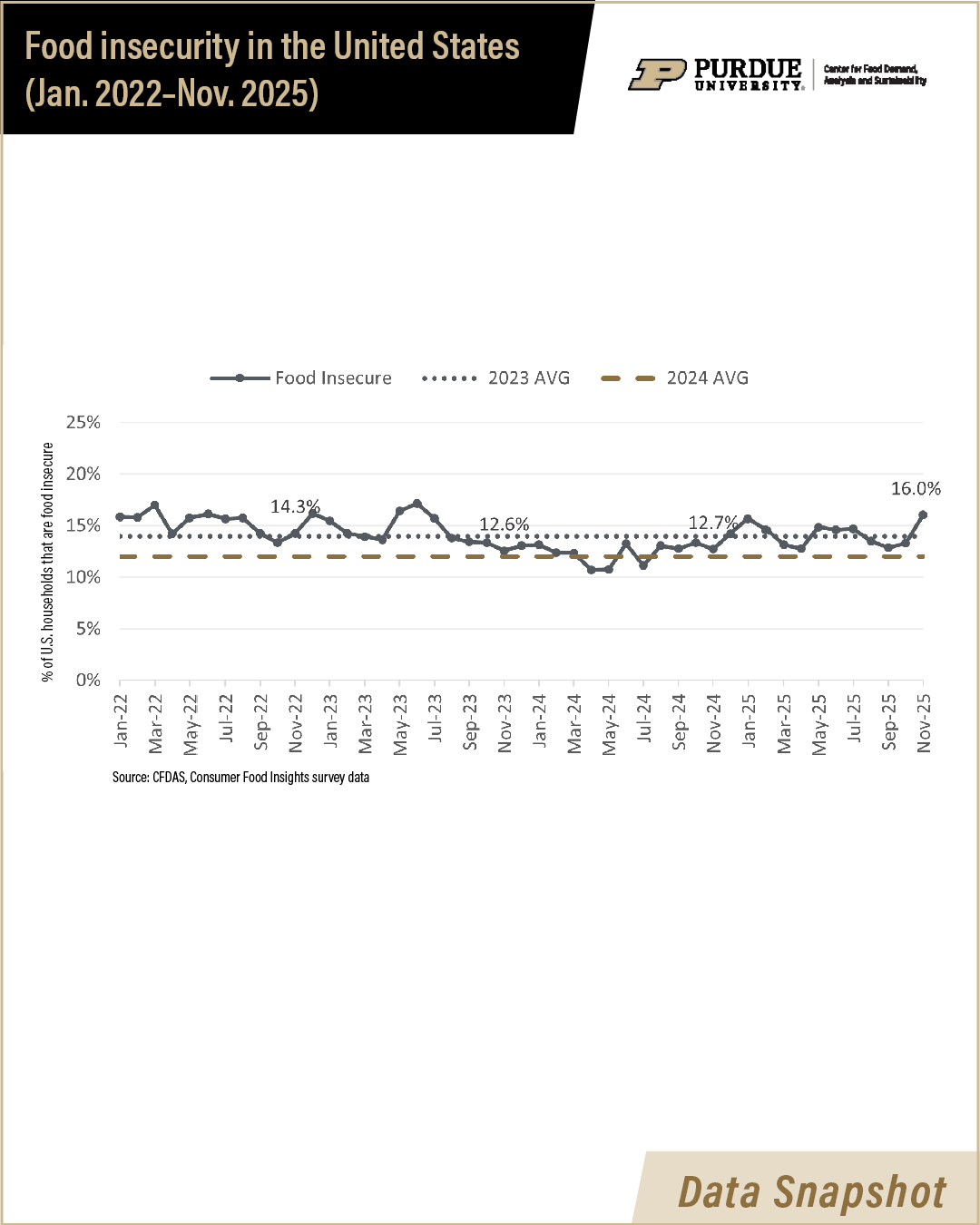
The Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainability has measured food insecurity in the United States since January 2022. CFDAS incorporates the USDA’s Six-item Short Form Food Security Module into the monthly Consumer Food Insights (CFI) survey of 1,200 American consumers.
Food insecurity was highest in 2022 and 2023, when inflation reached historical highs and food inflation rose above 10%. U.S. food insecurity fell to 12.5% in 2024, as food inflation fell to near 2%.
Both food insecurity and food inflation have crept up in 2025. Through November, the food insecurity rate in the U.S. has been 14.2%. The food insecurity rate rose sharply in November 2025, from 13.3% in October to 16% in November. The food insecurity rate among SNAP participants rose 10 percentage points, from 36% in recent years to 46% in November 2025.
In addition to ongoing inflation, potential contributing factors include a shutdown of the U.S. federal government, which created uncertainty around funding for federal nutrition assistance programs, and changes to the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program enacted as part of Public Law 119-21.
Continue to follow along with our U.S. Household Food Insecurity Rate dashboard and monthly CFI Reports for updated trends and in-depth analysis.
December 9, 2025