pumpkin diseases
Bacterial leaf spot
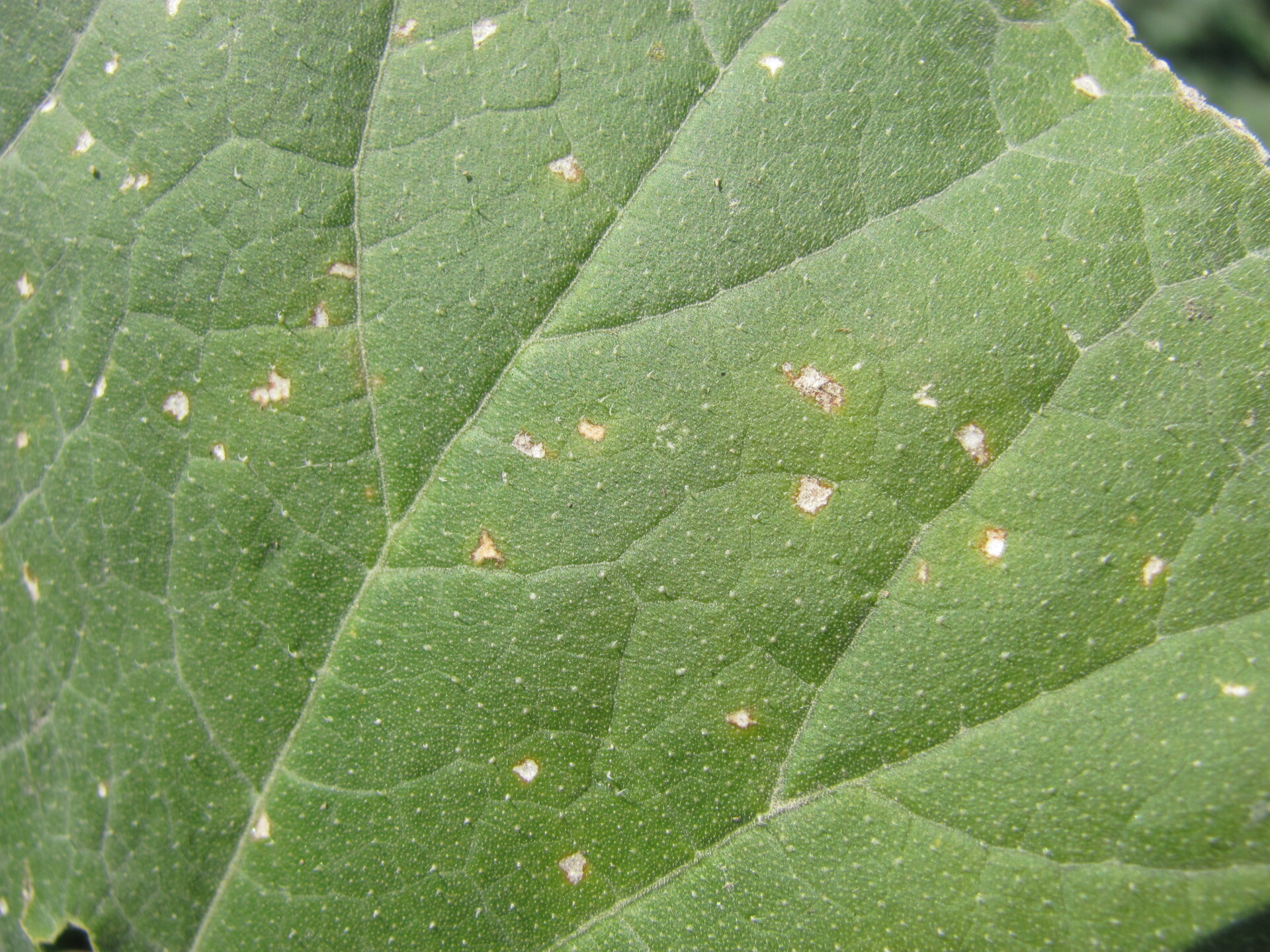
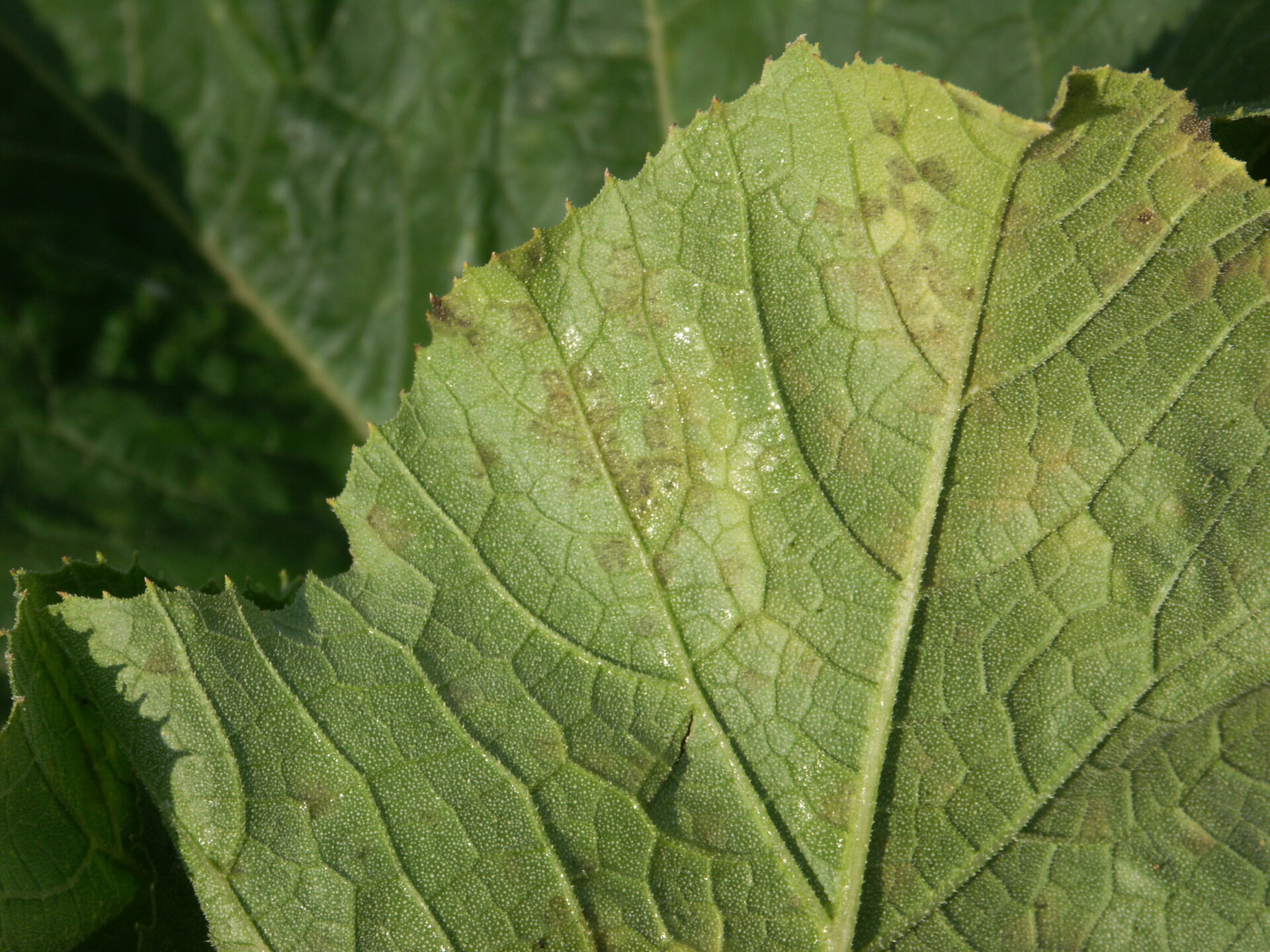
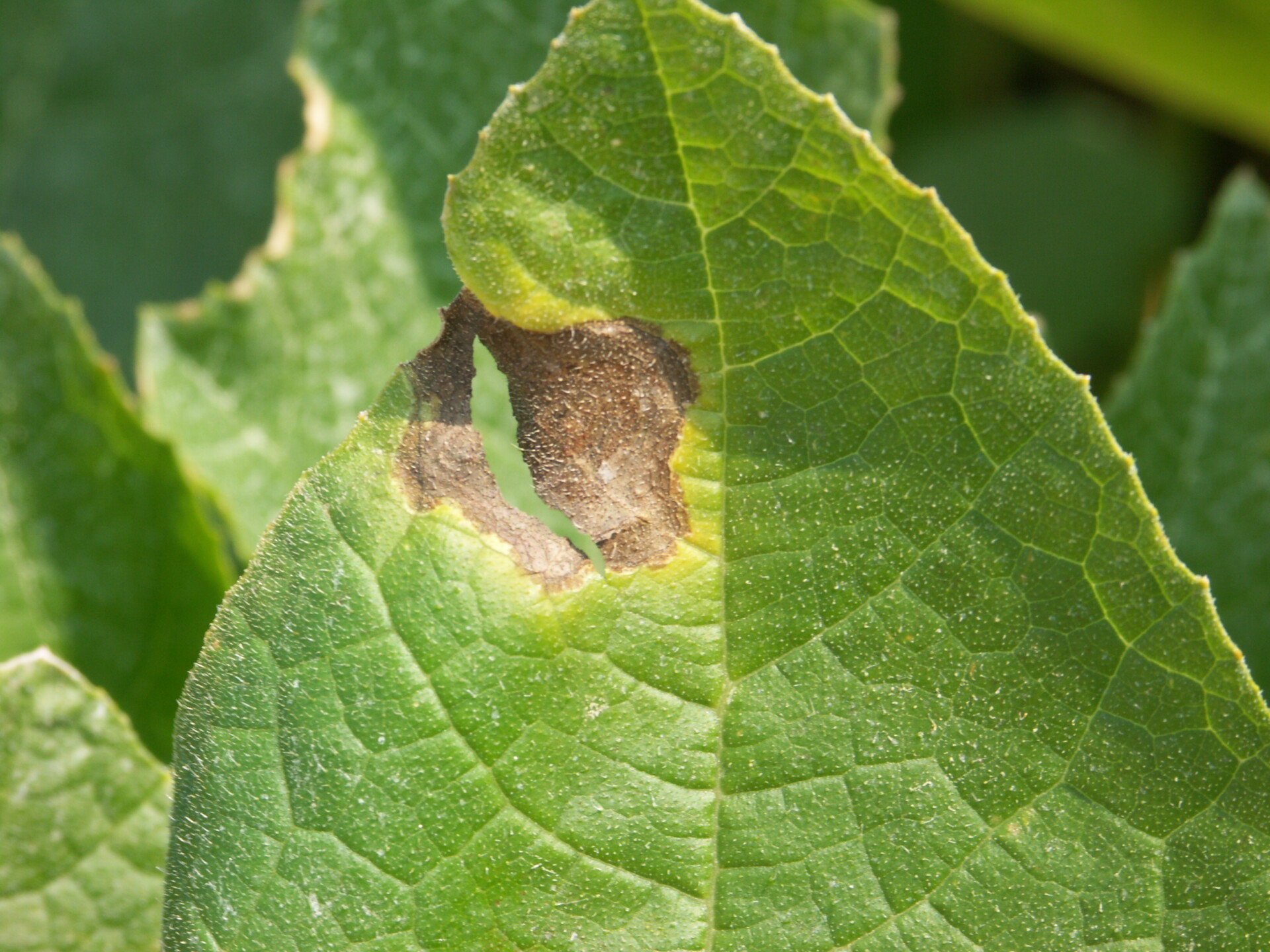
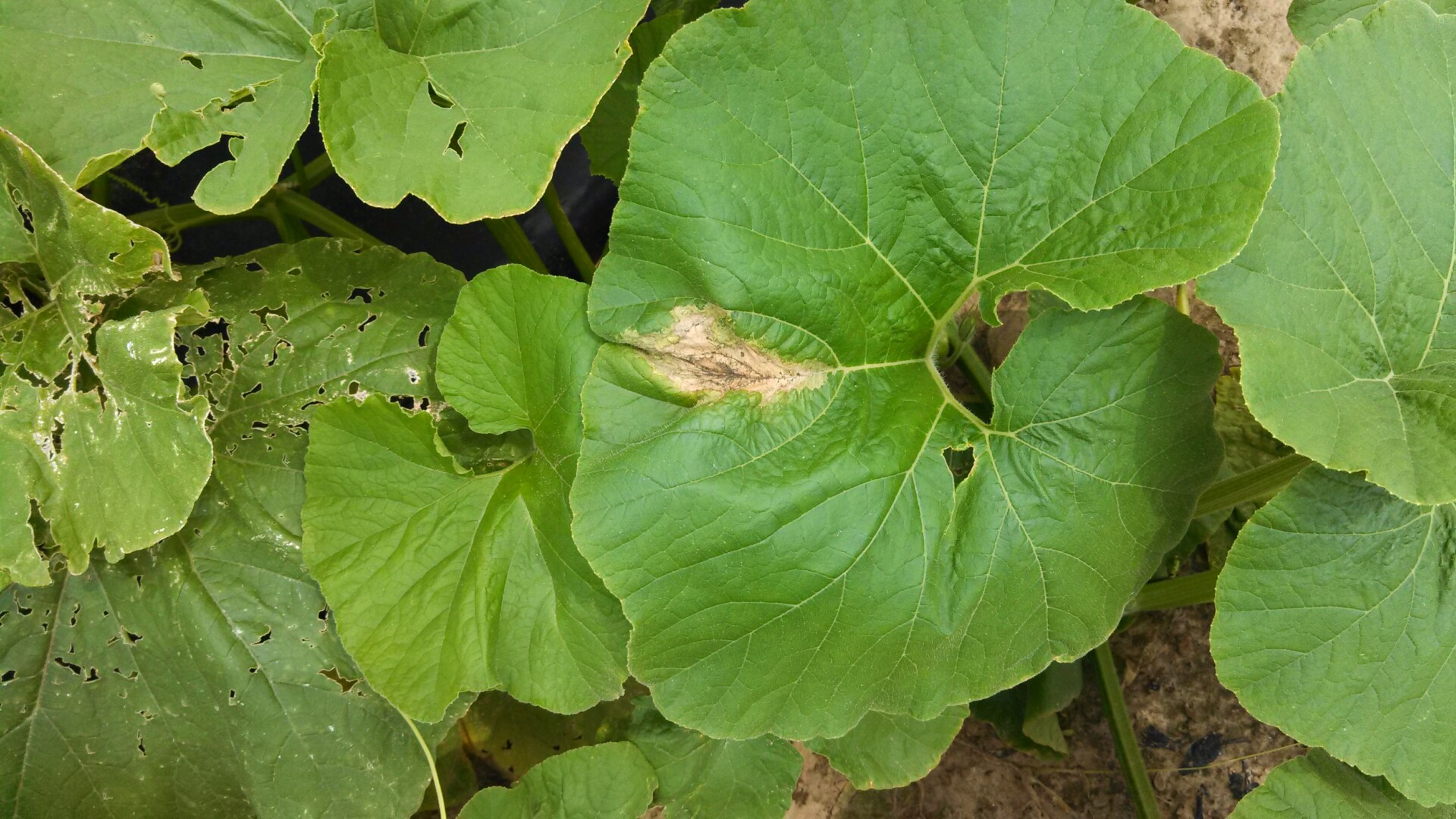
