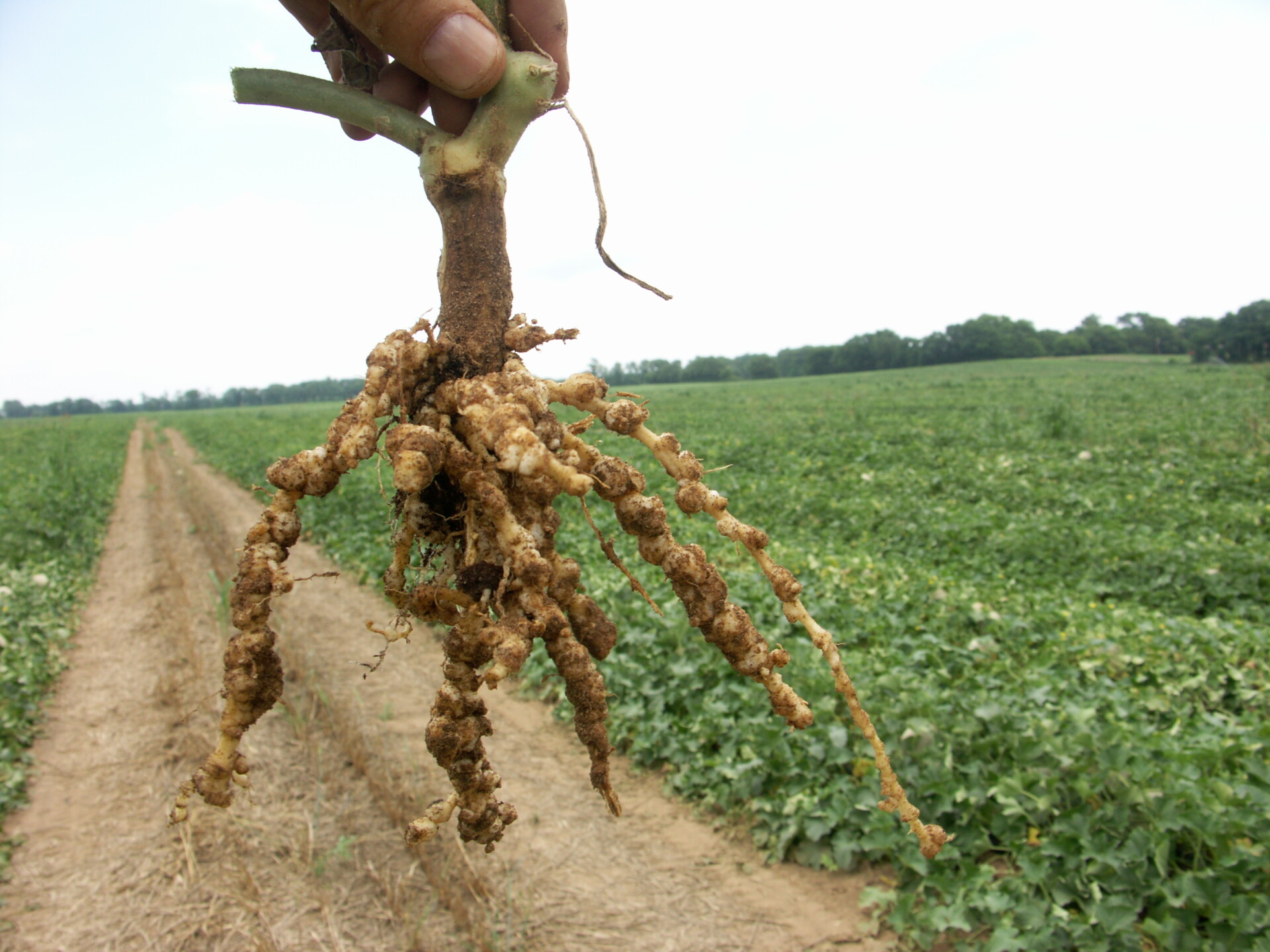
cantaloupe diseases
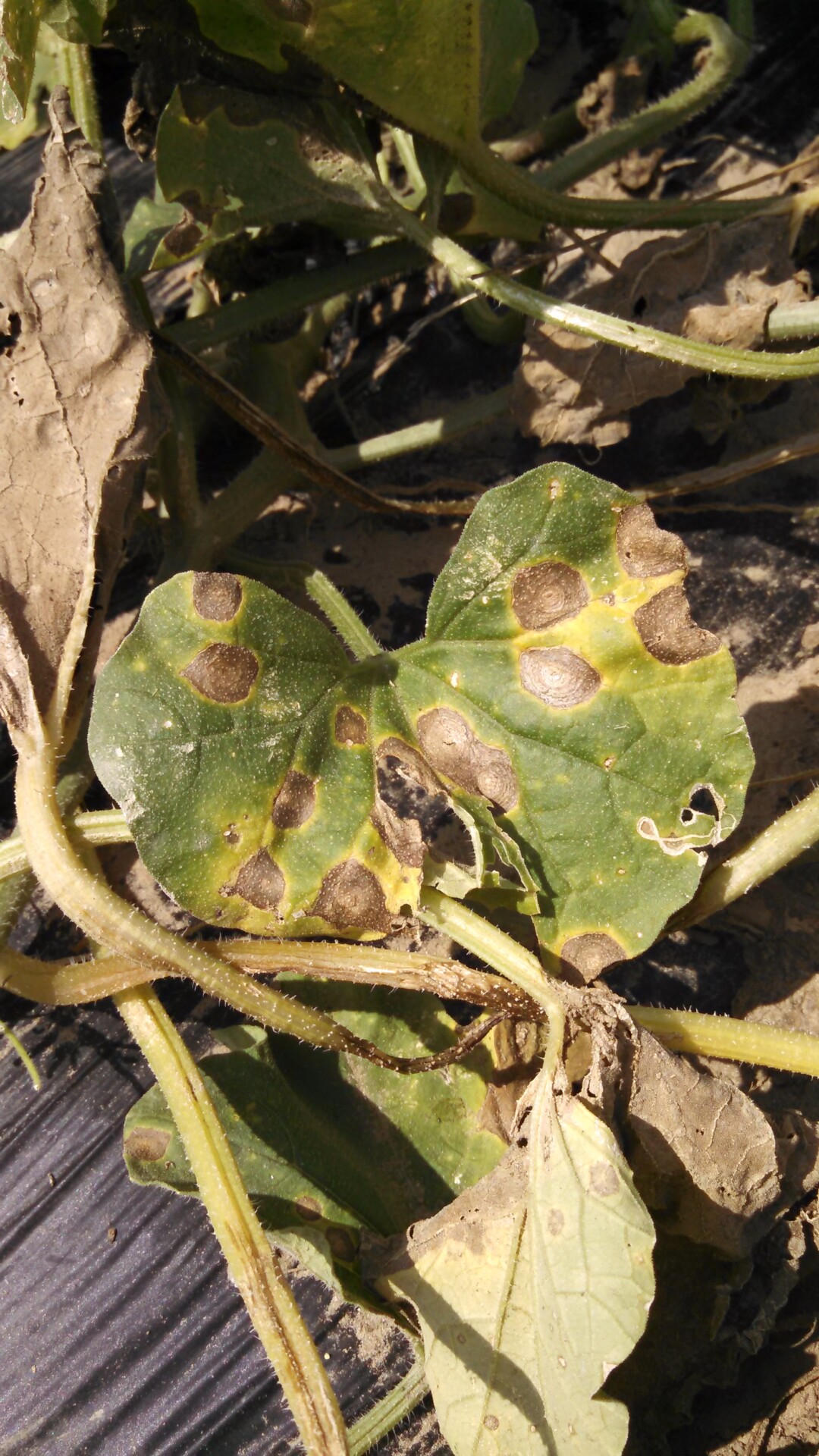
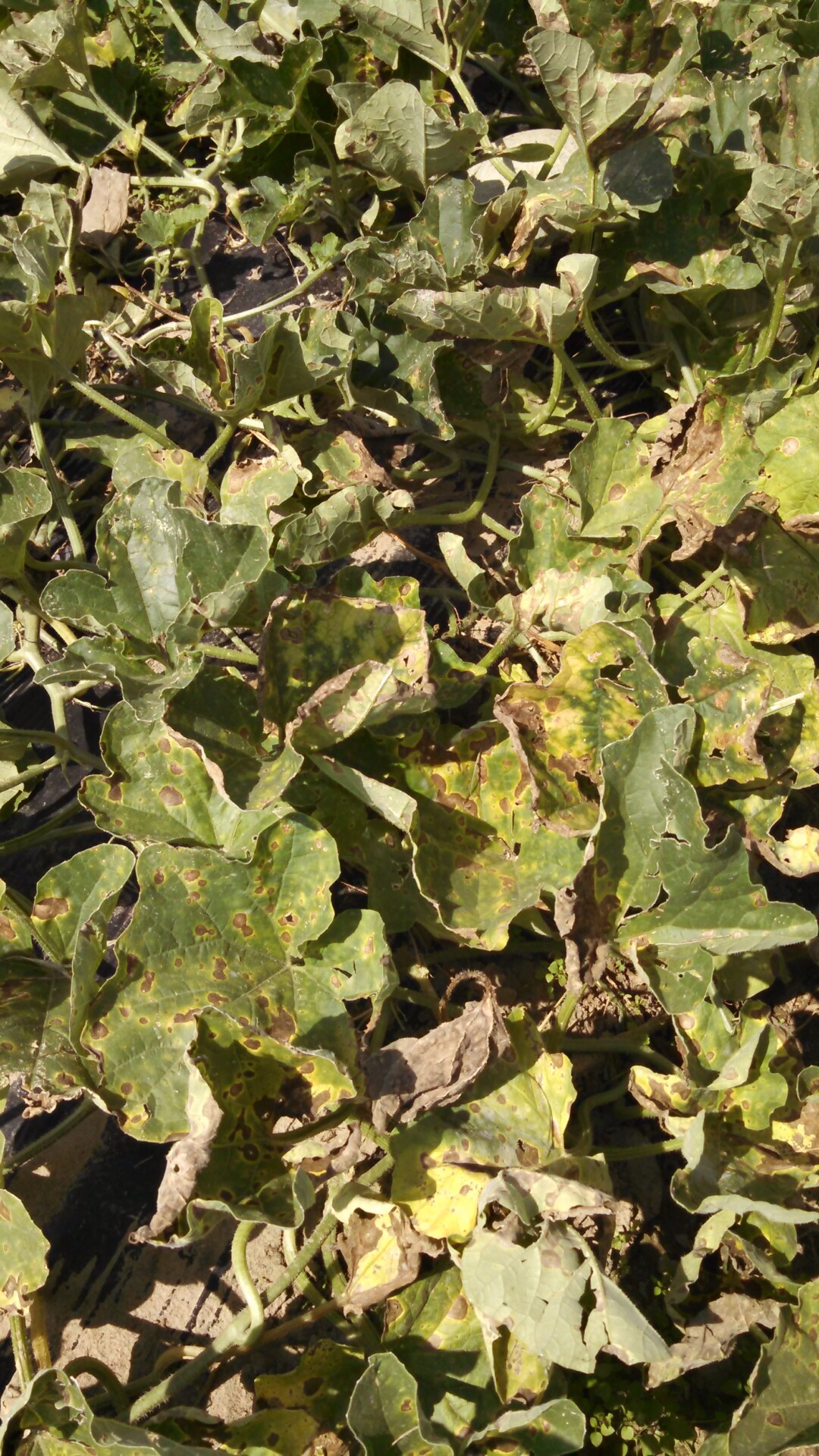
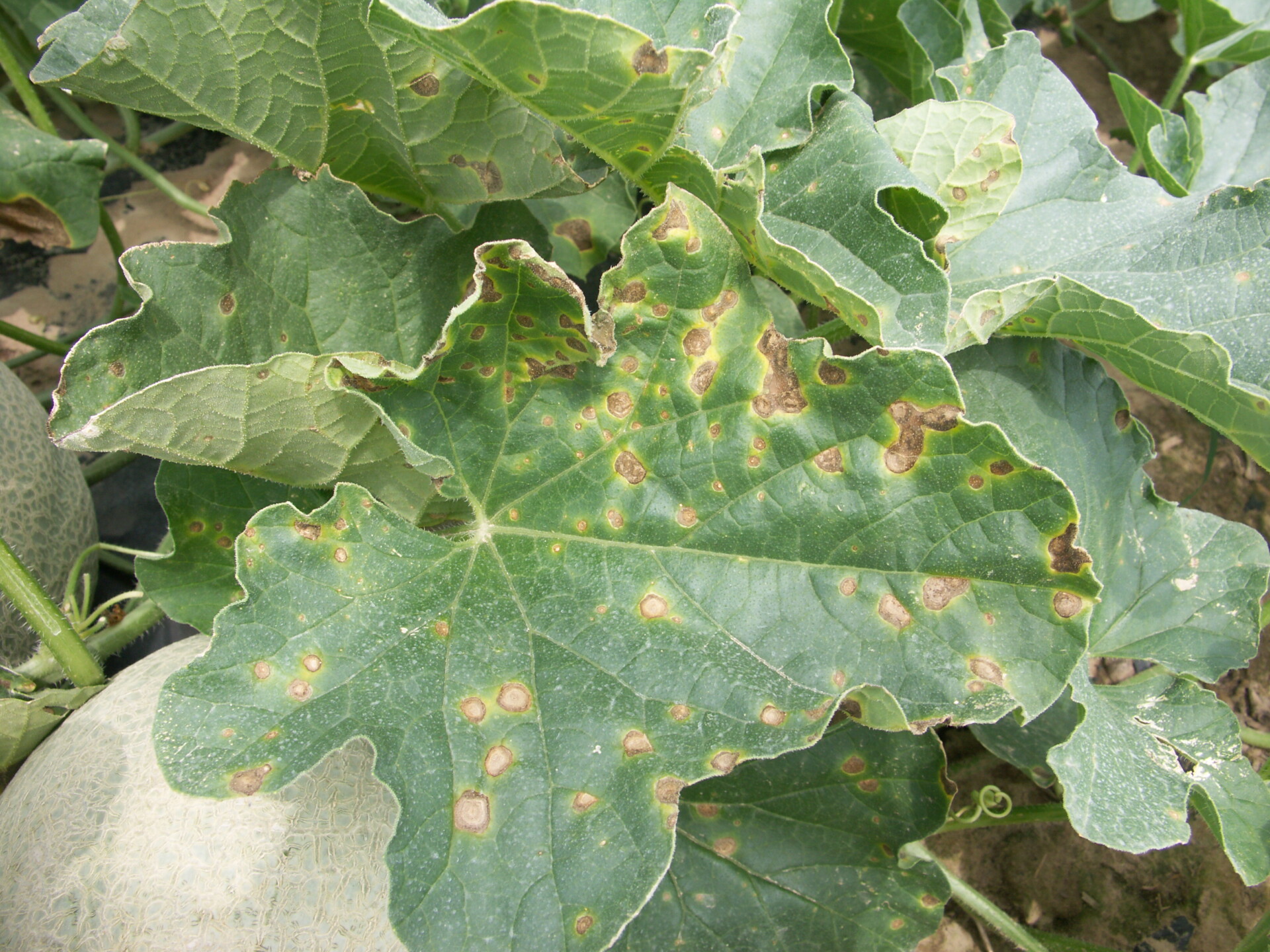
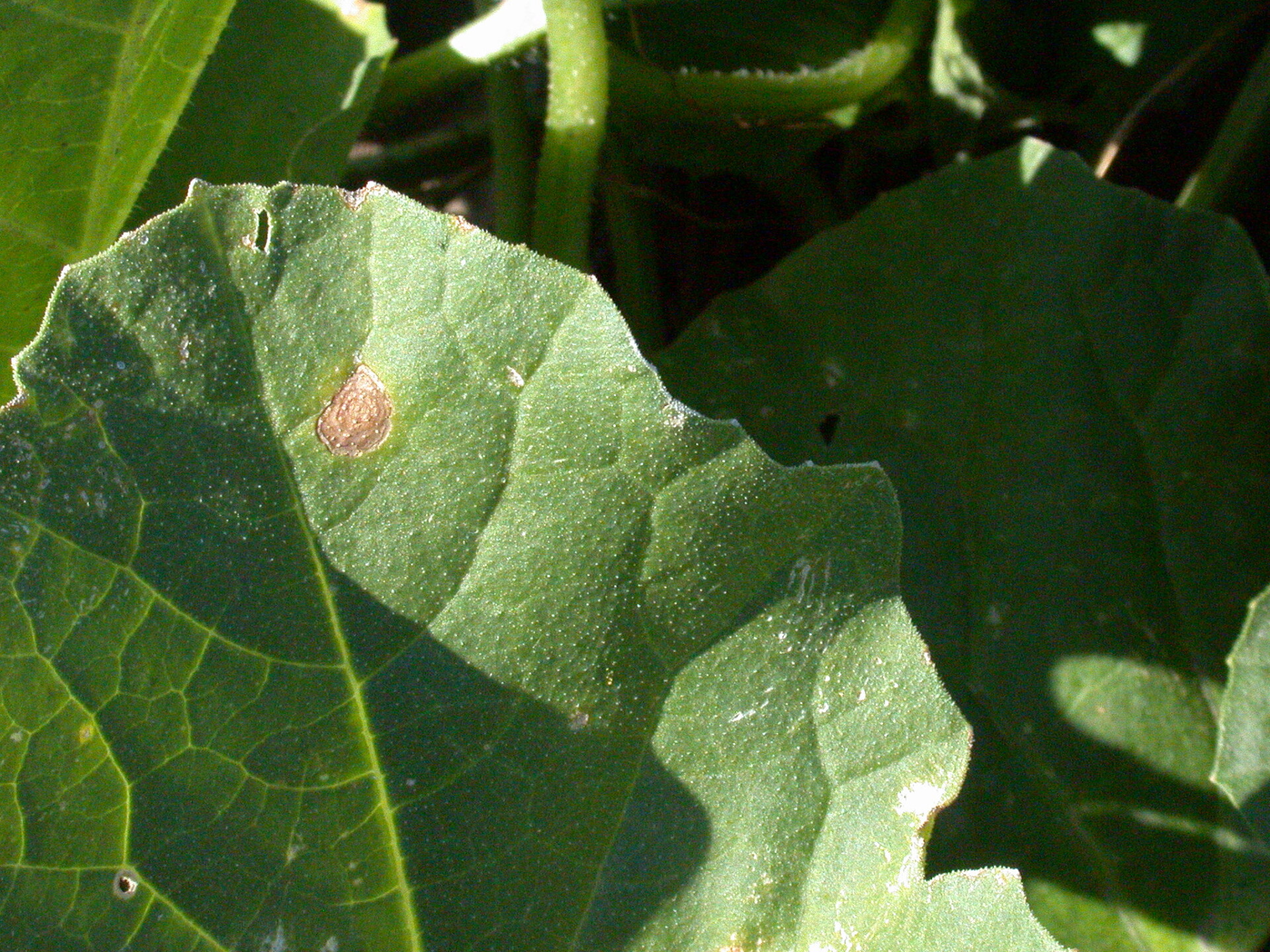
