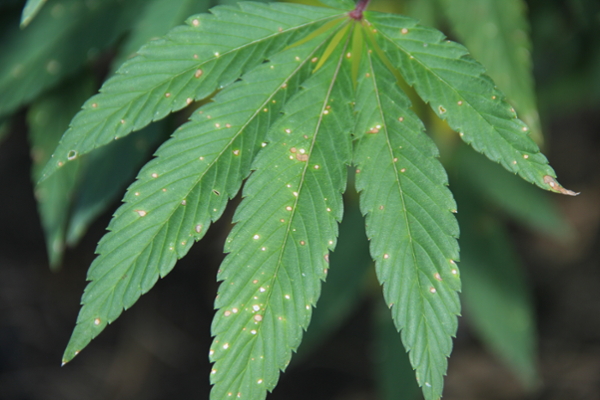
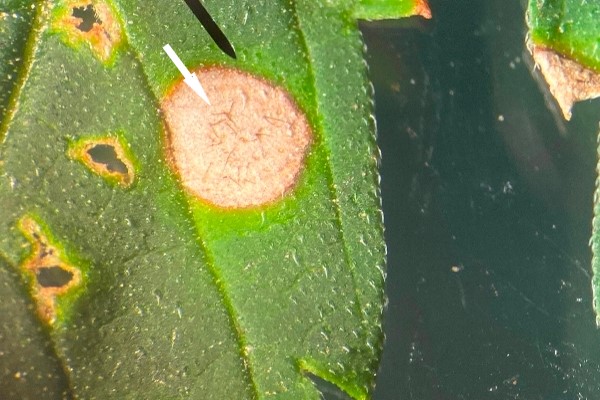
Hemp leaf spot
Hemp leaf spot sometimes called Bipolaris leaf spot is caused by Drechslera gigantea. Lesions begin as light green spots on the leaves that progress to round, white-to-tan spots. It may be confused with other leaf spots. Non-hemp plants in or near the field may be infected as well. Warm and wet conditions are conducive to disease.
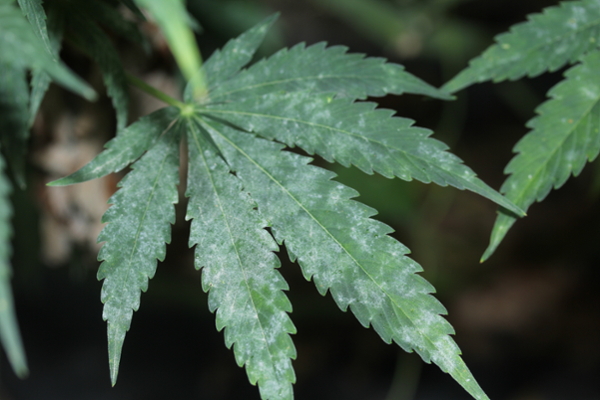
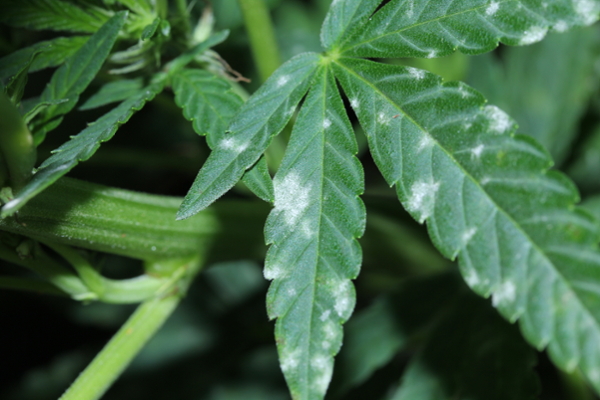
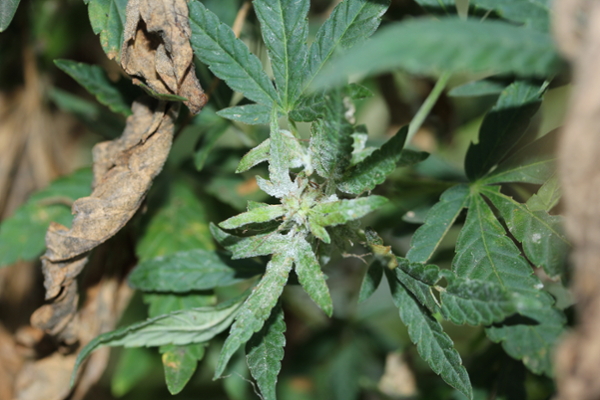
Powdery mildew
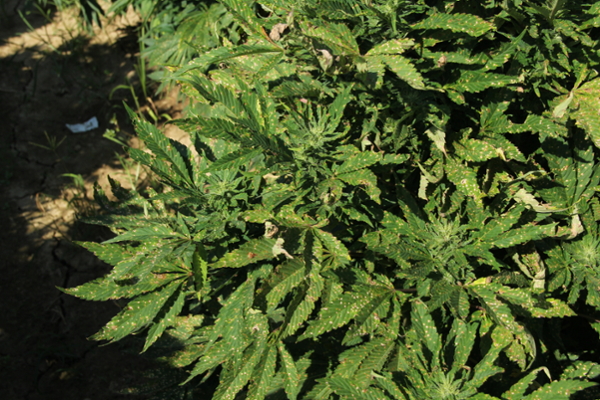