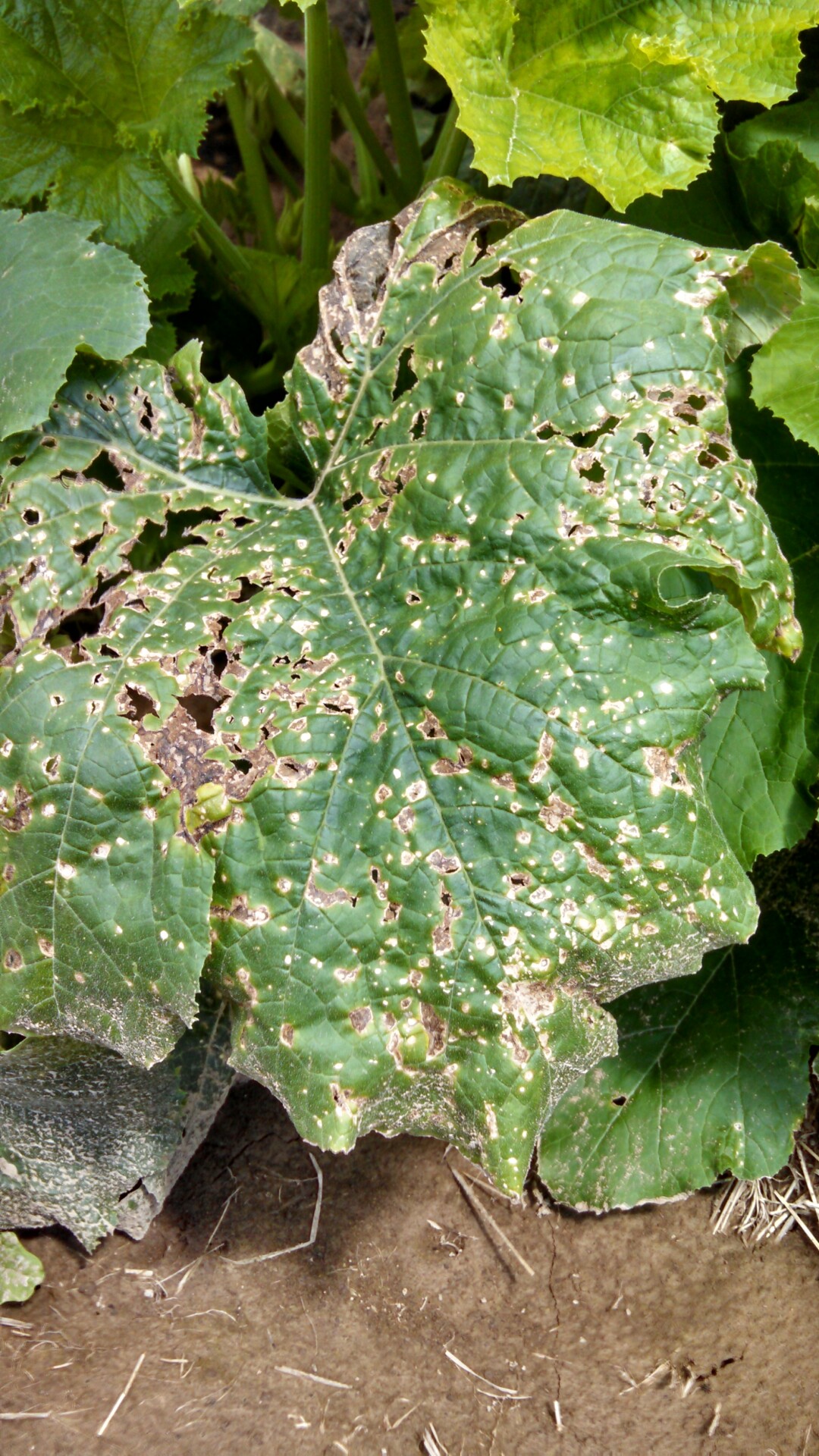 Figure 1. Lesions of bacterial leaf spot on a pumpkin leaf are often a light brown and maybe somewhat angular in shape.
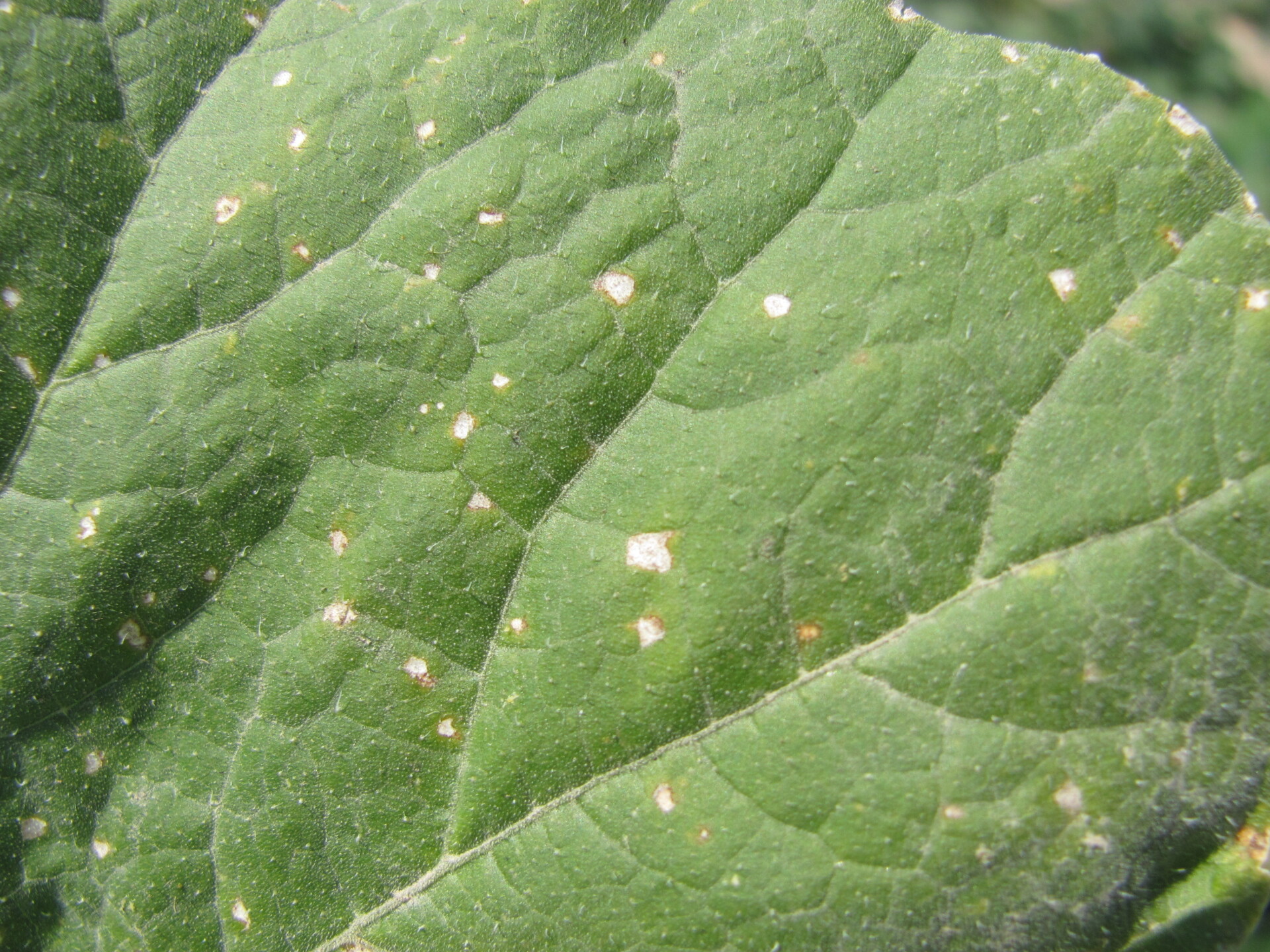