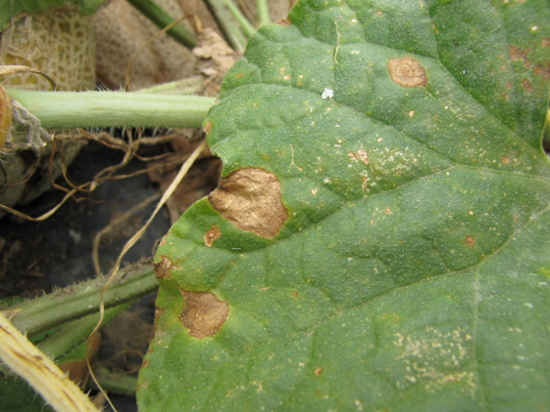
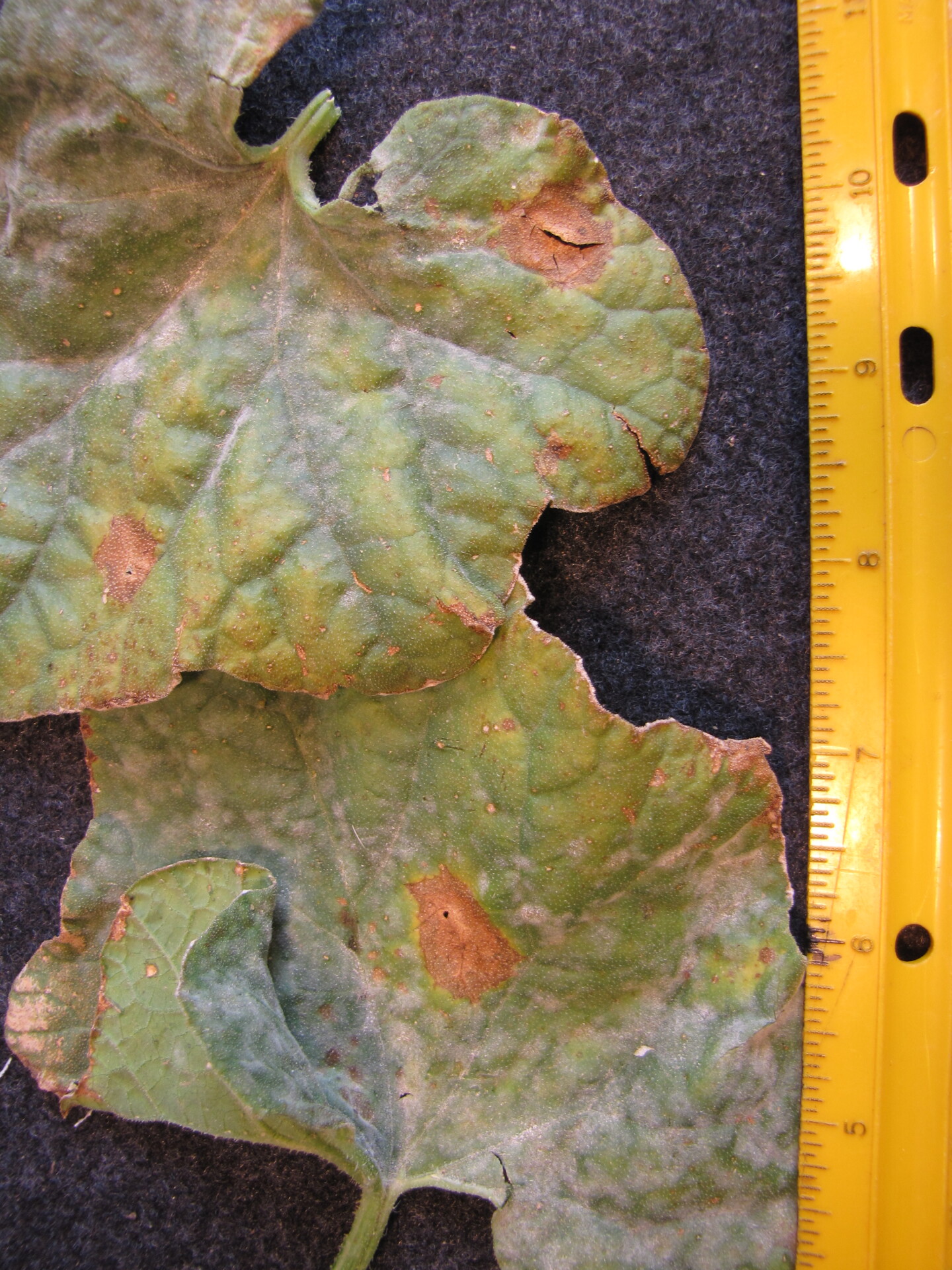
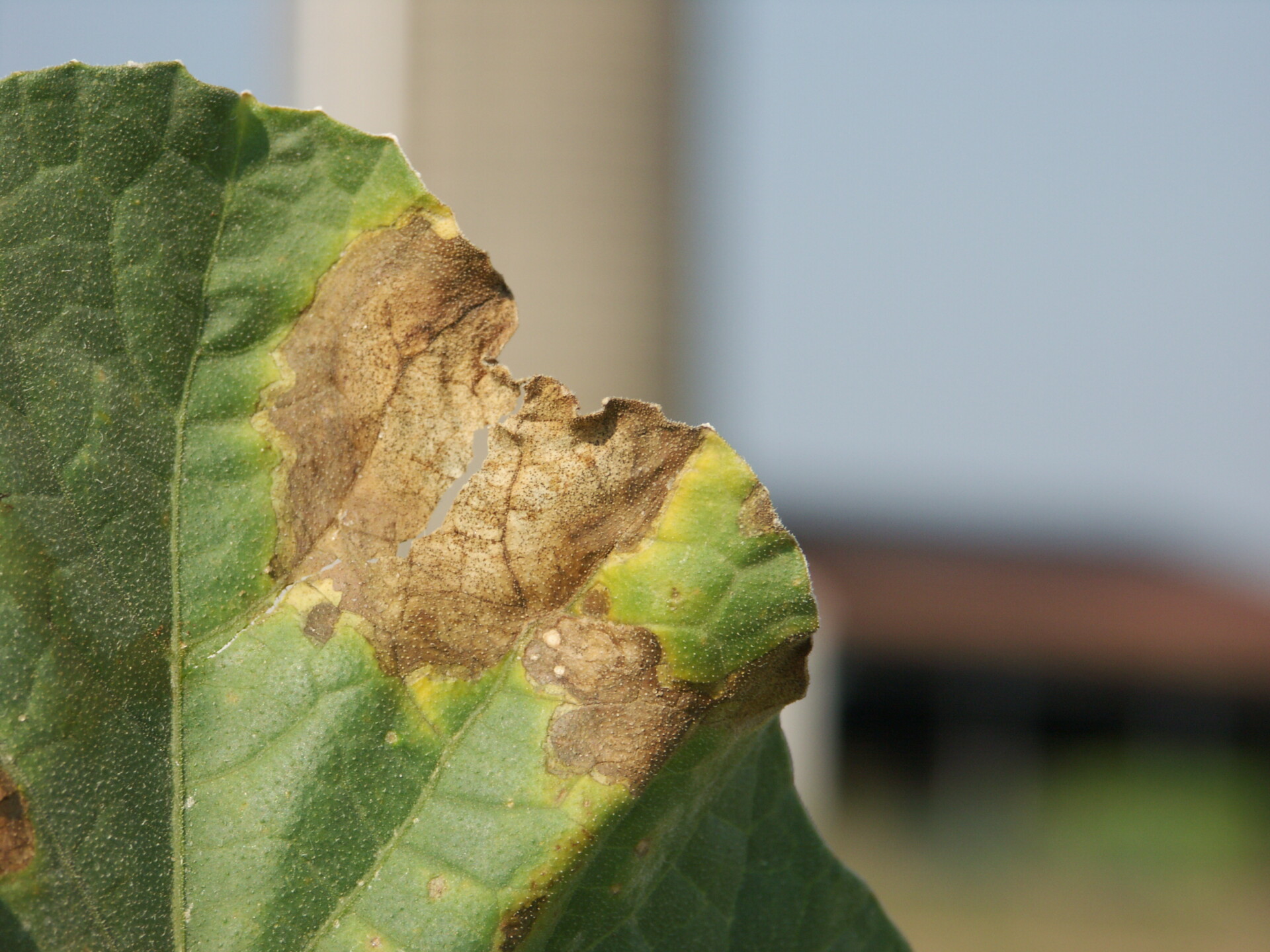
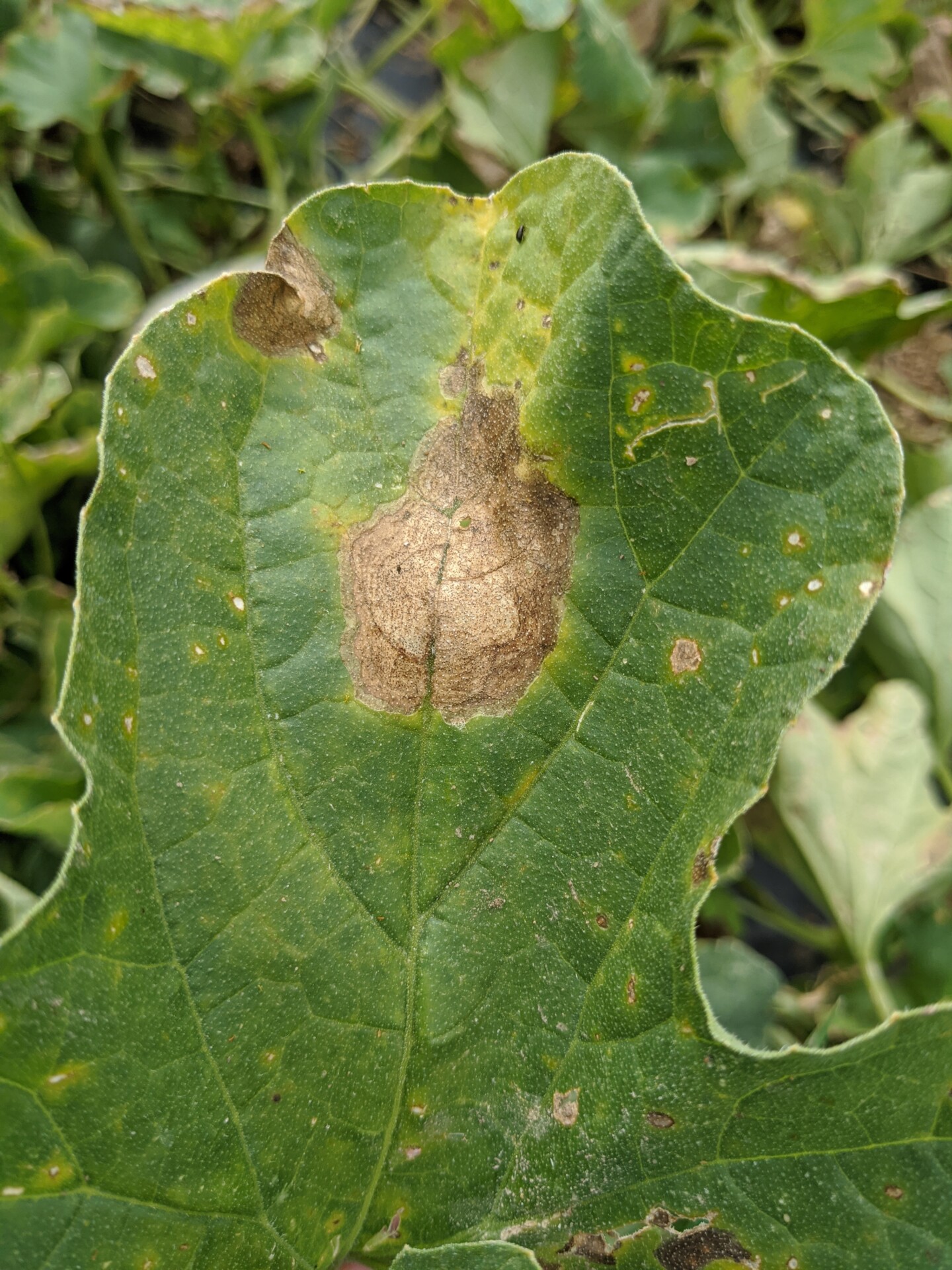
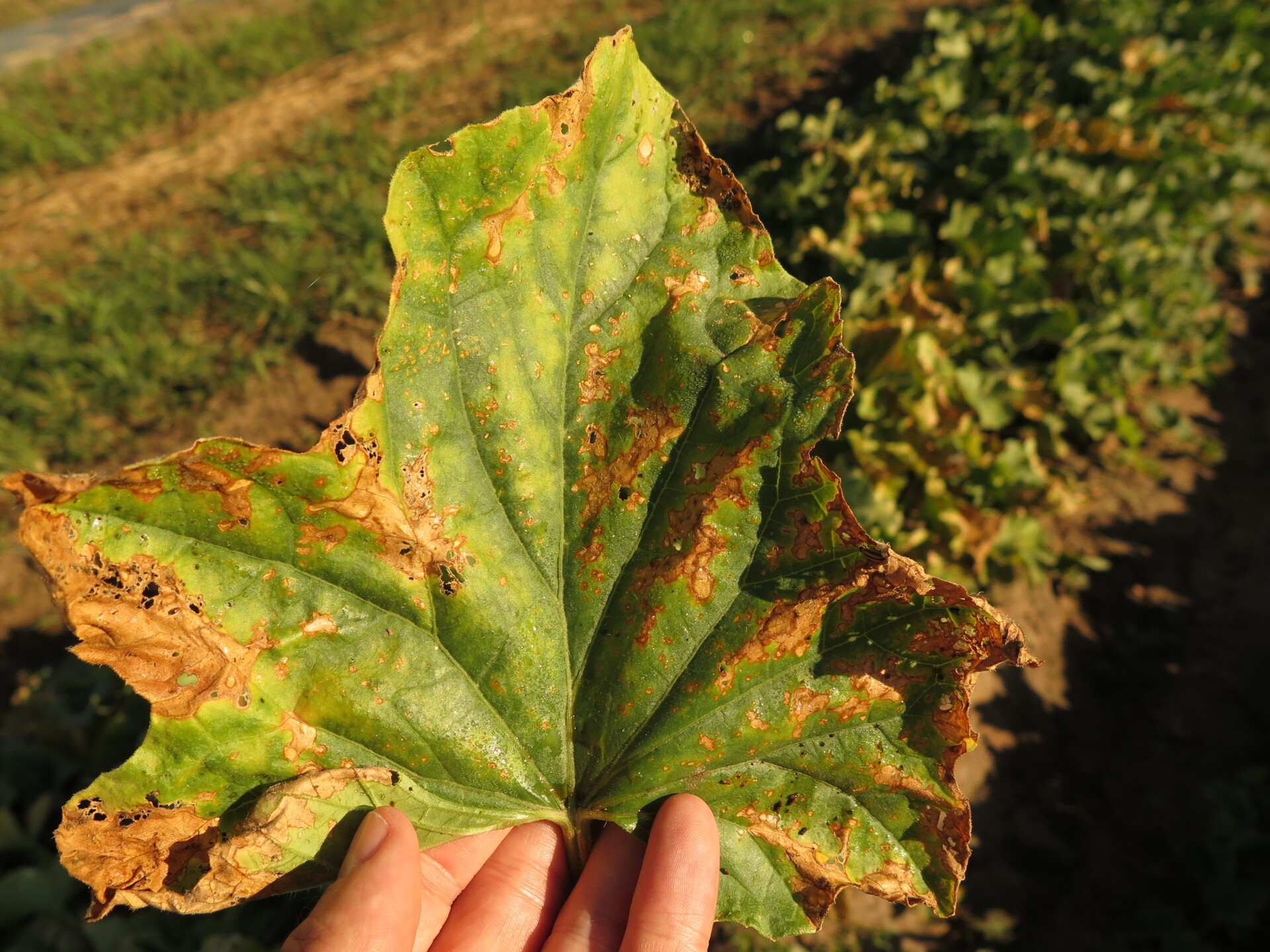