Powdery mildew in hemp is caused by multiple species from different genera. A powdery white appearance can be patchy or widespread on leaves and flowers. Warm to high daytime temperatures and humid nights, shade or low light intensity are conducive to disease.
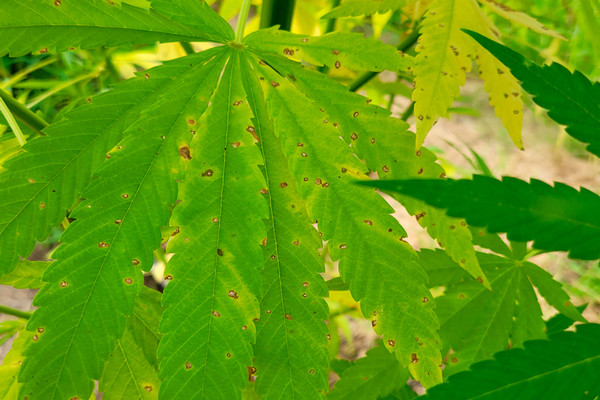
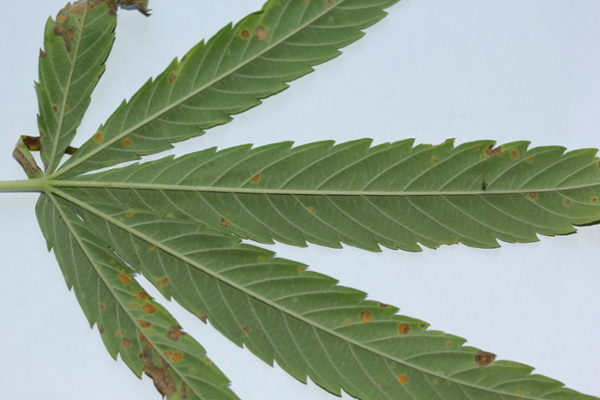
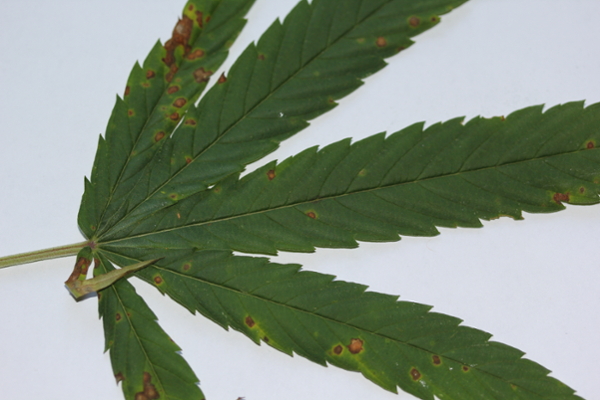
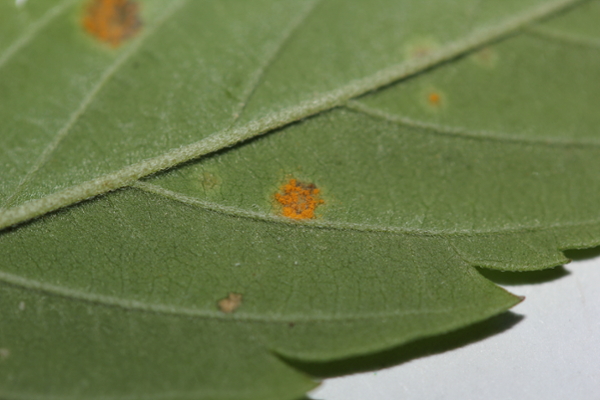
Rust
Rust on hemp is caused by the pathogen Uredo kriegeriana. Lesions appear as light to dark brown with a yellow halo on the topside of leaves. Orange pustules with visible spores are found on the underside of the leaves. Moderate temperatures and high humidity appear conducive to disease; however, the exact conditions are unknown for this species.