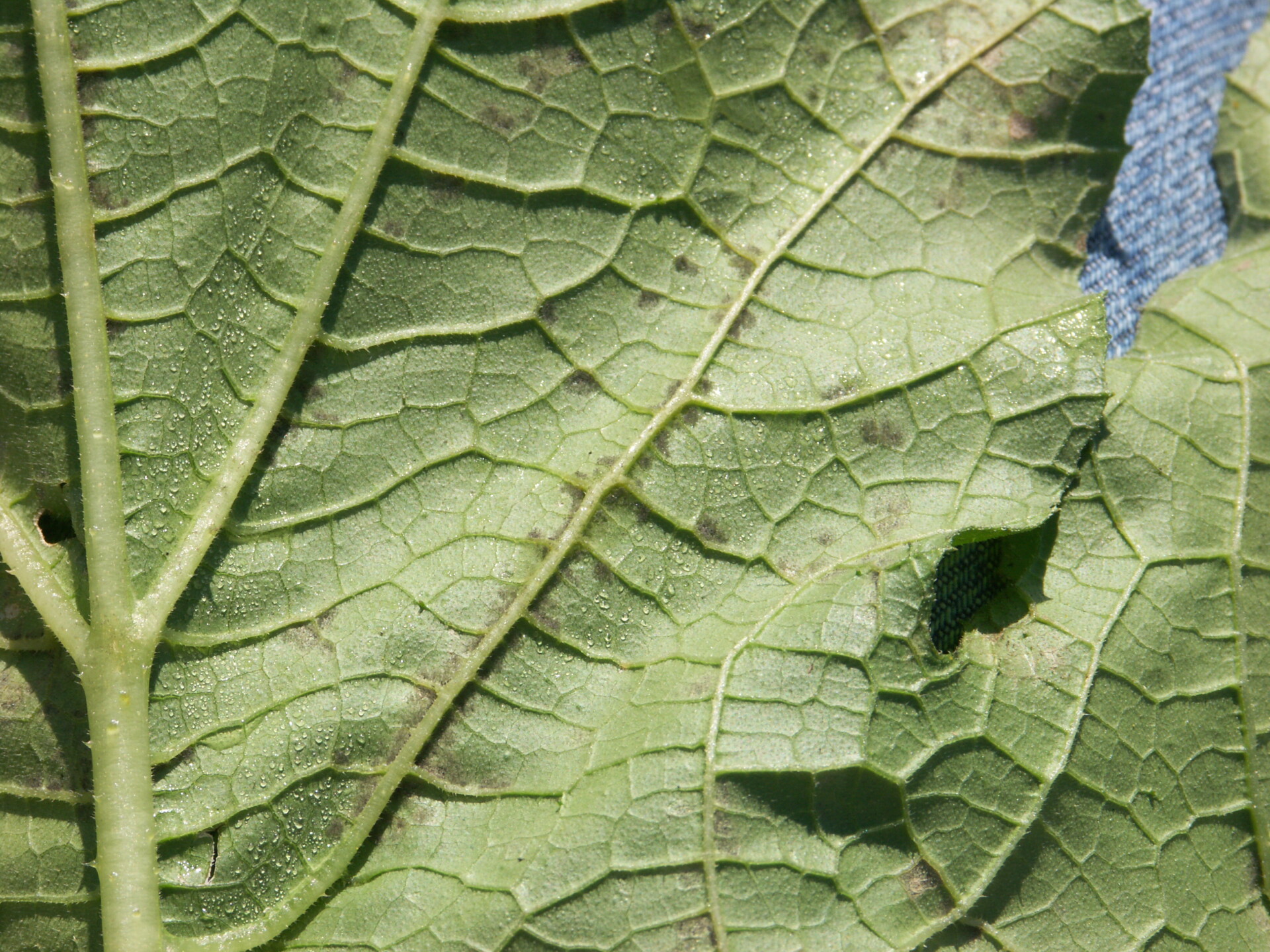
Figure 1. Lesions of bacterial leaf spot on a pumpkin leaf are often a light brown and maybe somewhat angular in shape.  Figure 3. The bacterial spot lesions on