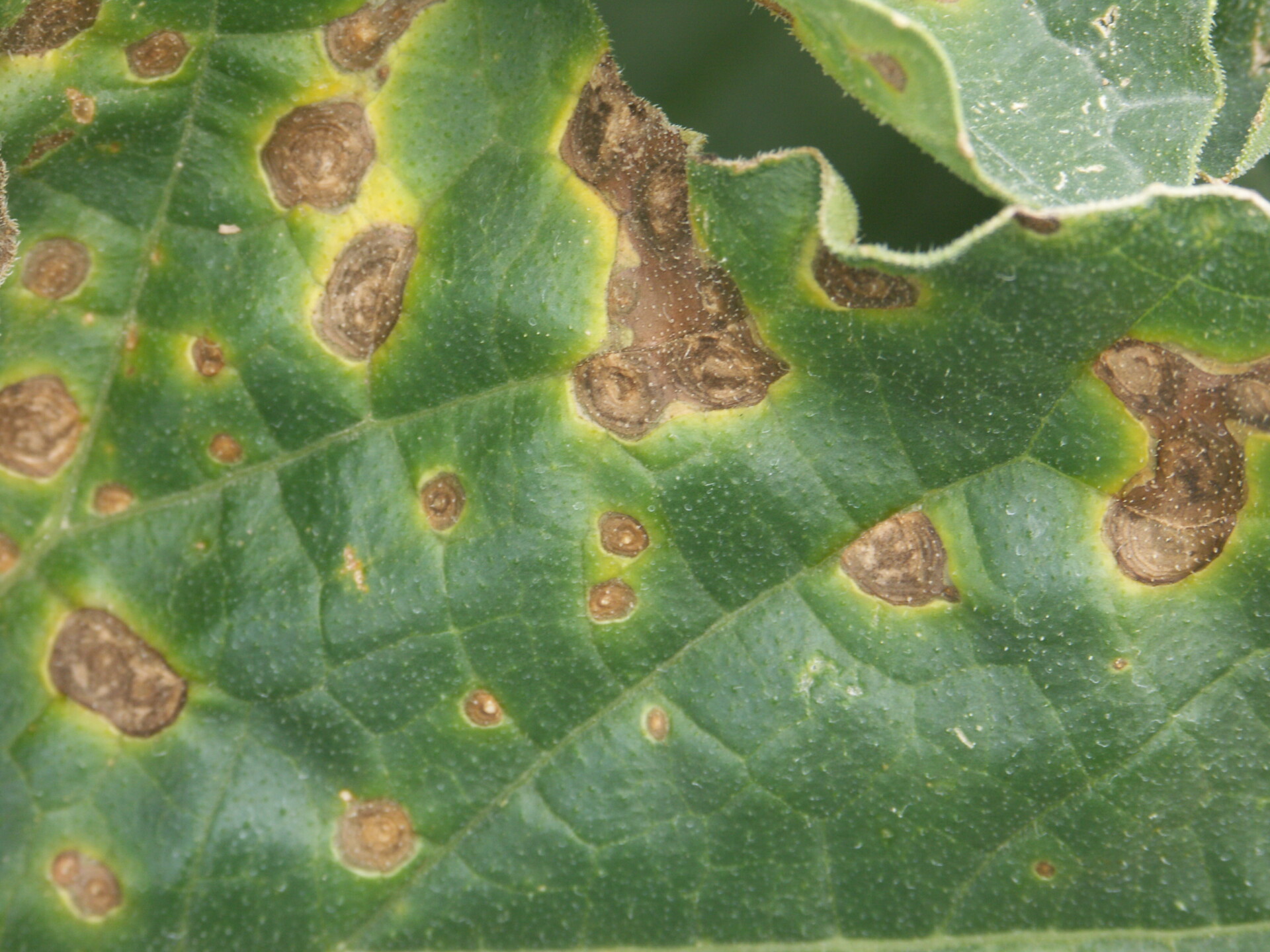
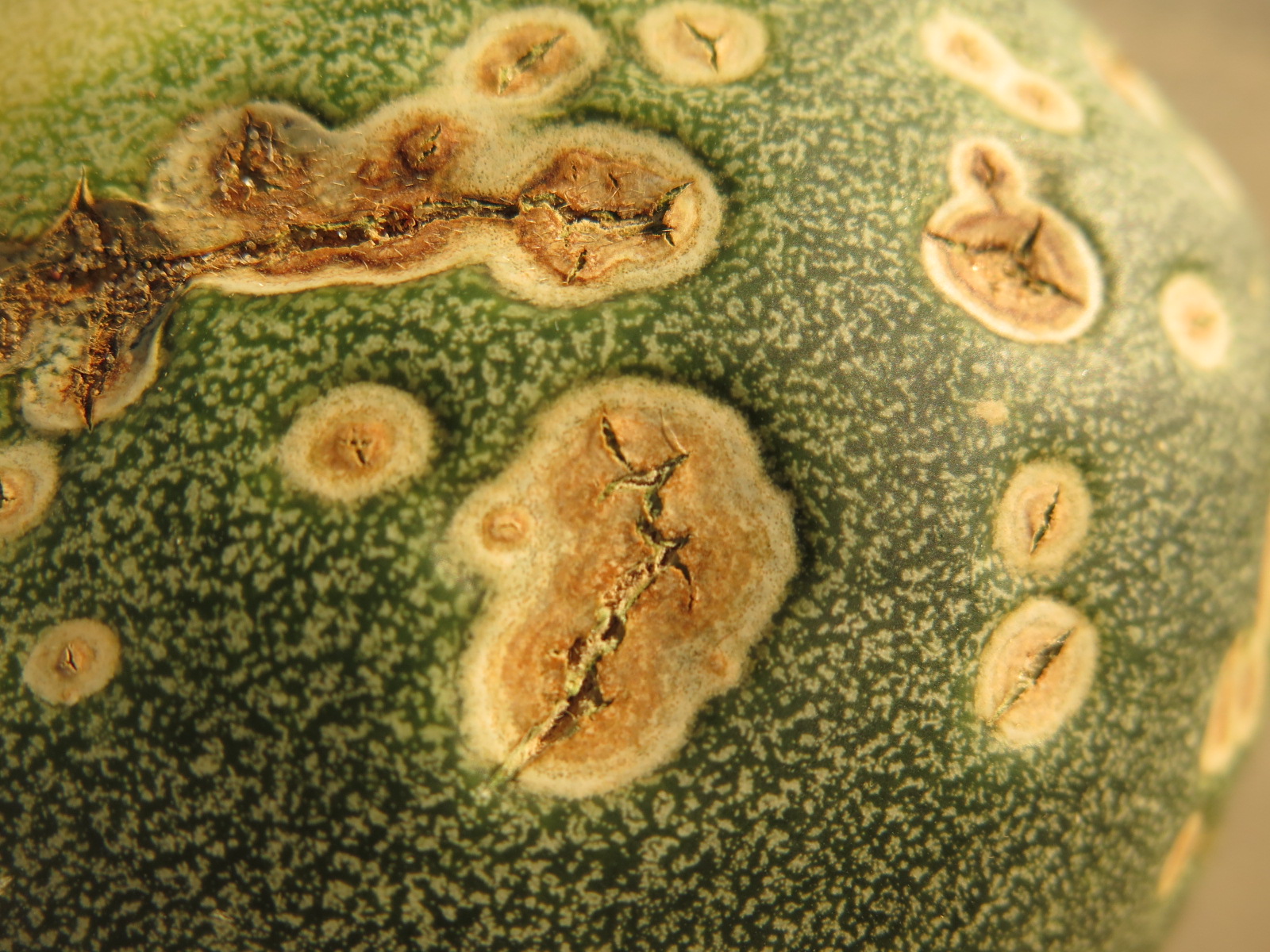
Alternaria Leaf Blight
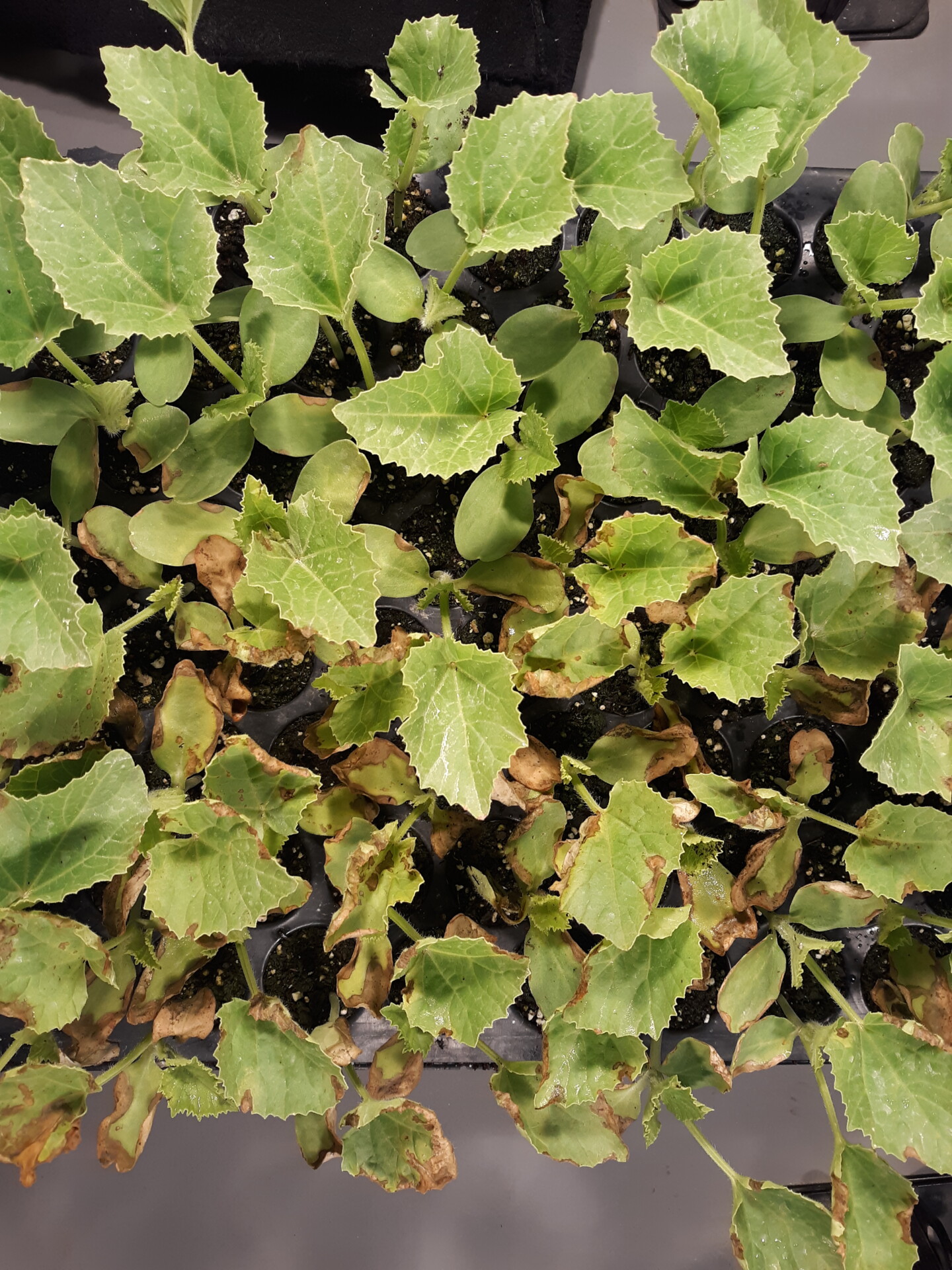
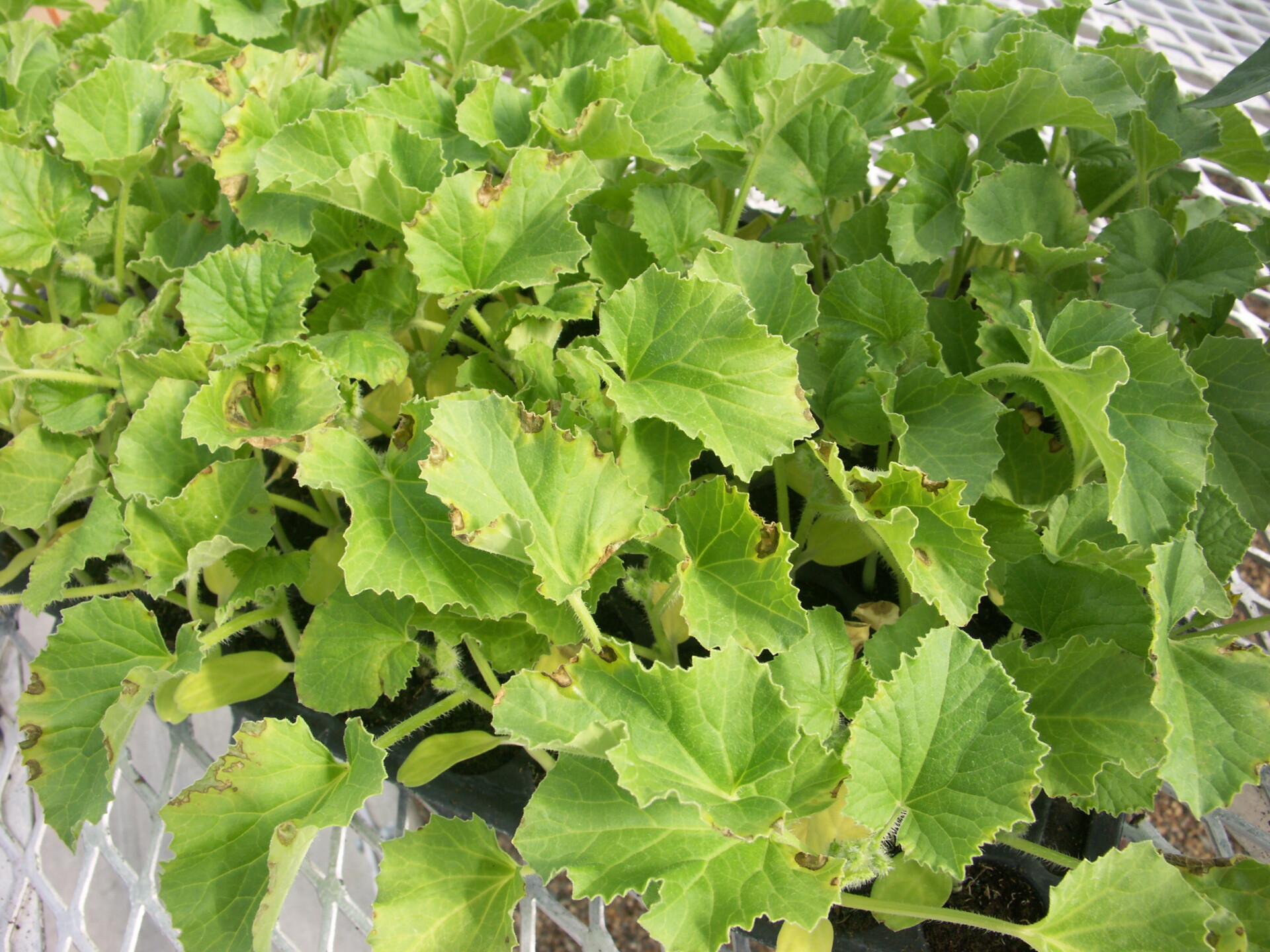
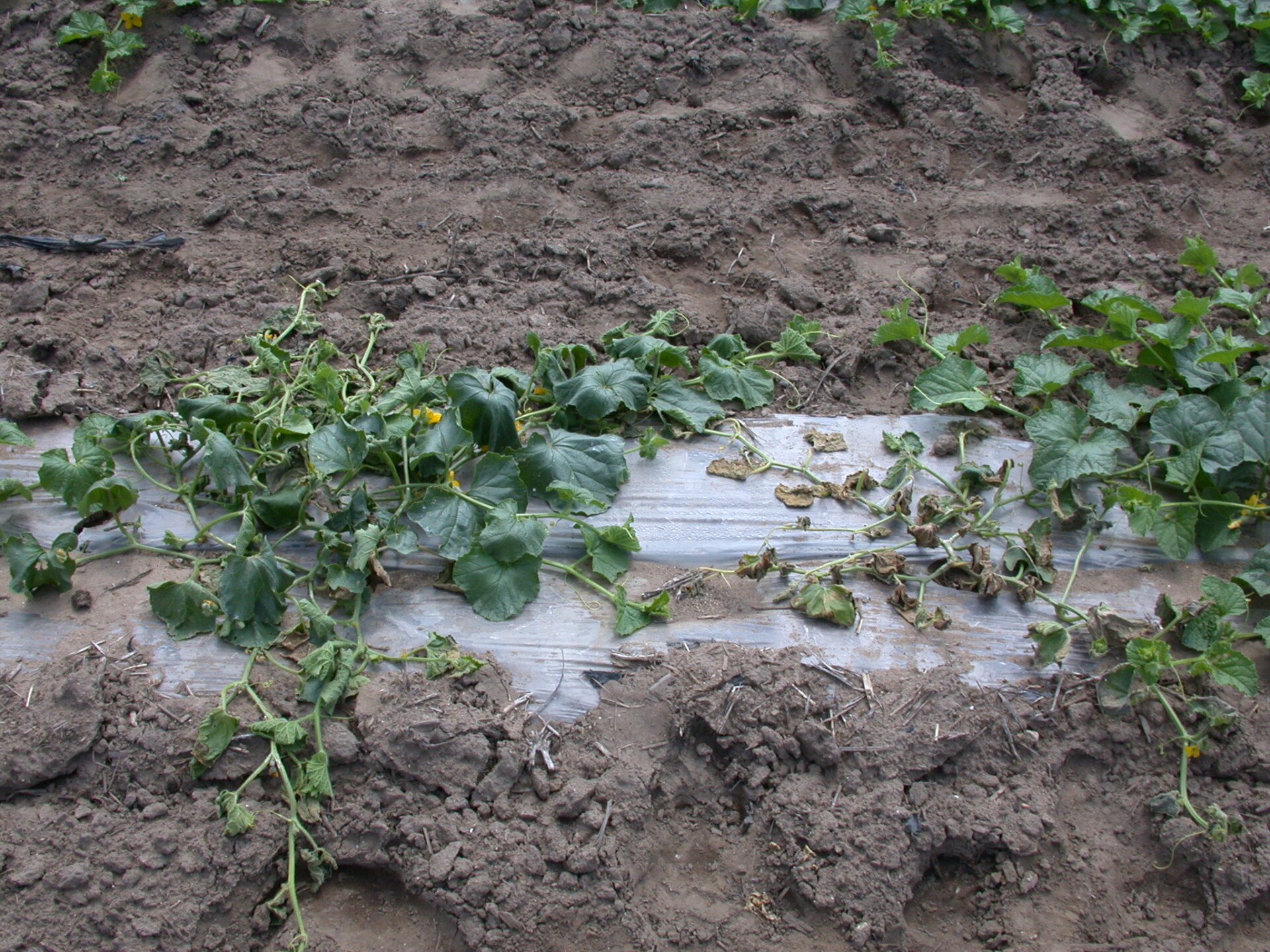