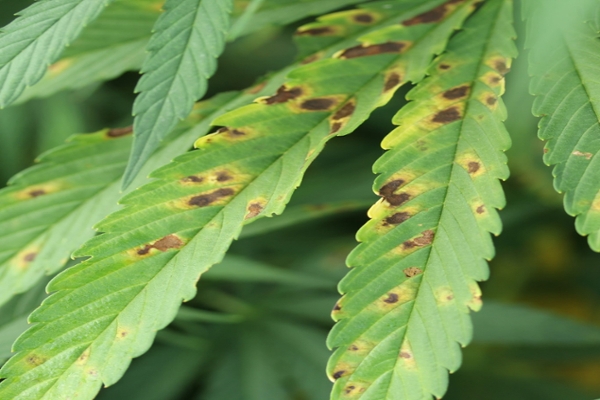
Septoria leaf spot
Septoria leaf spot on hemp is caused by Septoria cannabis. Spots begin as yellow flecks and progress to darker brown lesions with yellow halos. The disease is often observed in older leaves first. Warm, humid, and rainy conditions are conducive to disease.
Crown and Bud Diseases
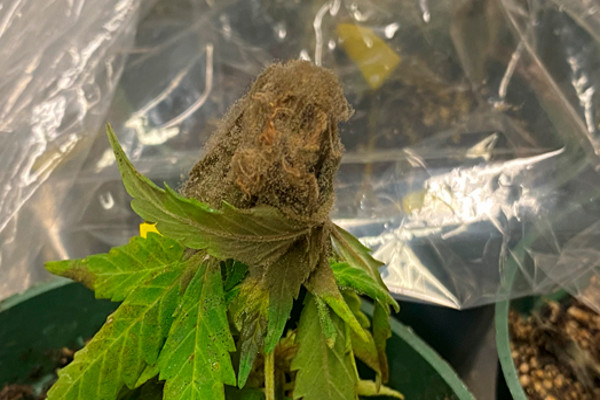
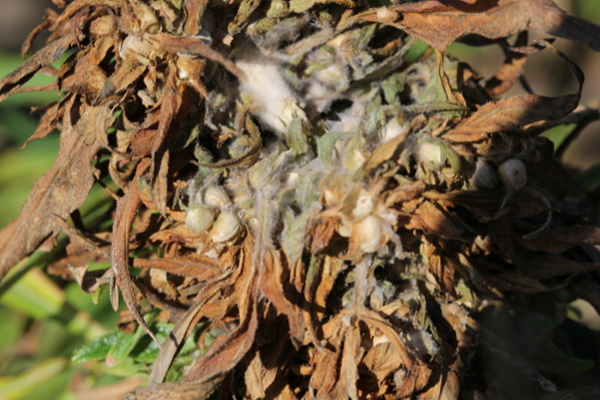
Gray mold
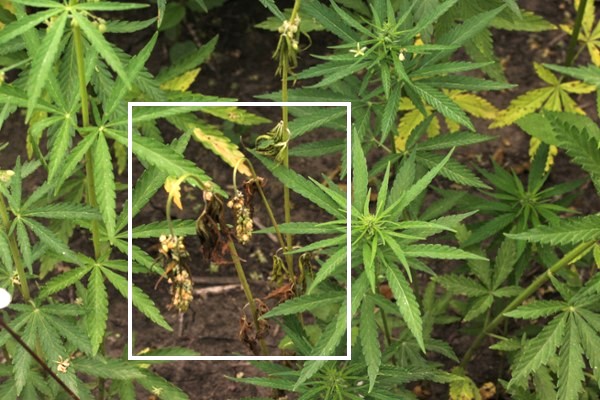
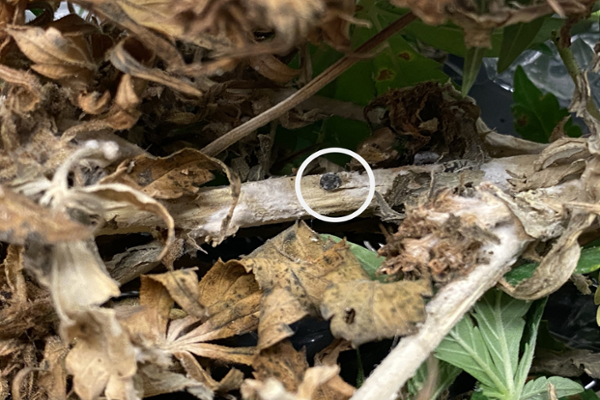
Gray mold is caused by Botrytis cinerea. Infection causes browning and dieback of grain or flower tissue and can also affect leaves, especially on injured plants. Gray mycelia may be visible and overwintering sclerotia look like rat droppings. Cloudy conditions, high humidity, and moderate temperatures are conducive to disease.