the leaf in the foreground are a darker necrotic shade than the lesions in Figure 1 and 2.
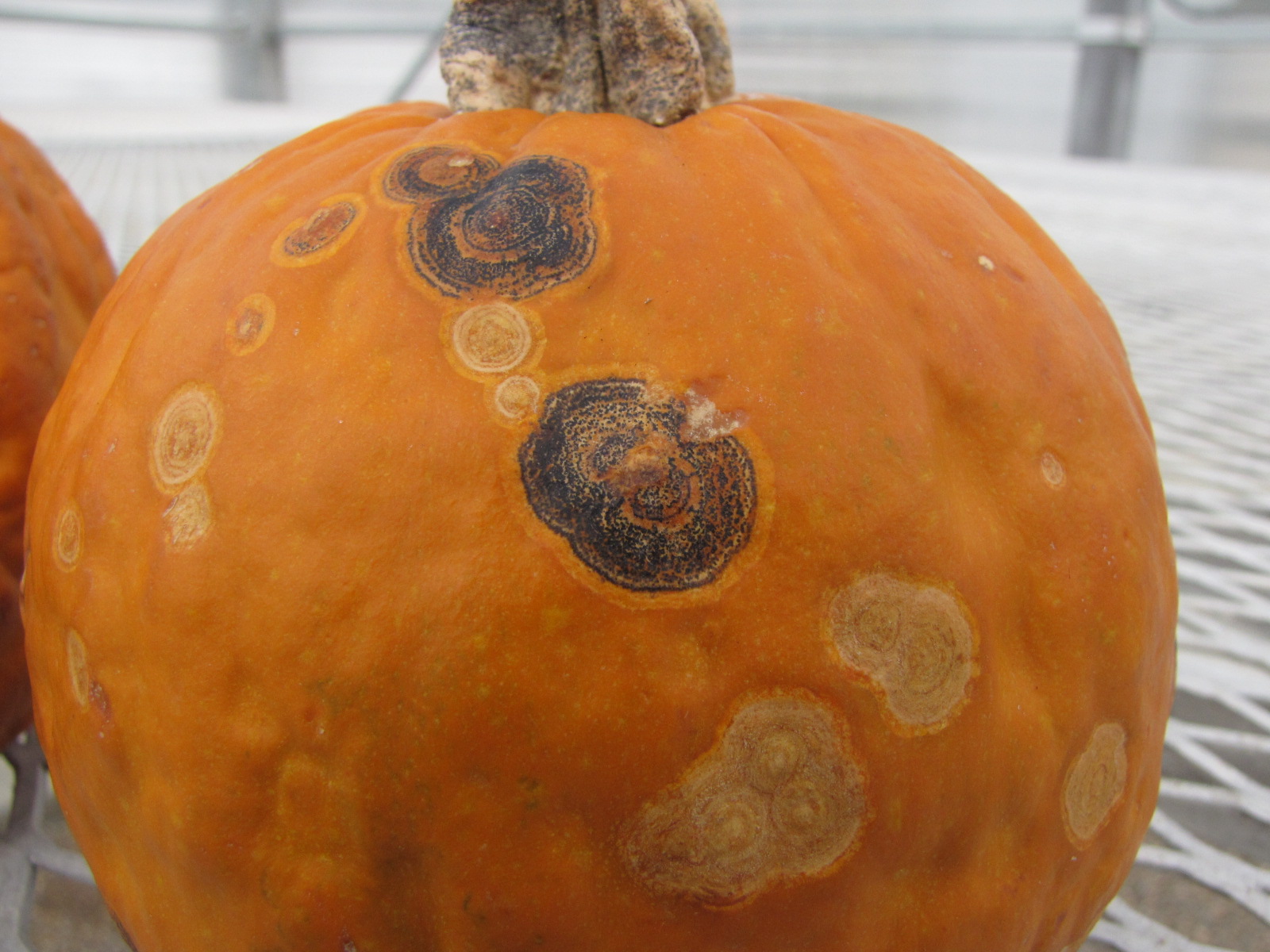
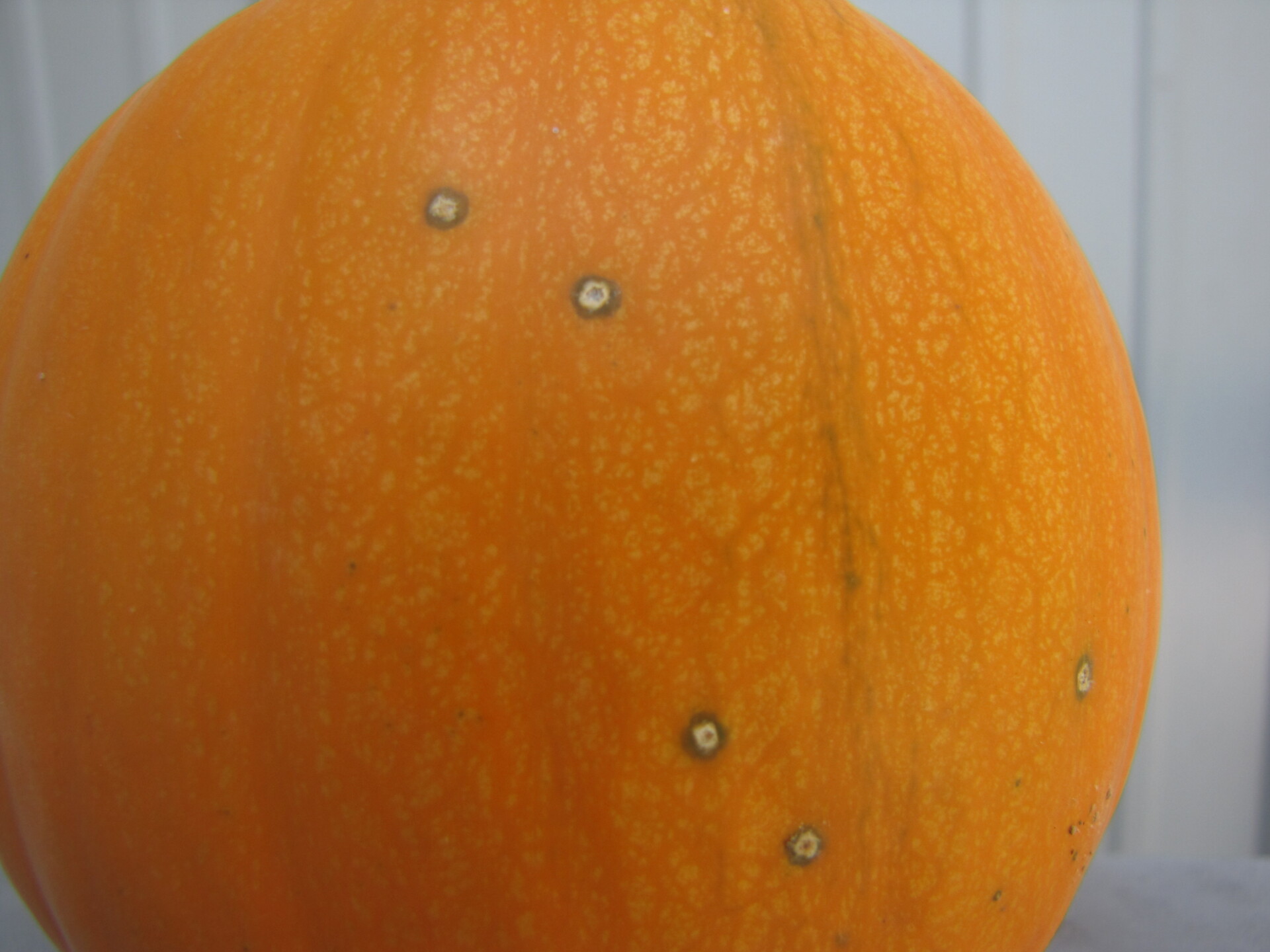
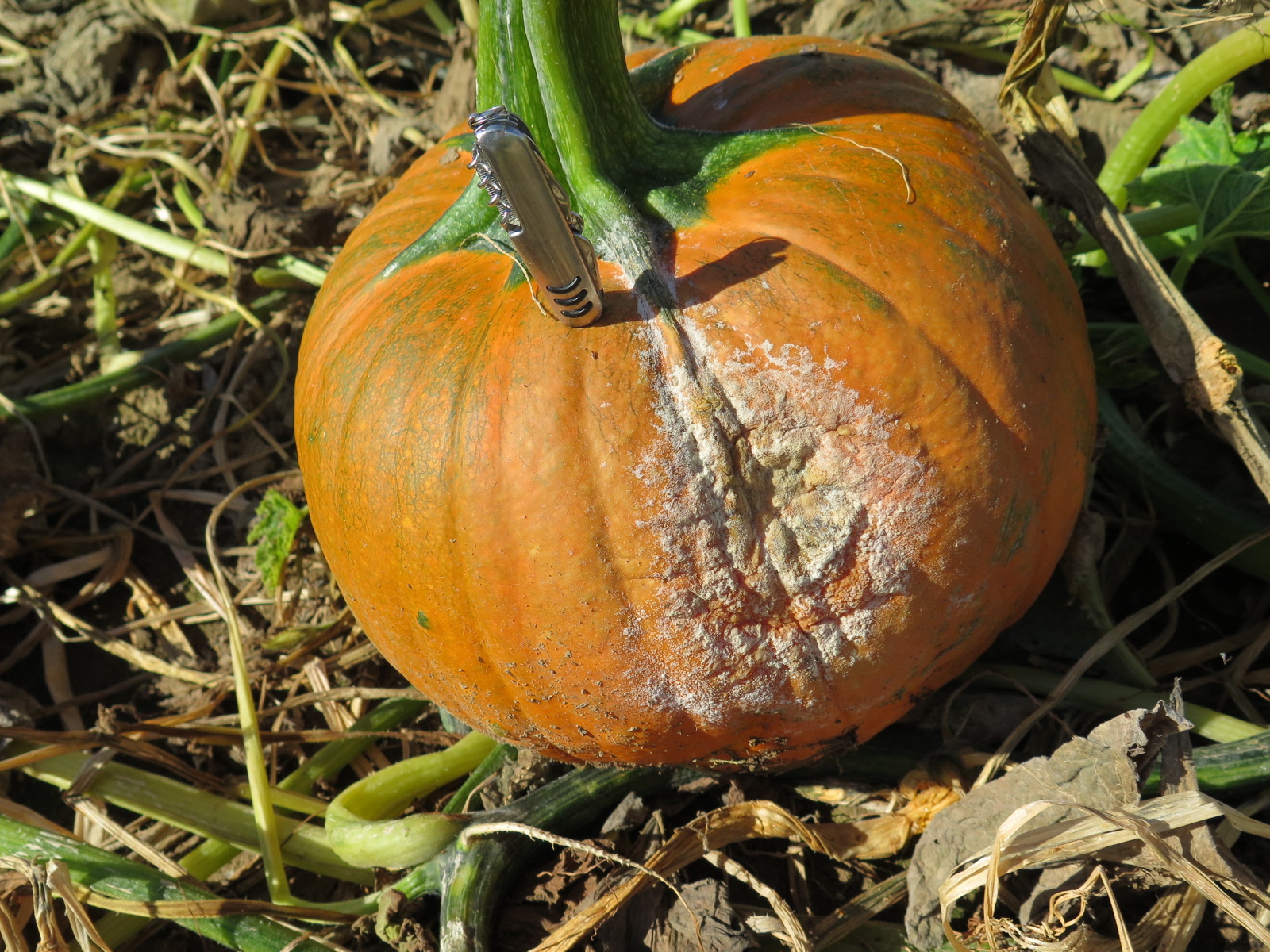