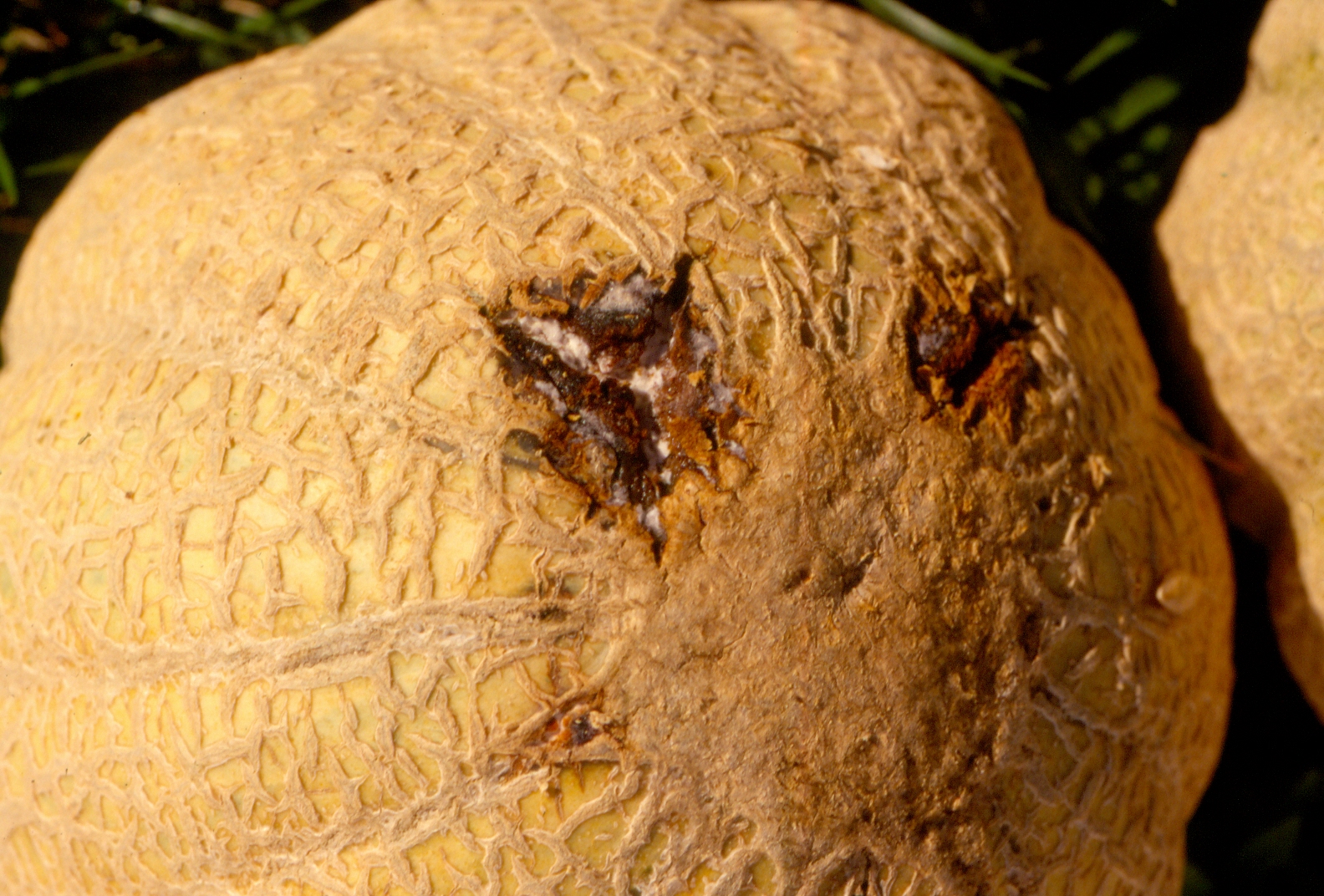
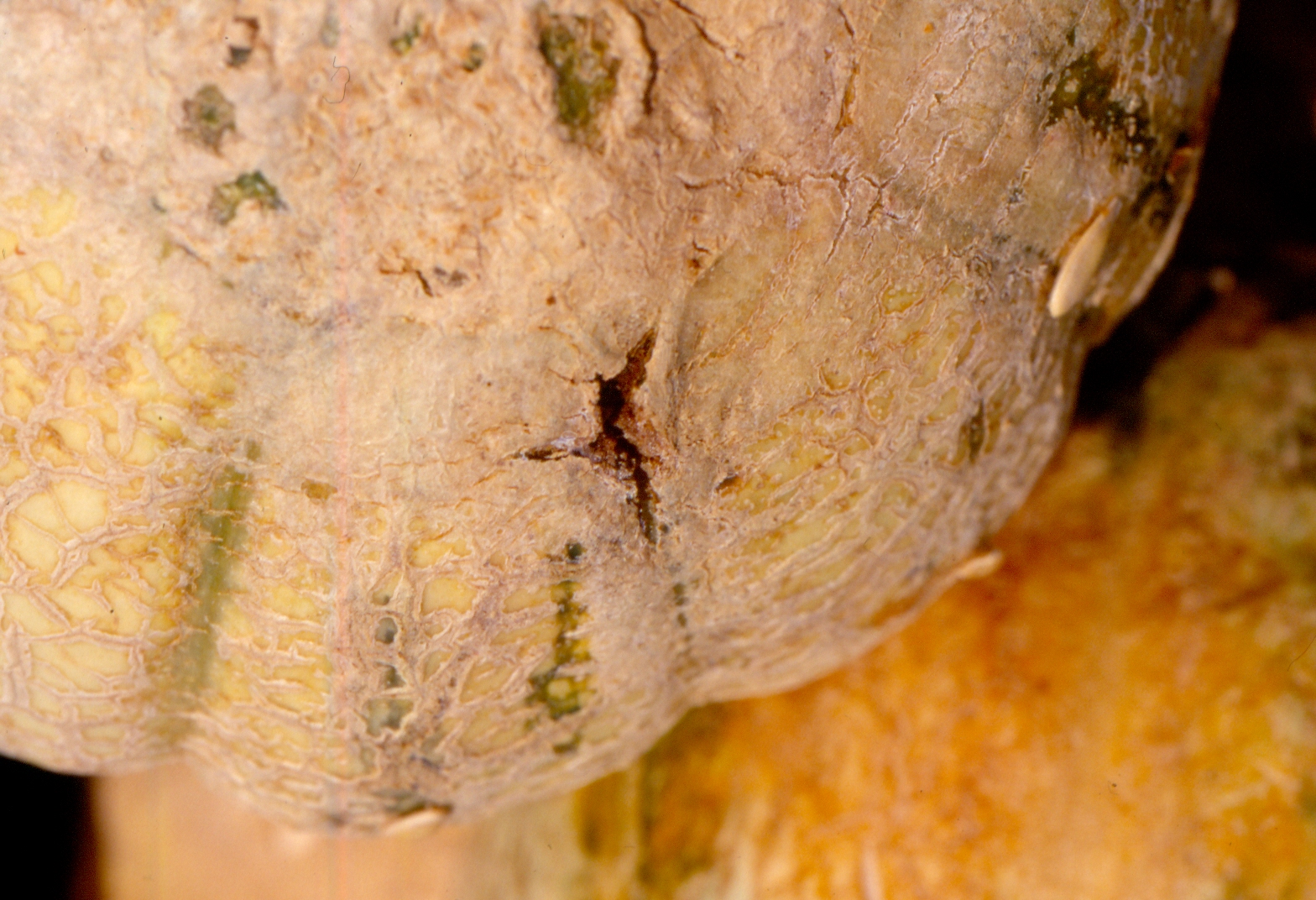
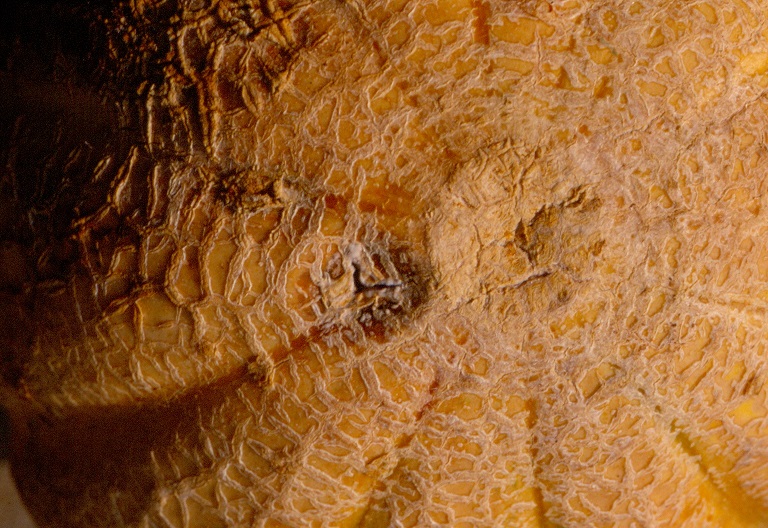
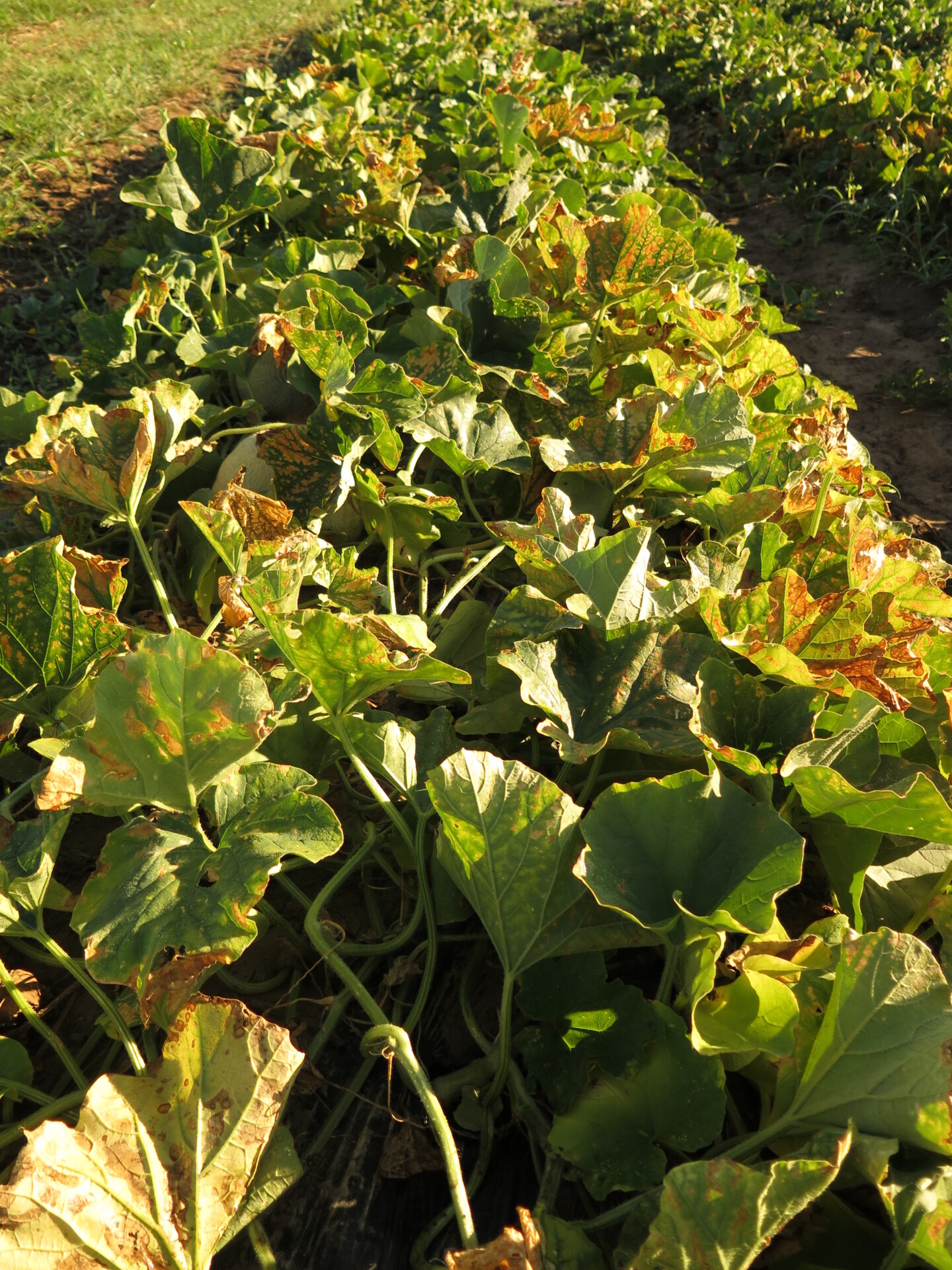
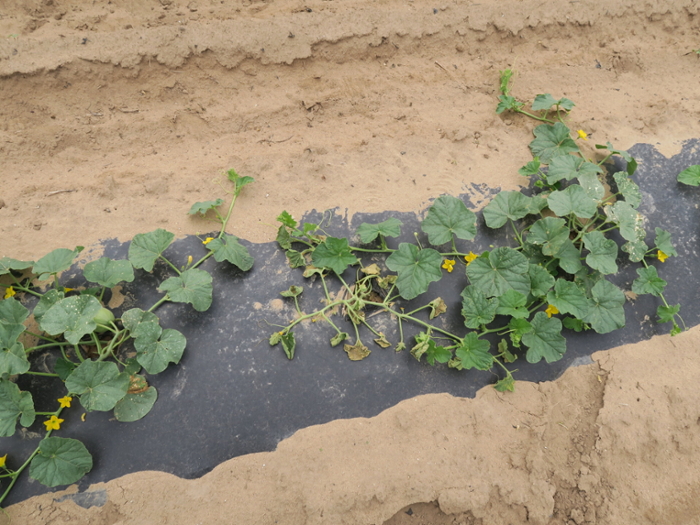
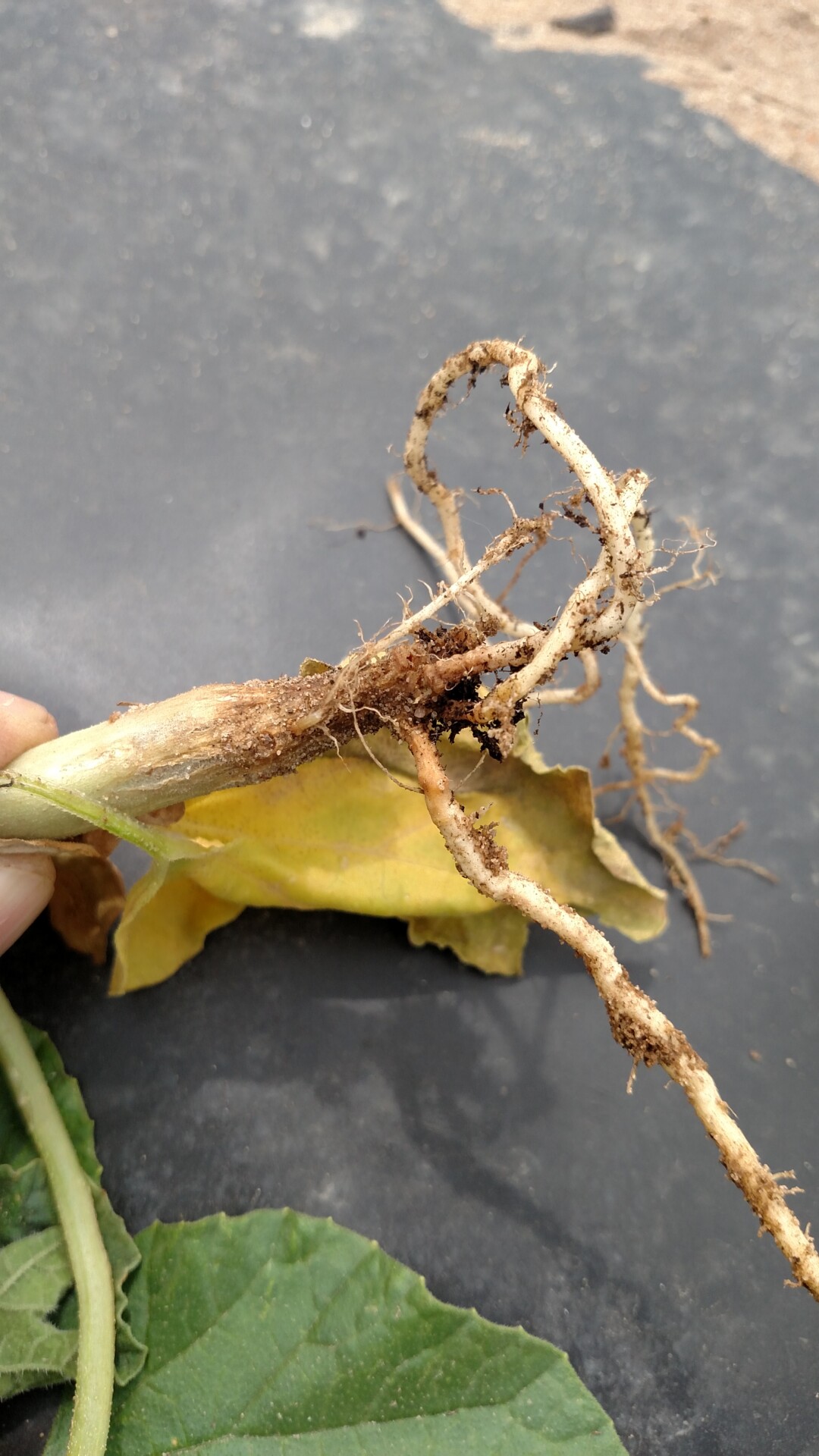