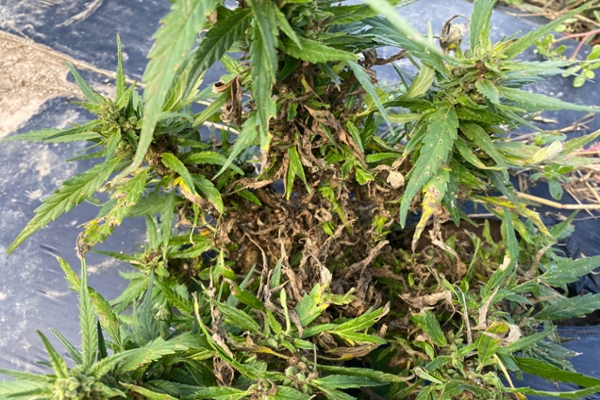
Fusarium head blight
Fusarium head blight is caused by multiple Fusarium species. Brown, dead tissue can be observed in both grain and flower structures. White mycelia growth is often observed when heads are broken open. Warm and humid conditions are conducive to disease.
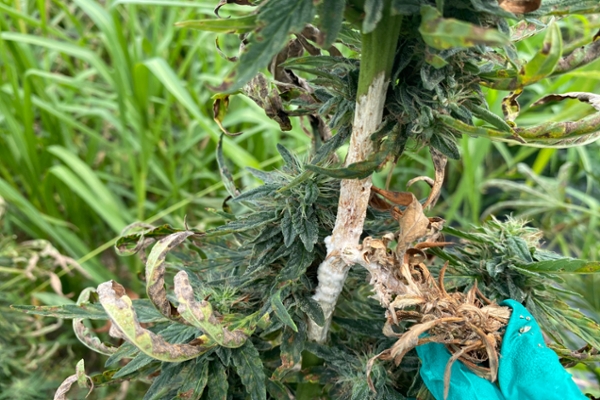
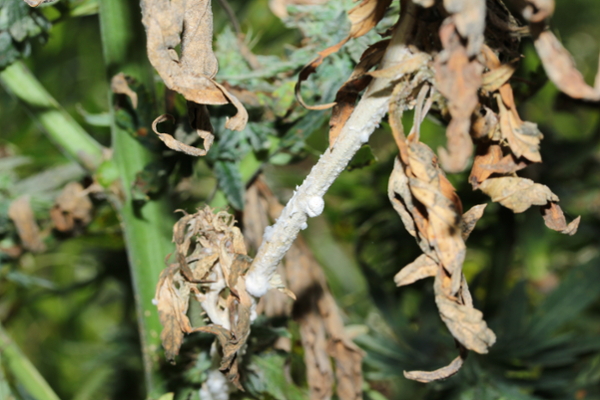
White mold
White mold is caused by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Portions of branches or whole plants can brown and wilt. White, fluffy mycelial growth is often observed. Black sclerotia may also be observed and are overwintering structures. Cool to moderate temperatures, high humidity, and moist soil are conducive to disease.