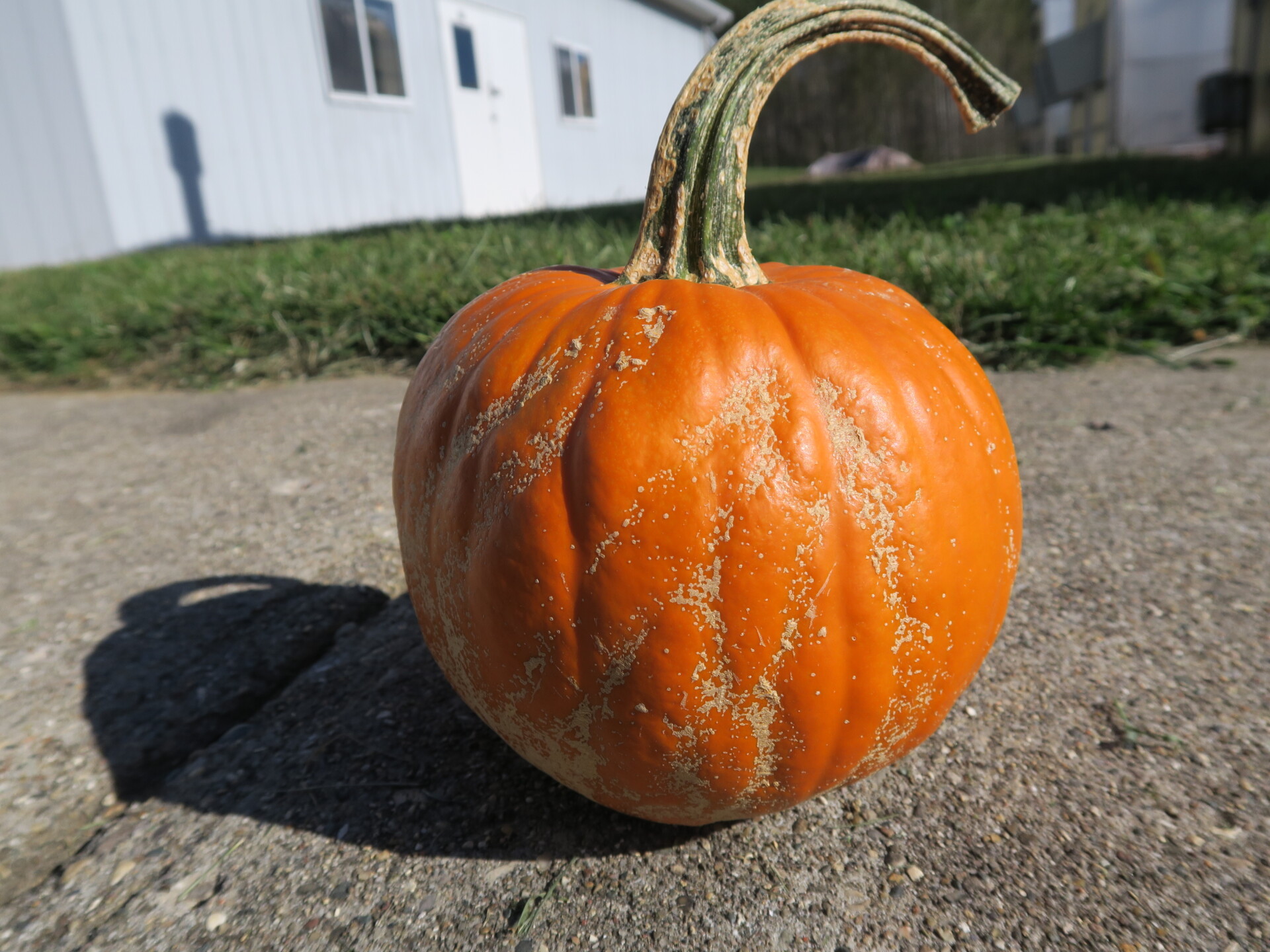
Figure 3. The bacterial spot lesions on the leaf in the foreground are a darker necrotic shade than the lesions in Figure 1 and 2. 