Bacterial Wilt
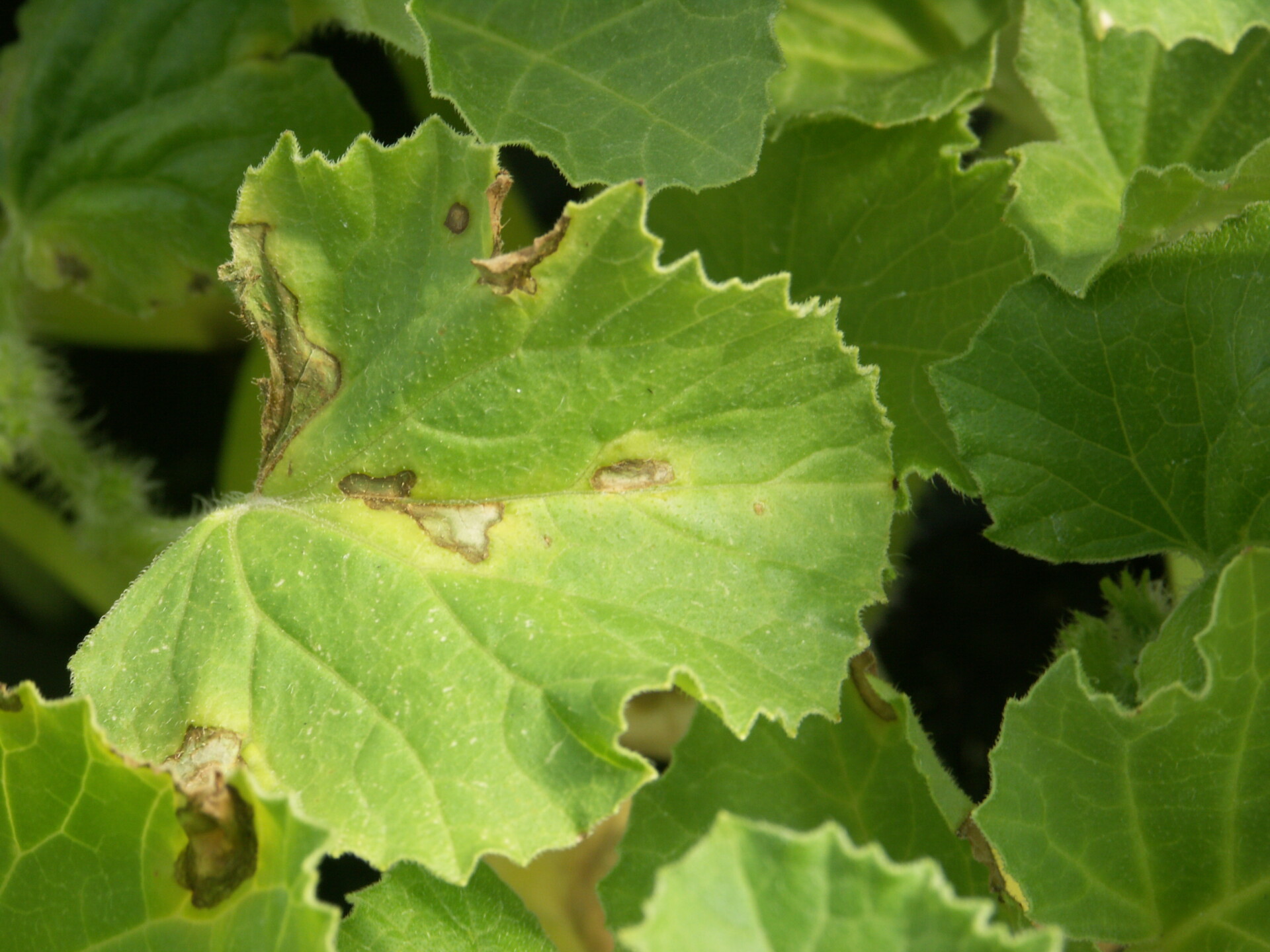
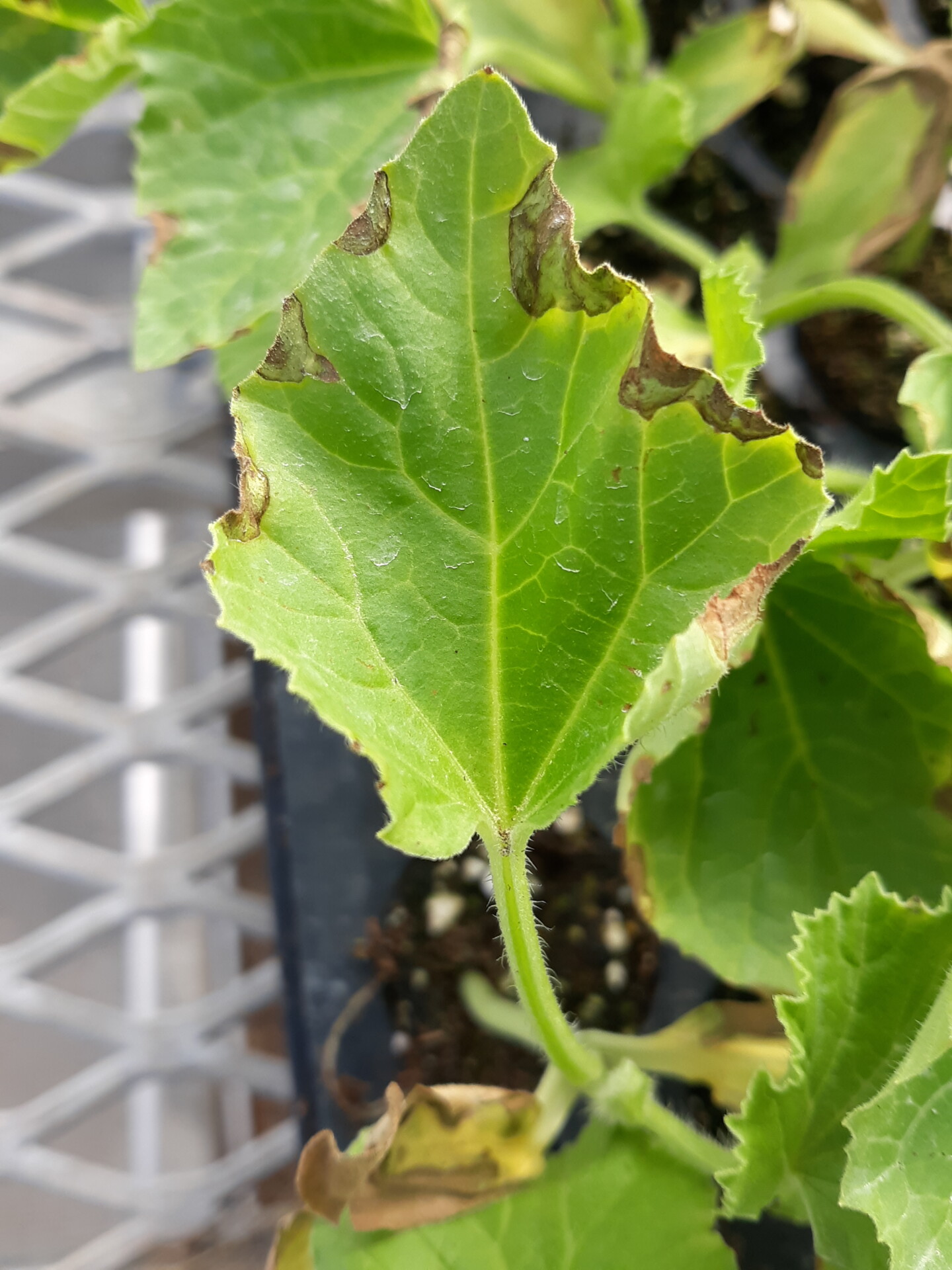
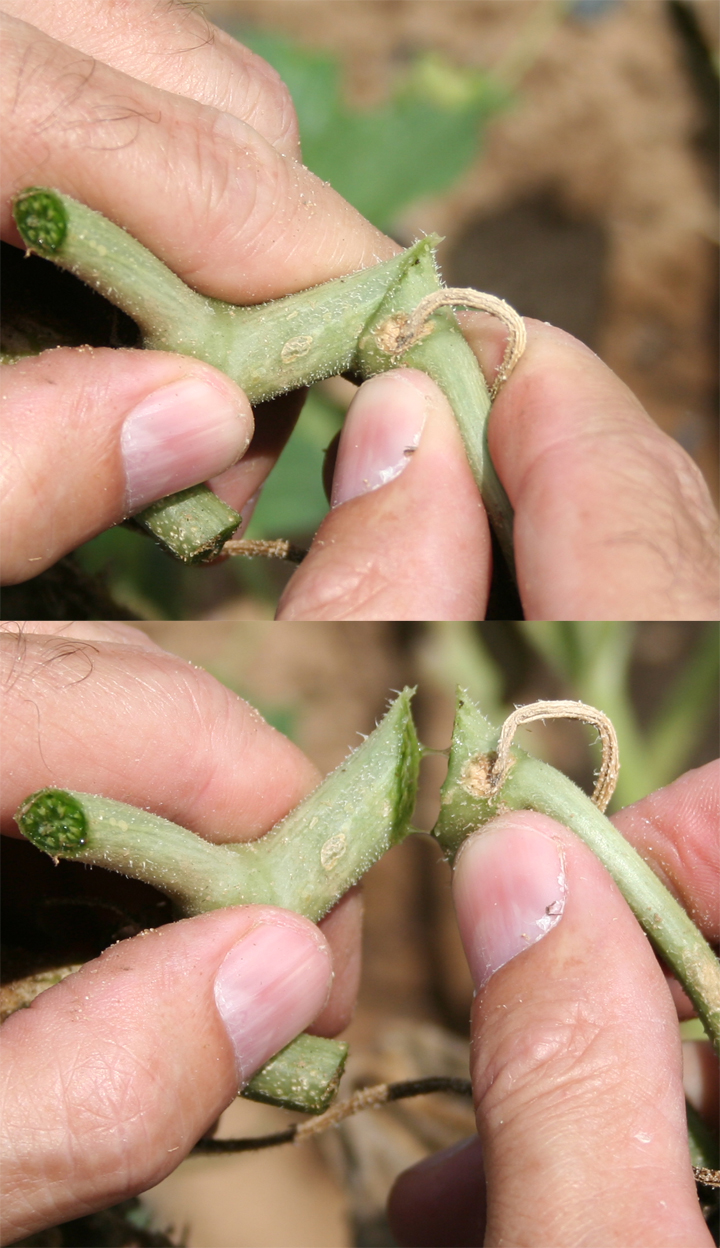
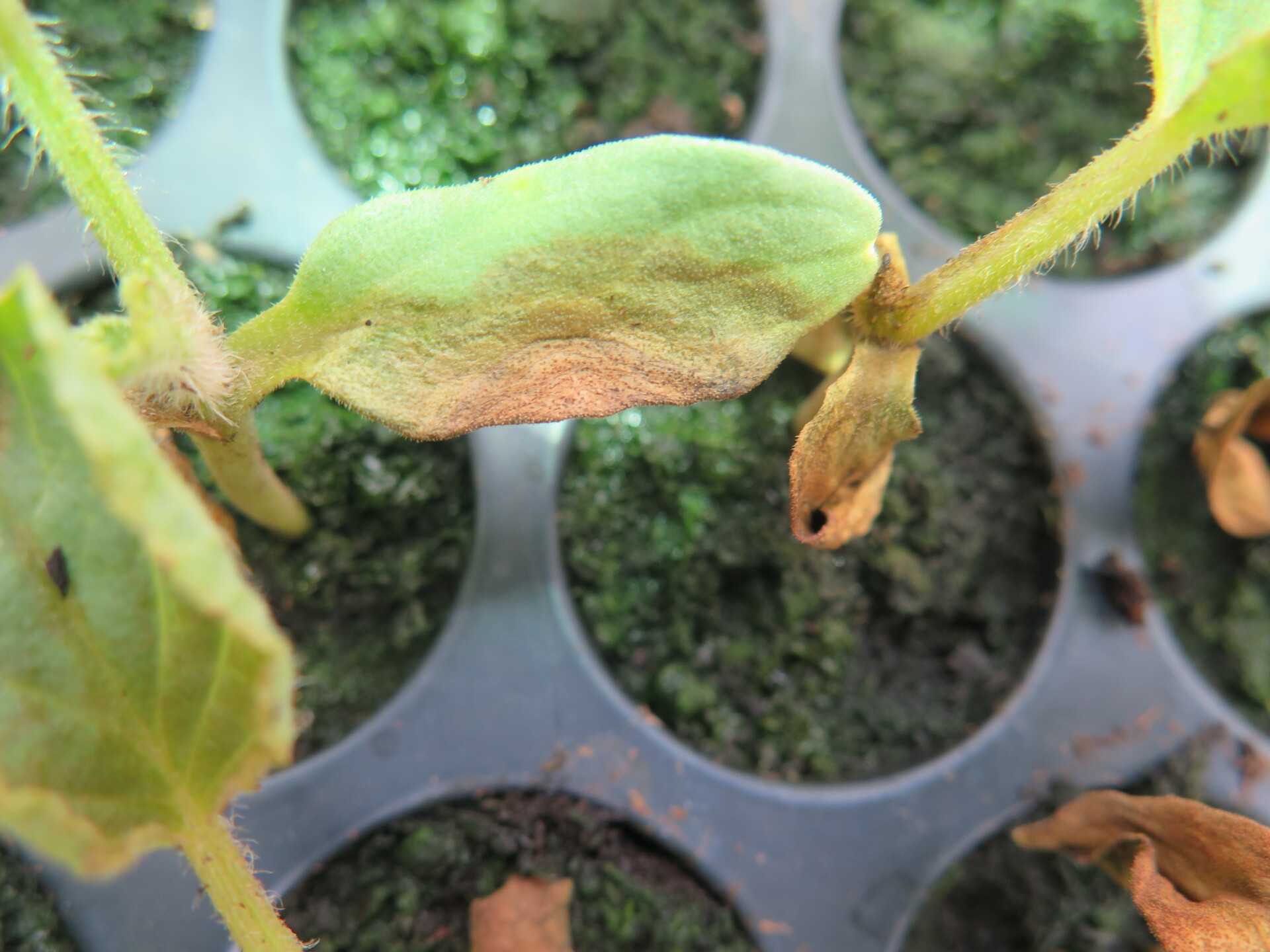
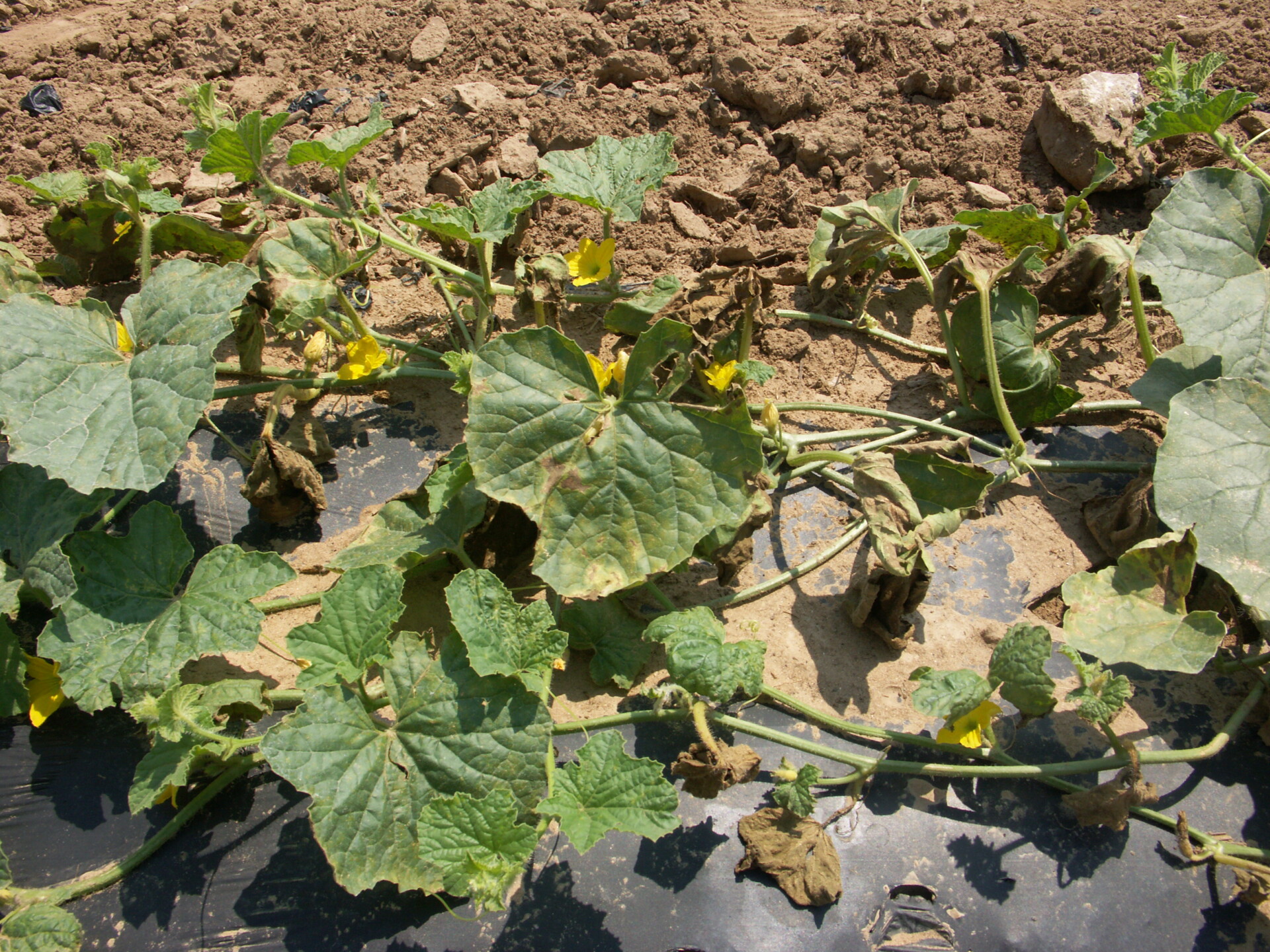
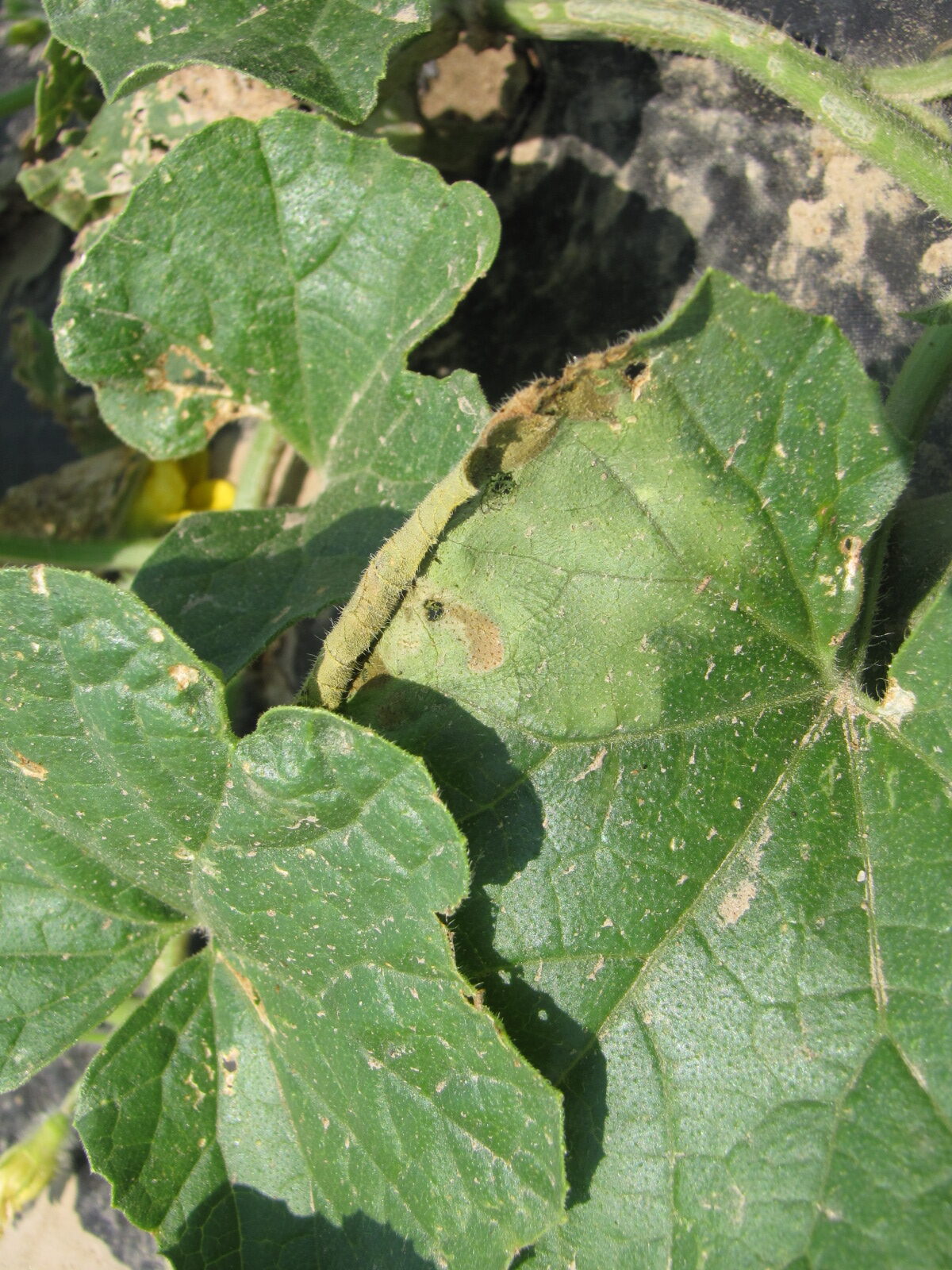 Figure 1. The wilted and collapsed area on the margin of this leaf is due to bacterial wilt of cantaloupe. Note also the areas of the leaf eaten by cucumber beetles.