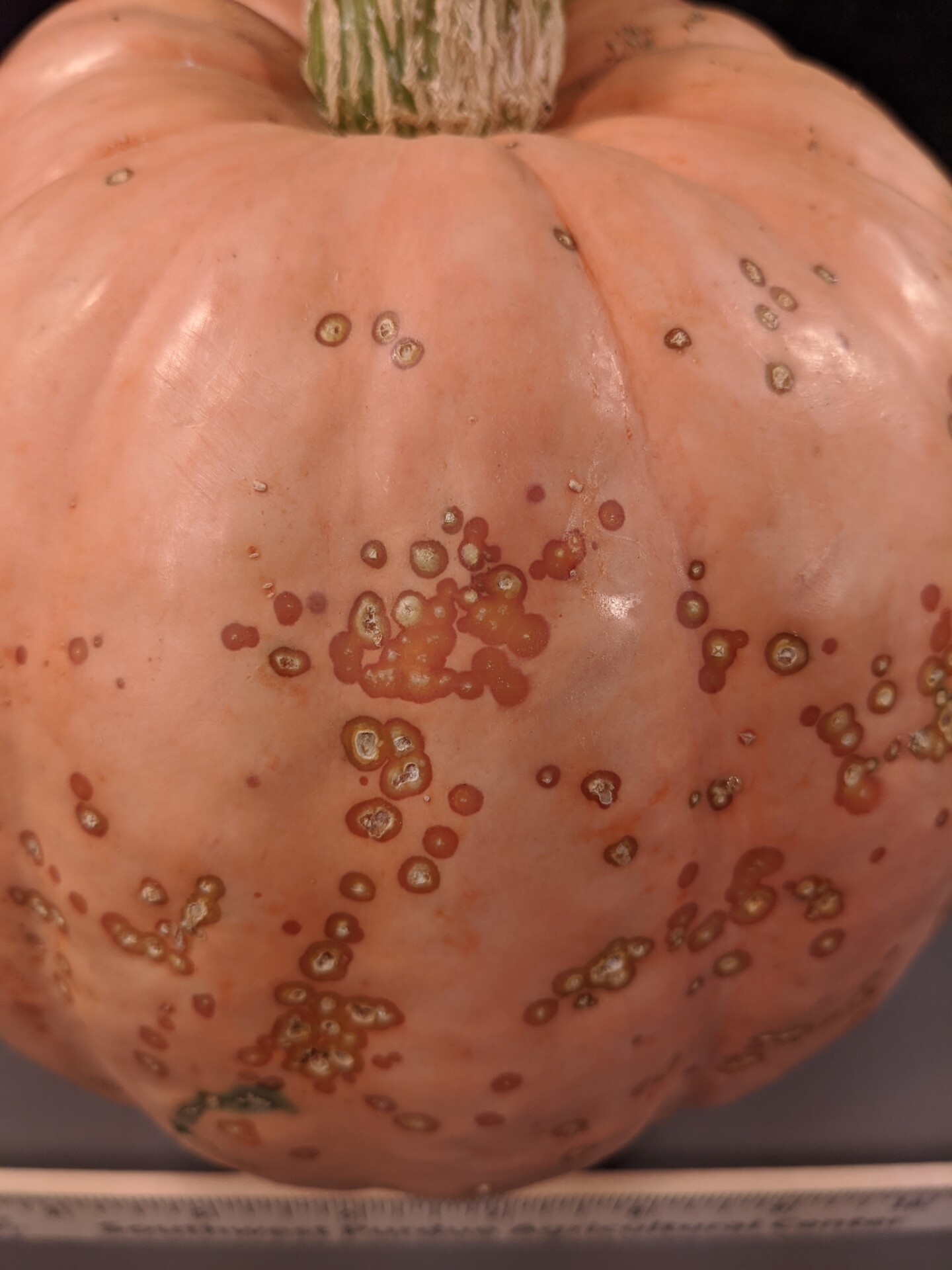 Figure 4. A specialty pumpkin with lesions of bacterial leaf spot of pumpkin. Note that lesions may have a water-soaked appearance. Older lesions may have a light necrotic center.
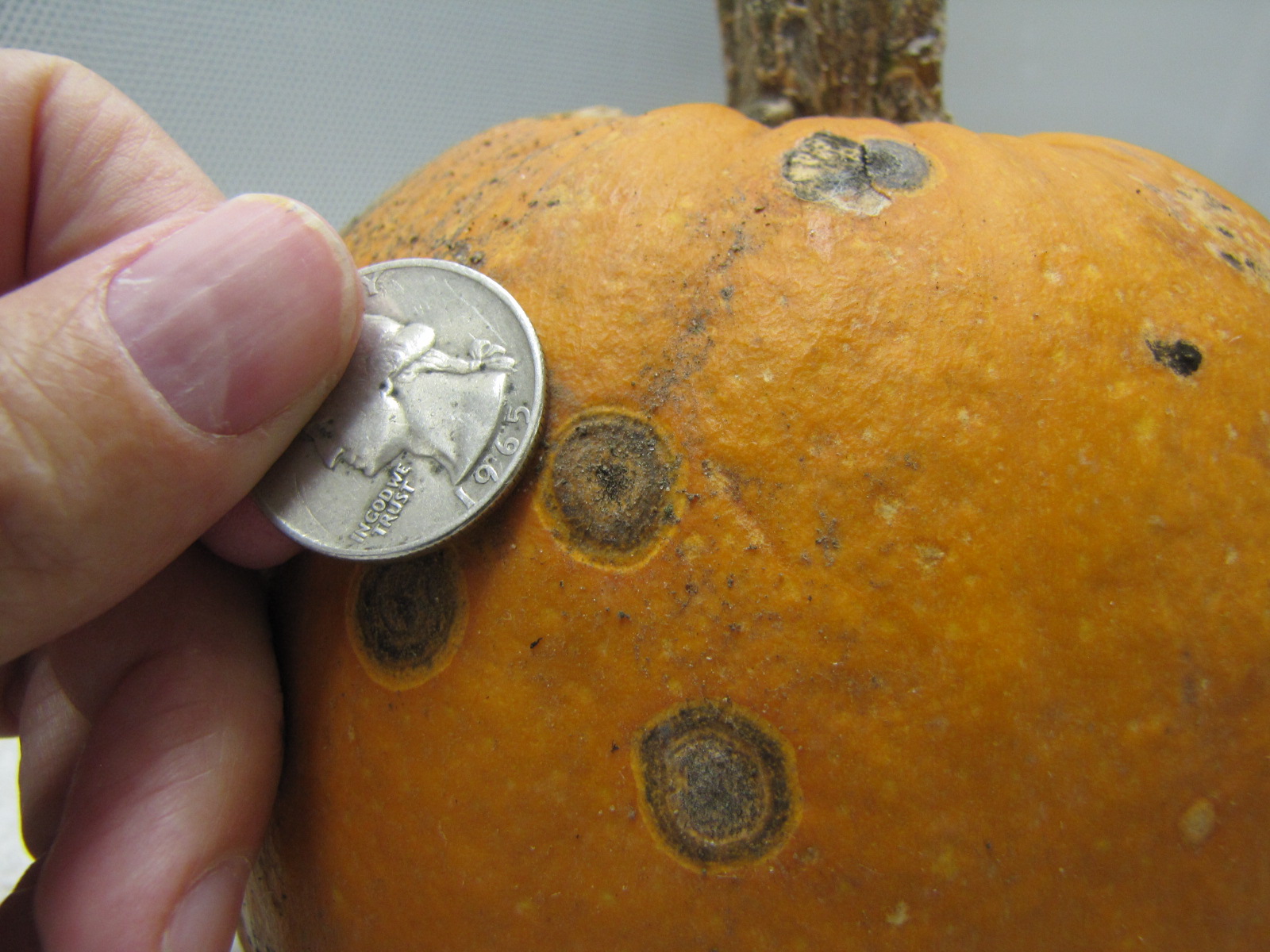
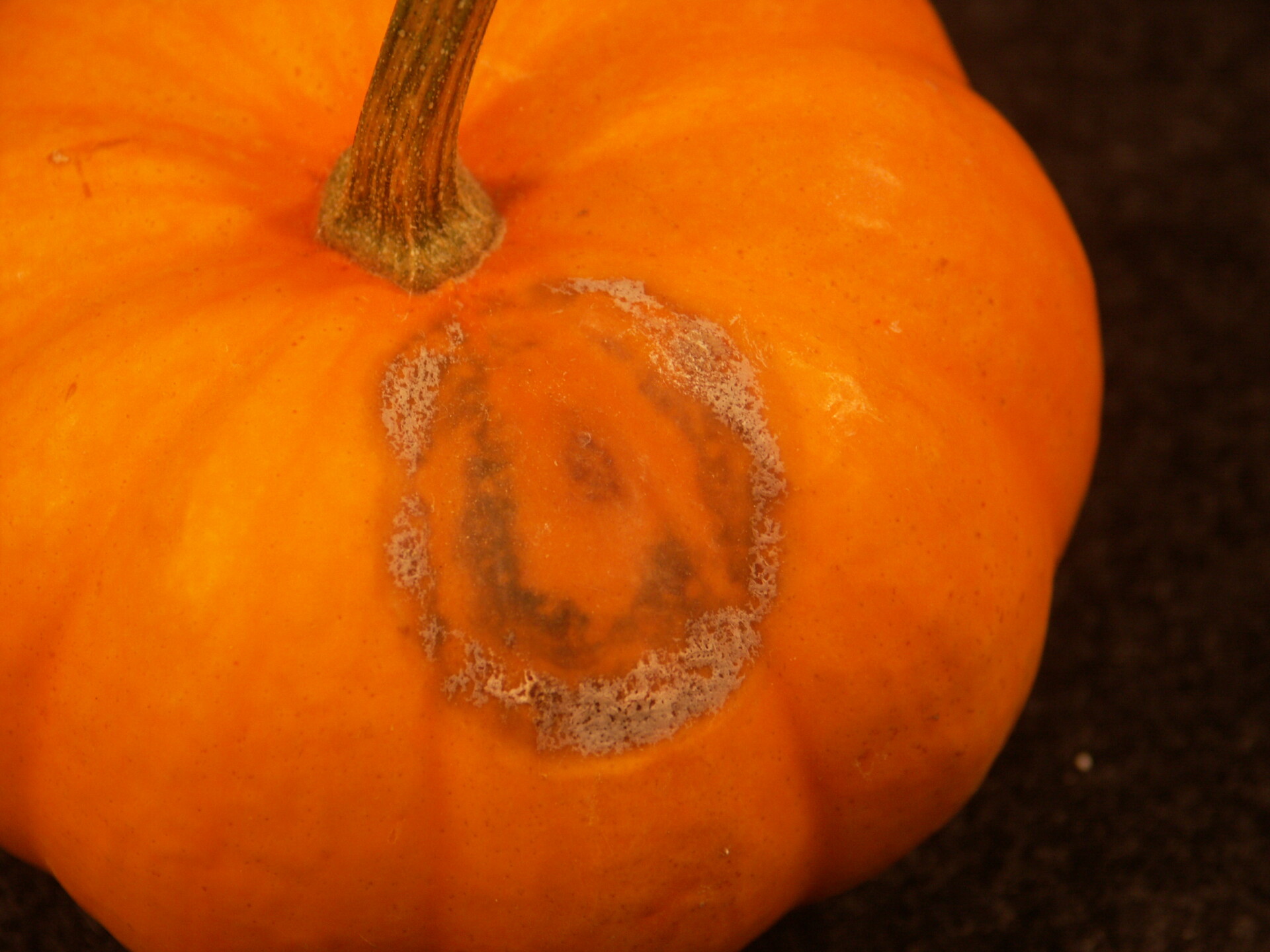