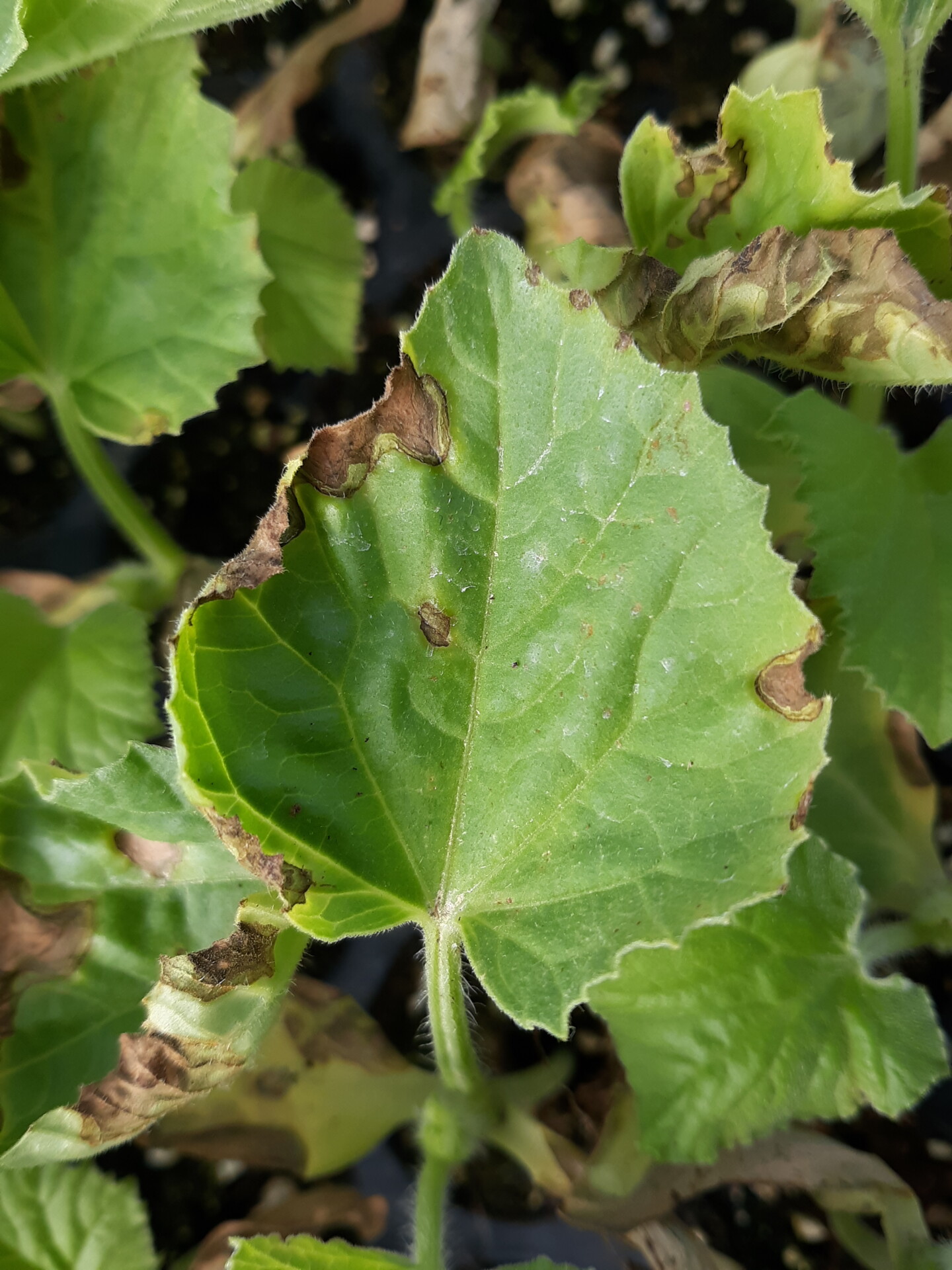
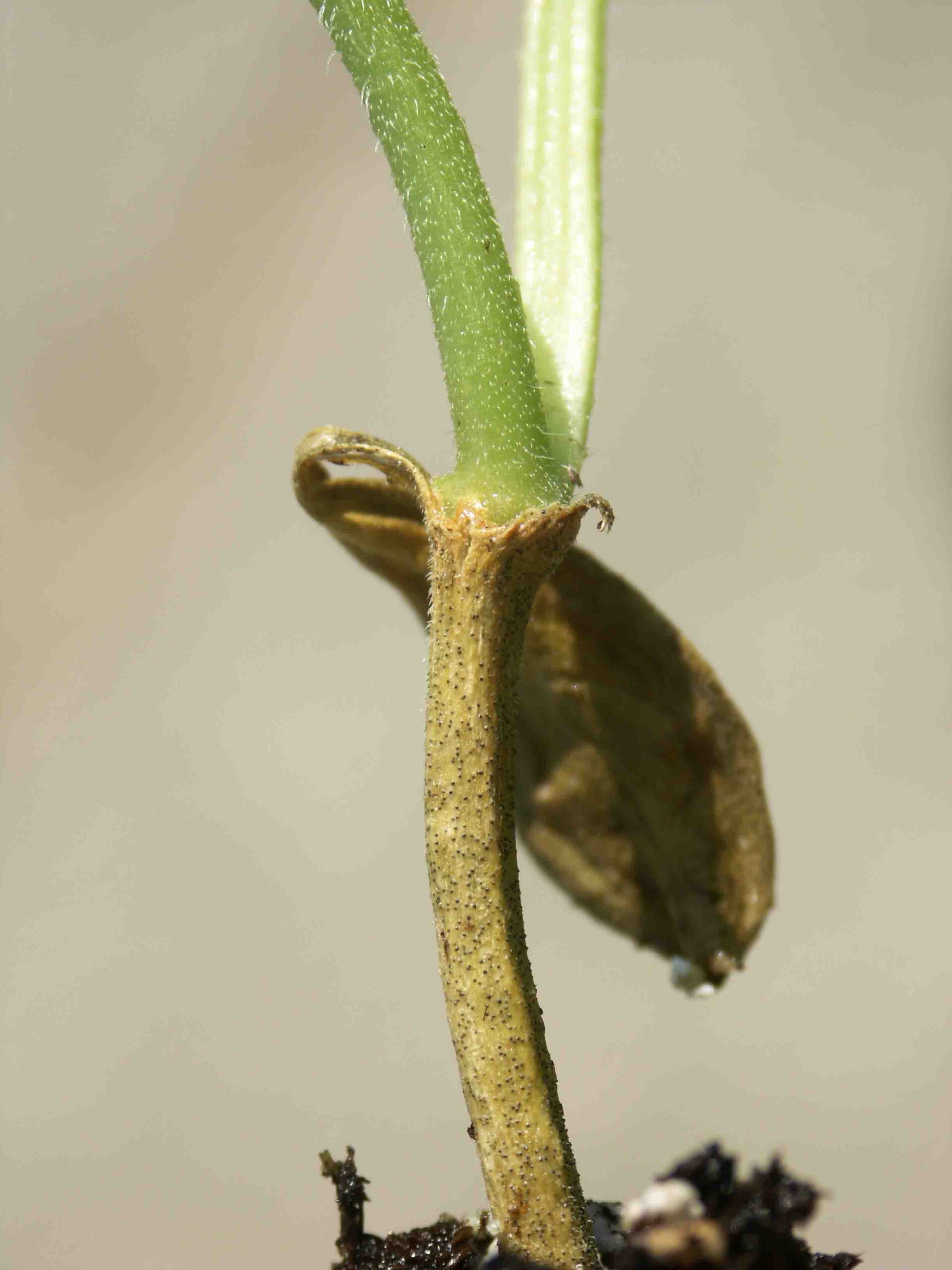
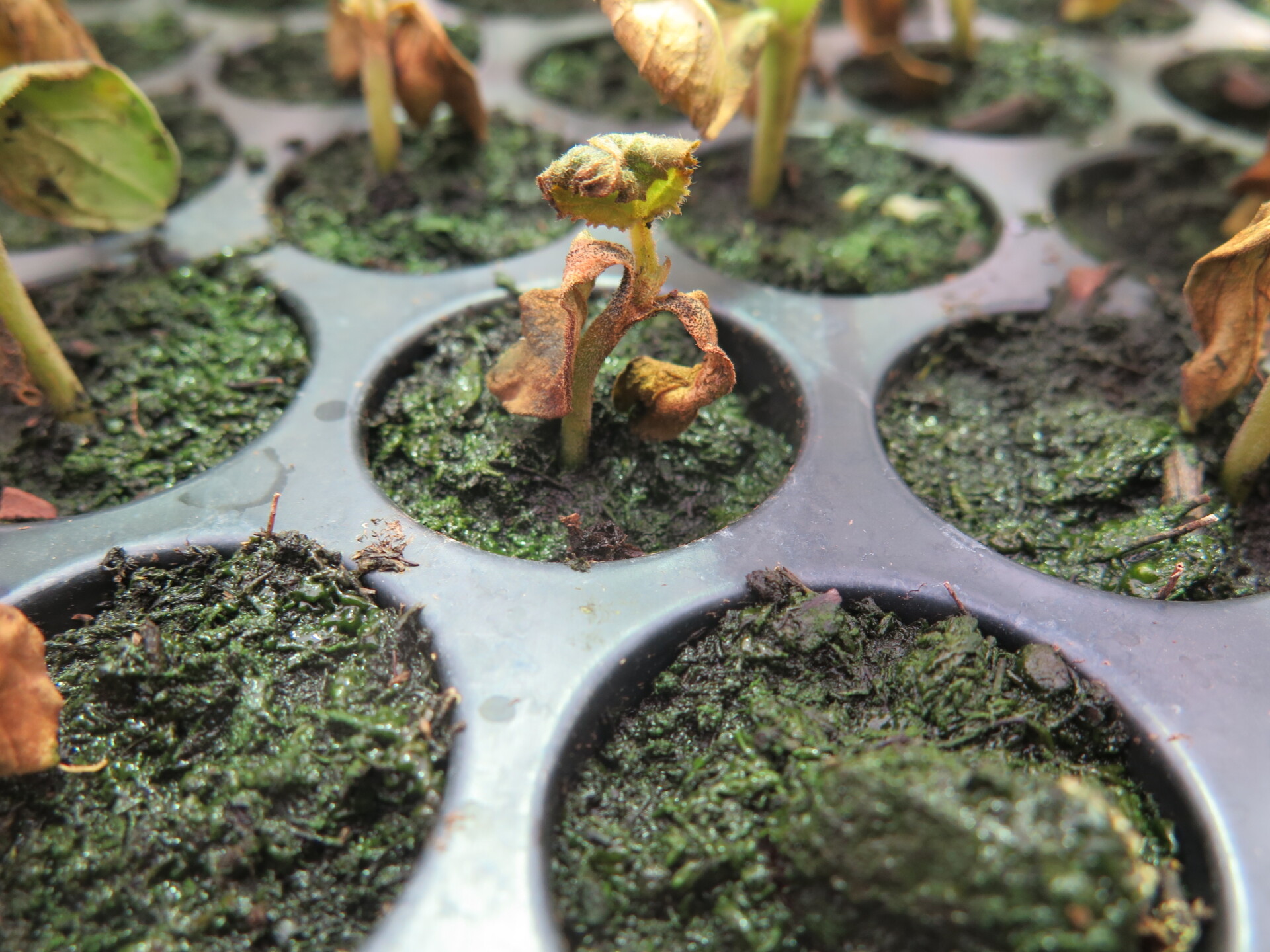
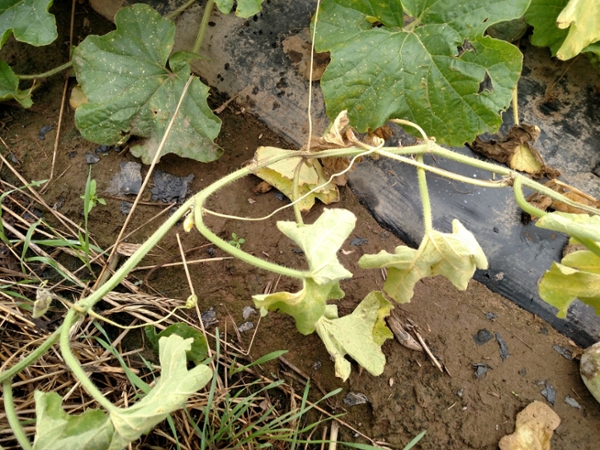
Figure 1. The wilted and collapsed area on the margin of this leaf is due to bacterial wilt of cantaloupe. Note also the areas of the leaf eaten by cucumber beetles.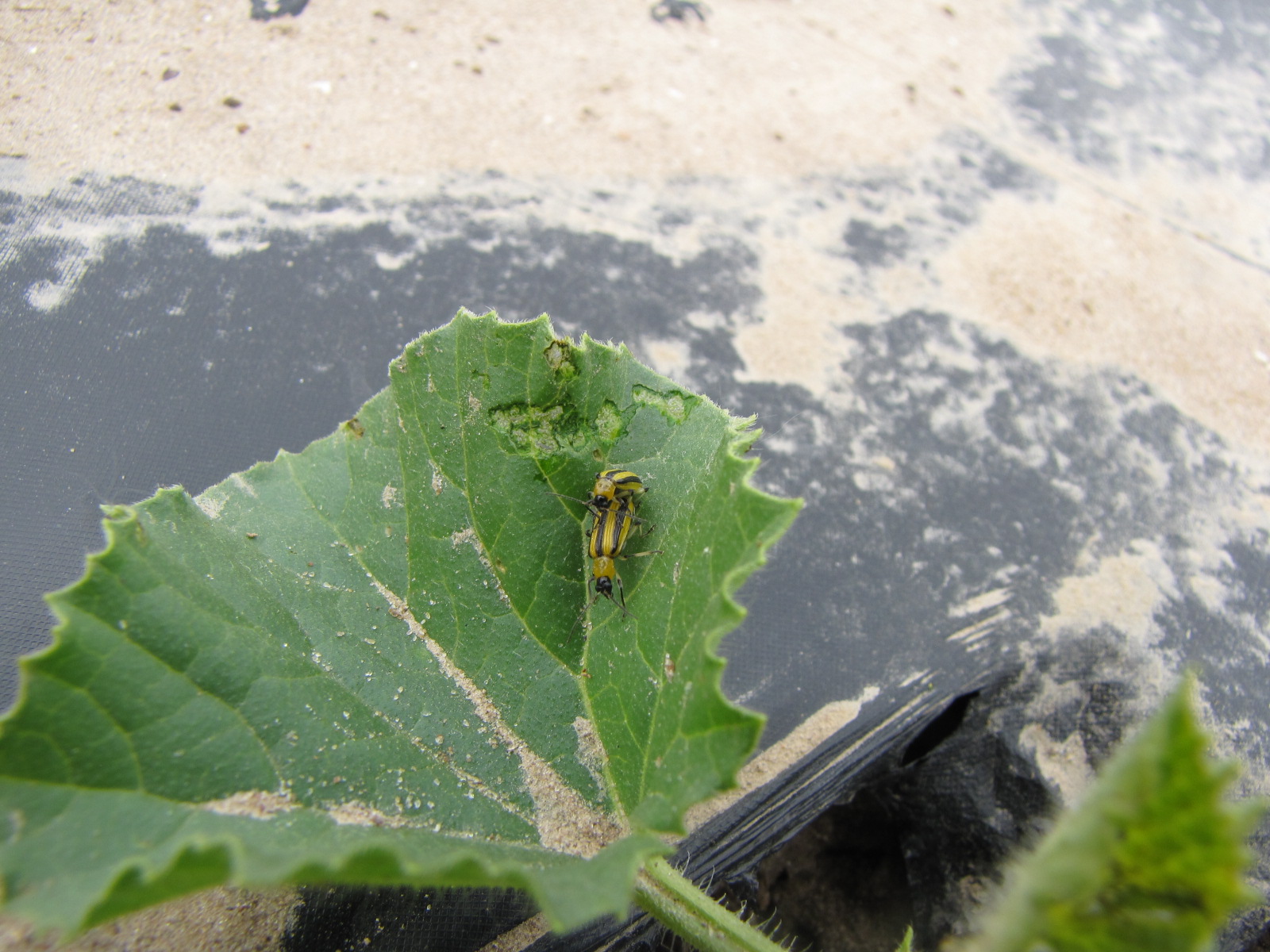  Figure 2. Cucumber beetle feeding can be observed on this cantaloupe leaf. If insect frass enters the area that has been fed upon, bacterial wilt may result.
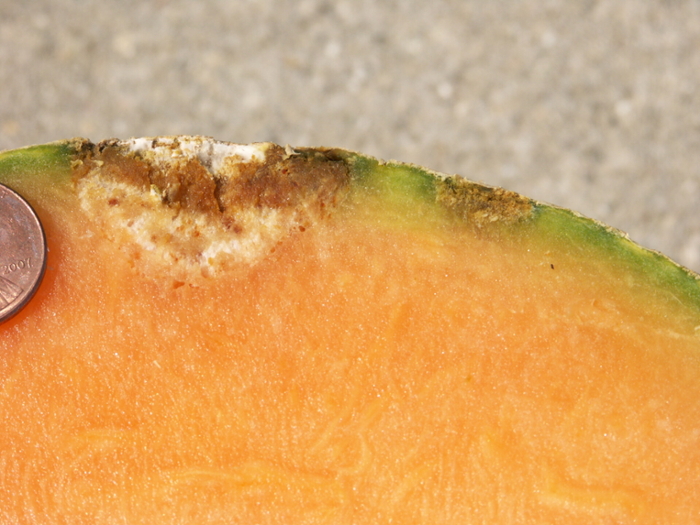
Figure 2. Cucumber beetle feeding can be observed on this cantaloupe leaf. If insect frass enters the area that has been fed upon, bacterial wilt may result. Phytophthora blight
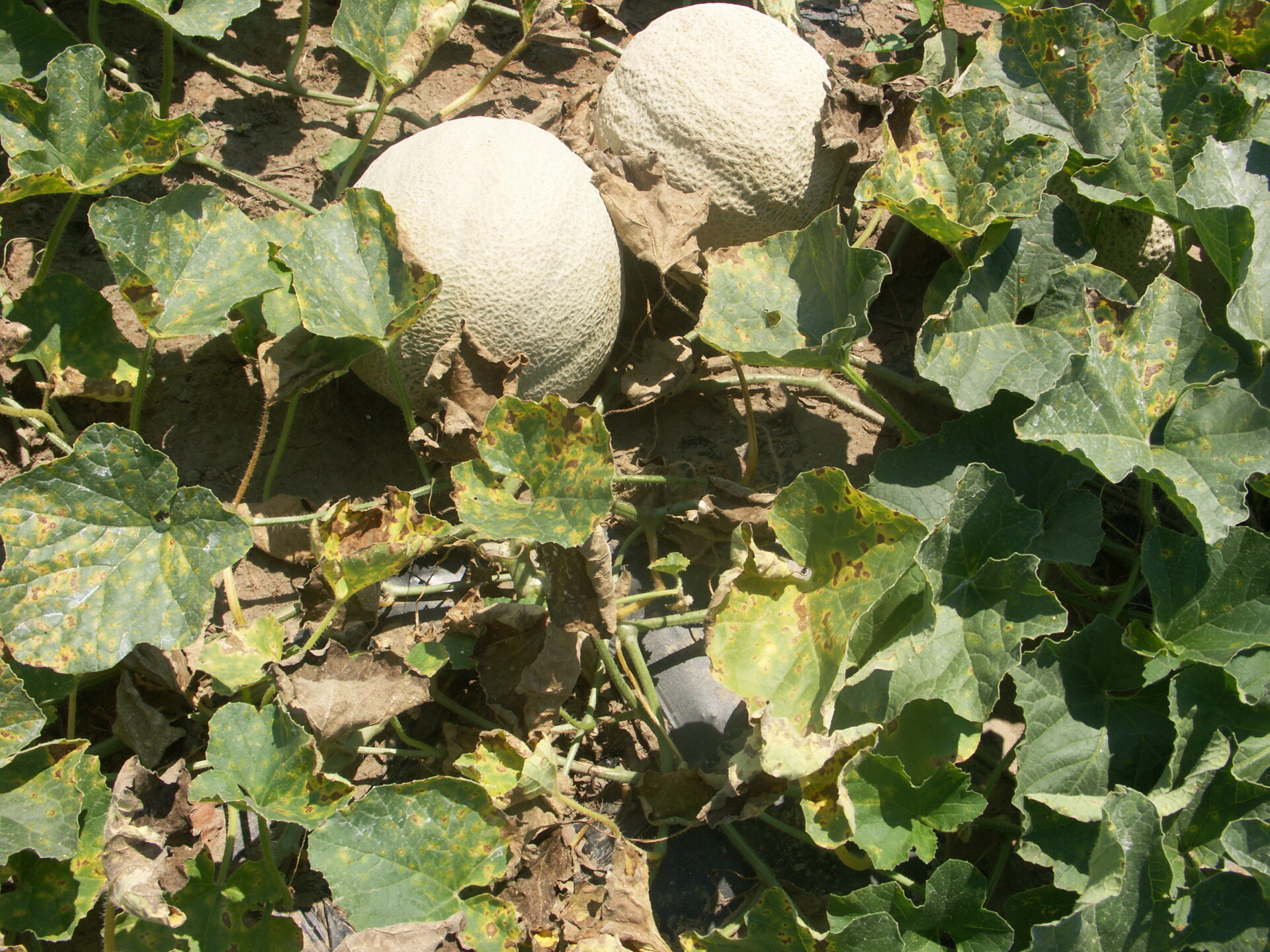
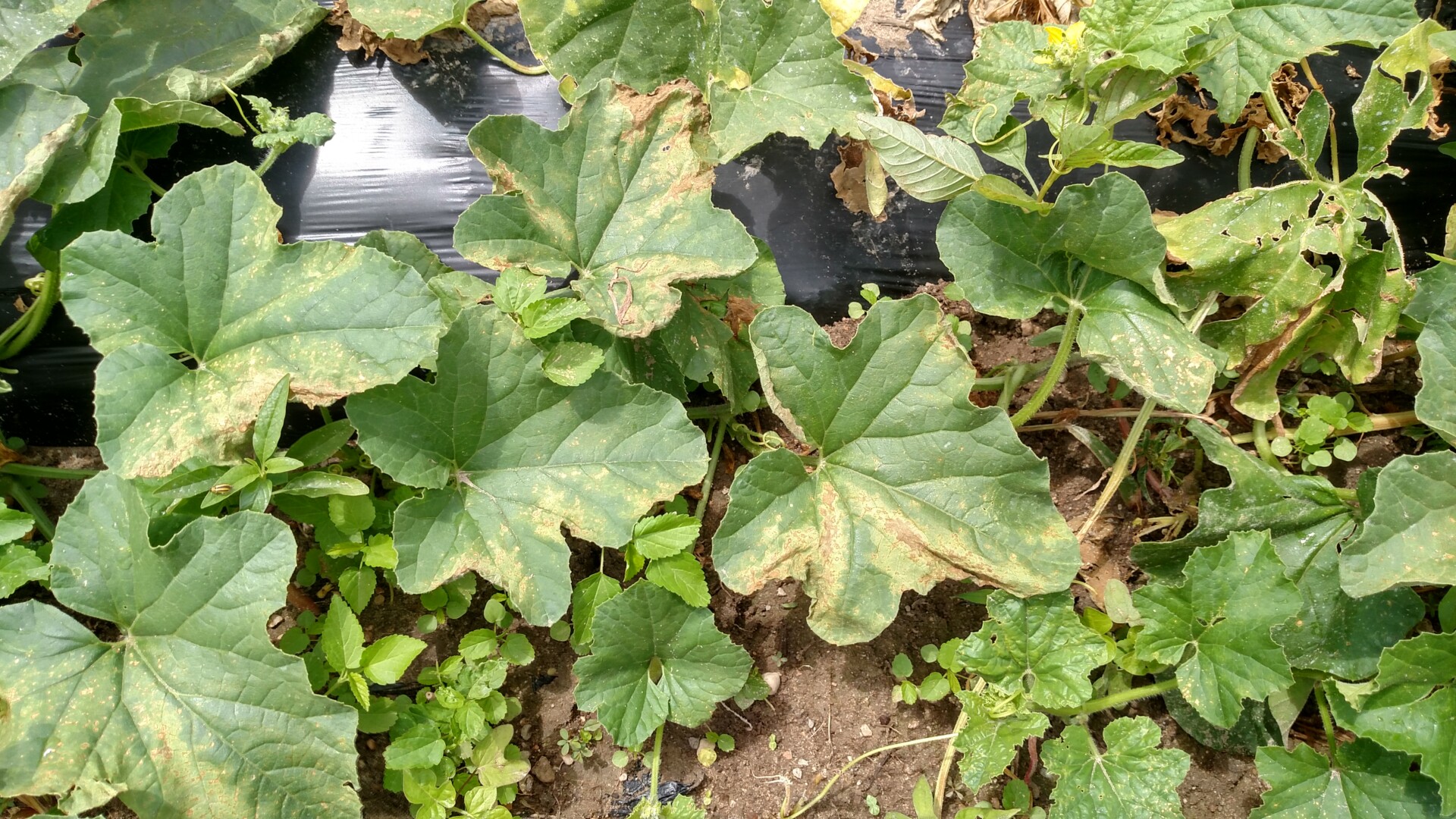
Powdery mildew
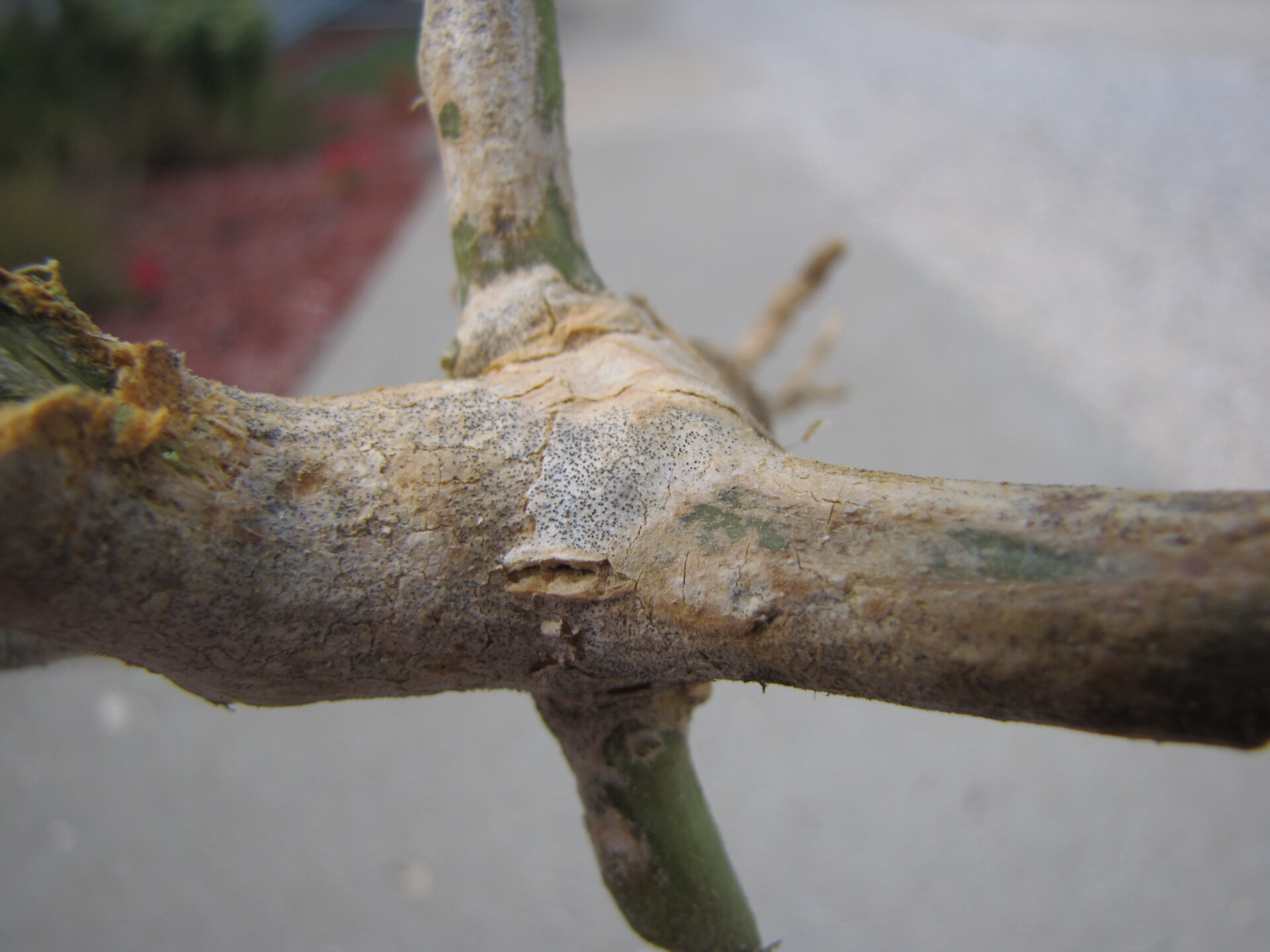
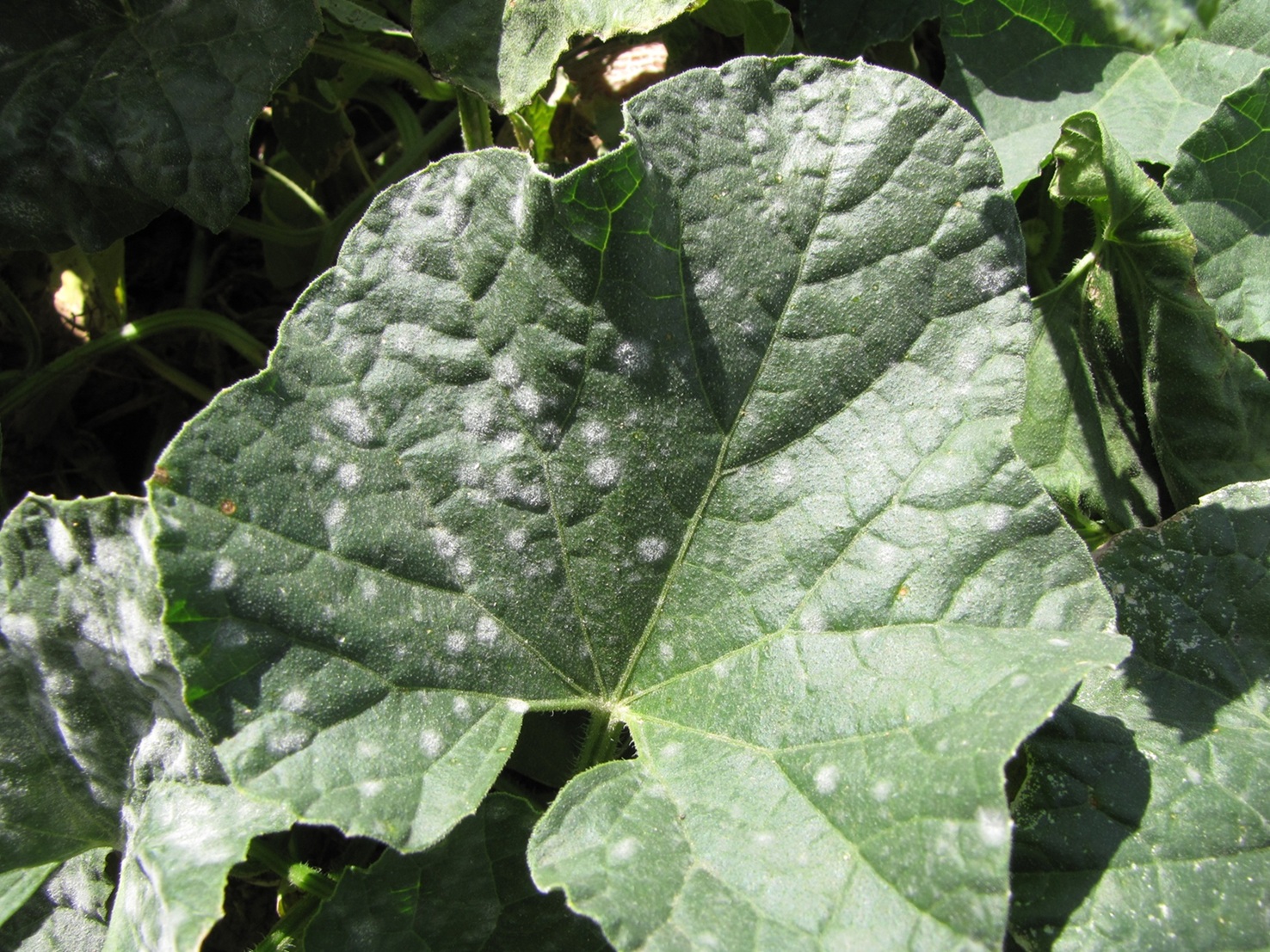 Figure 1. Colonies of powdery mildew are visible on the upper surface of this cantaloupe leaf.
Figure 1. Colonies of powdery mildew are visible on the upper surface of this cantaloupe leaf.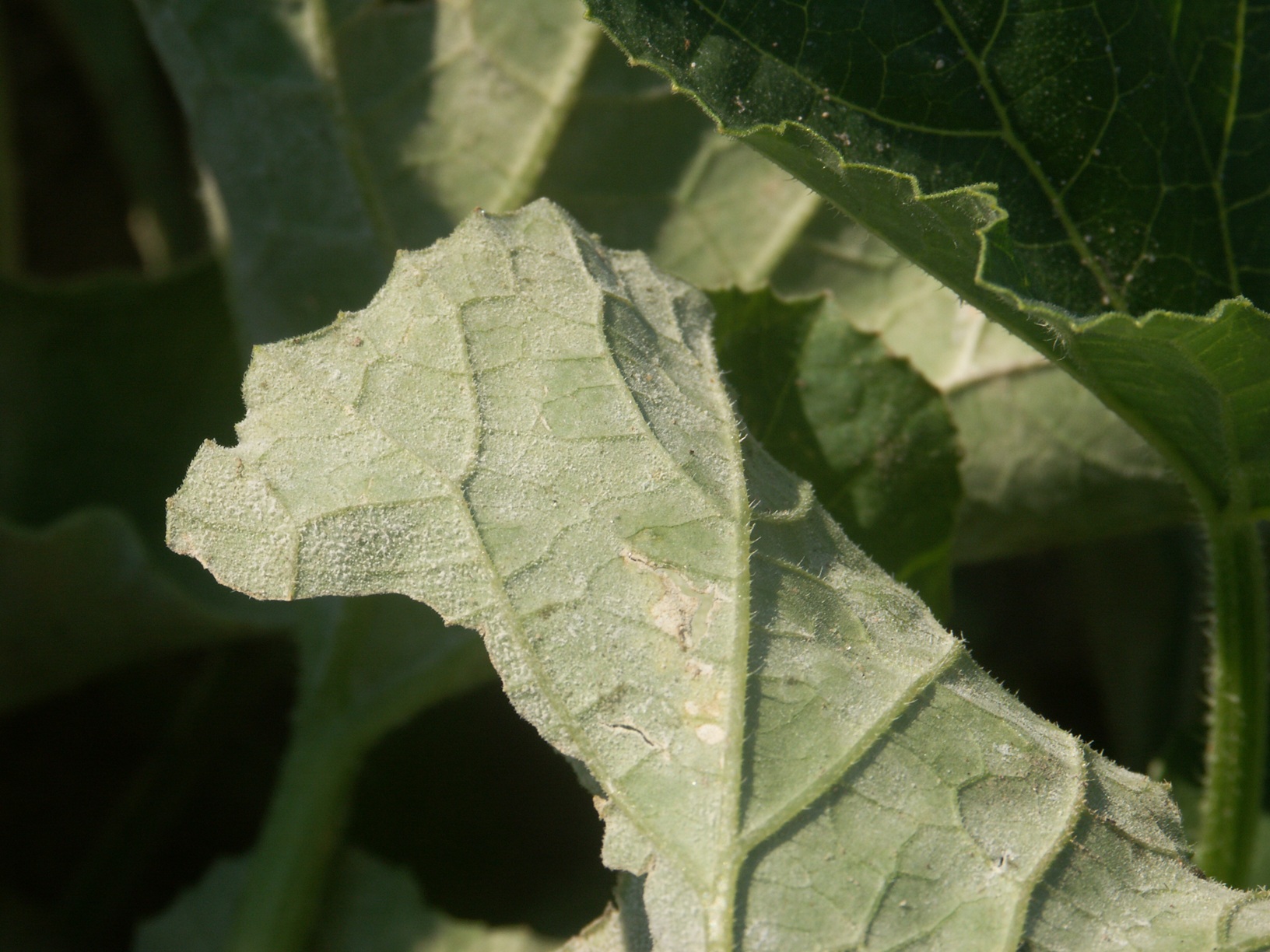  Figure 2. Sporulation of the powdery mildew fungus is visible on the lower surface of a cantaloupe leaf.
Figure 2. Sporulation of the powdery mildew fungus is visible on the lower surface of a cantaloupe leaf.