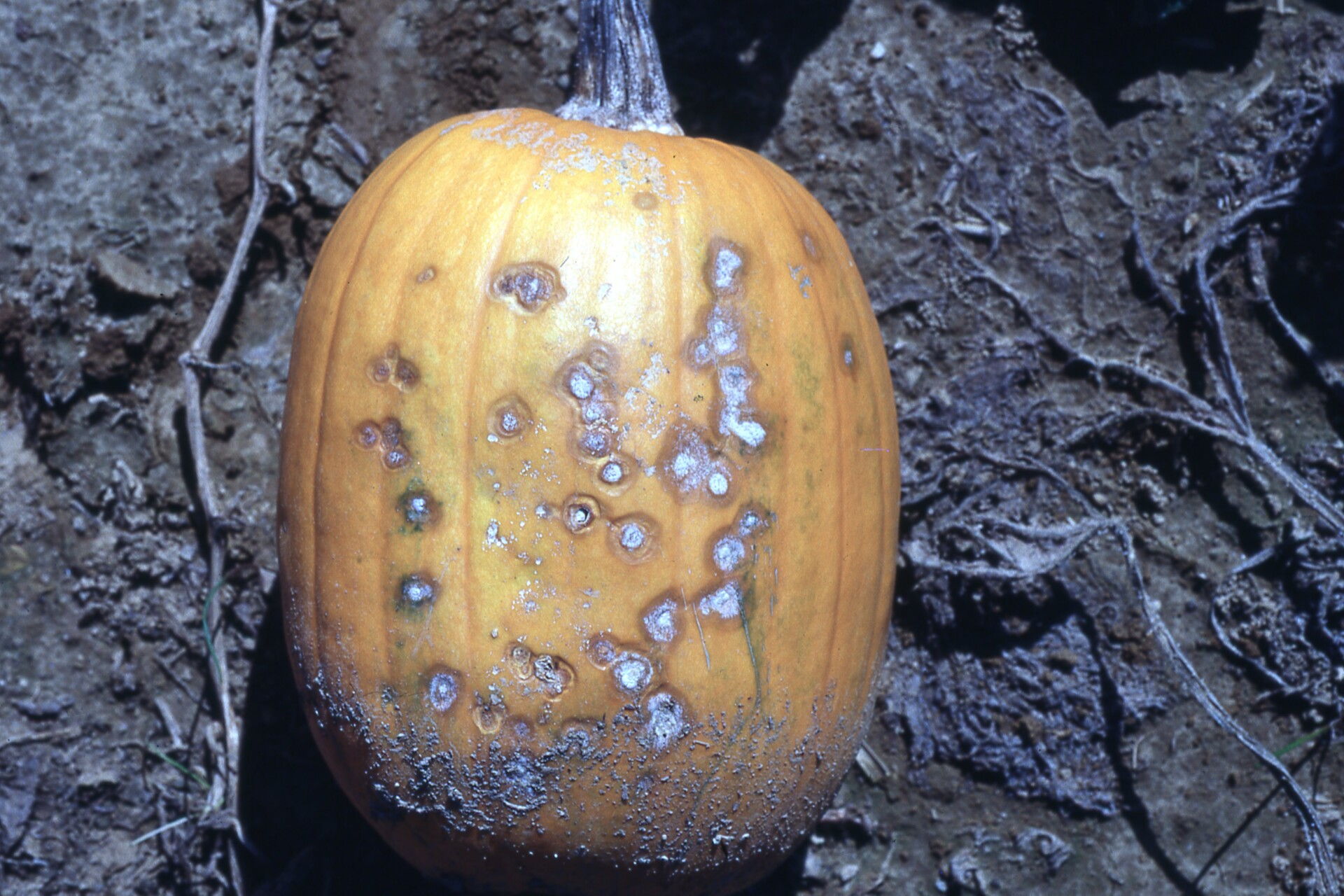
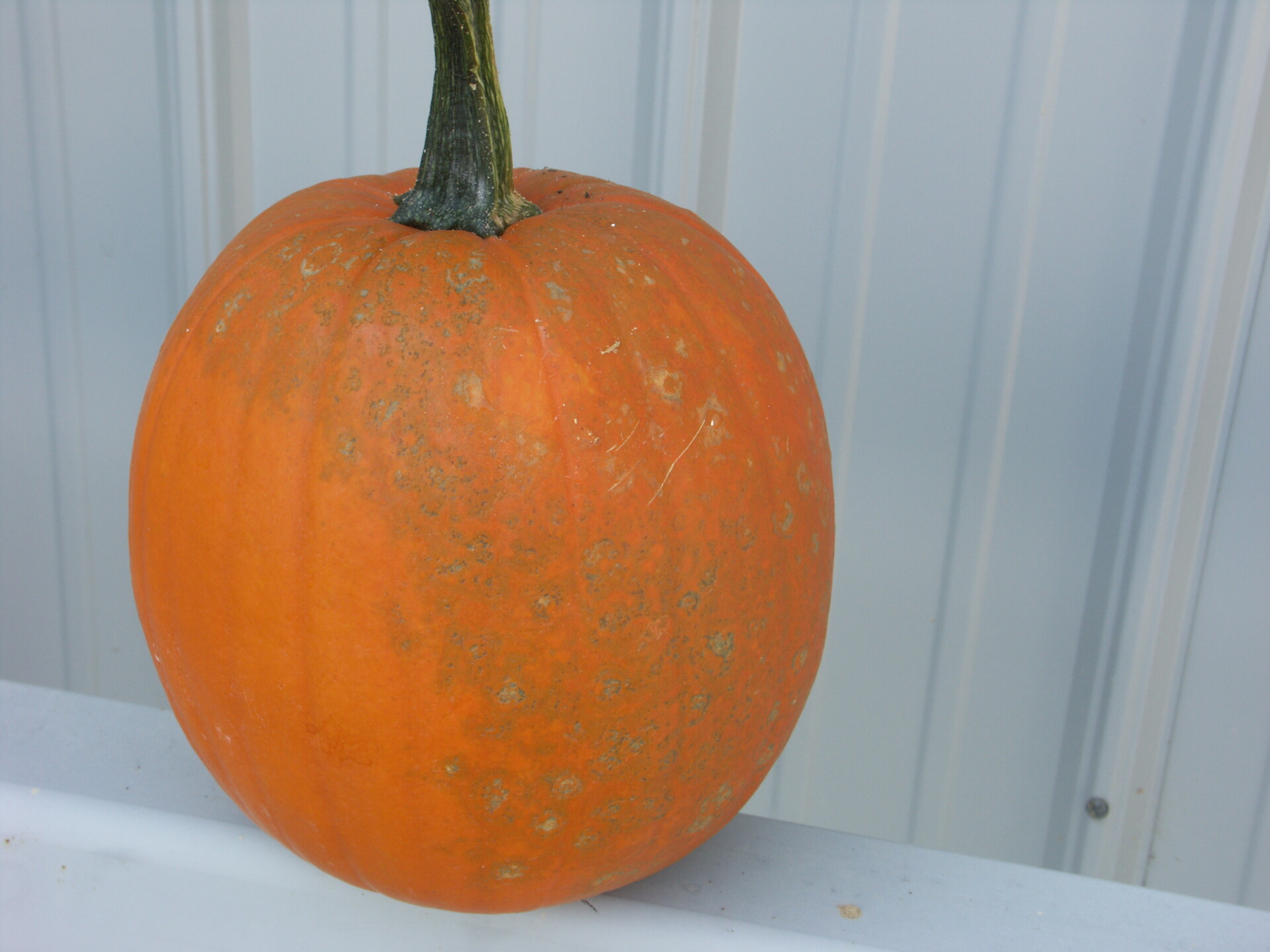
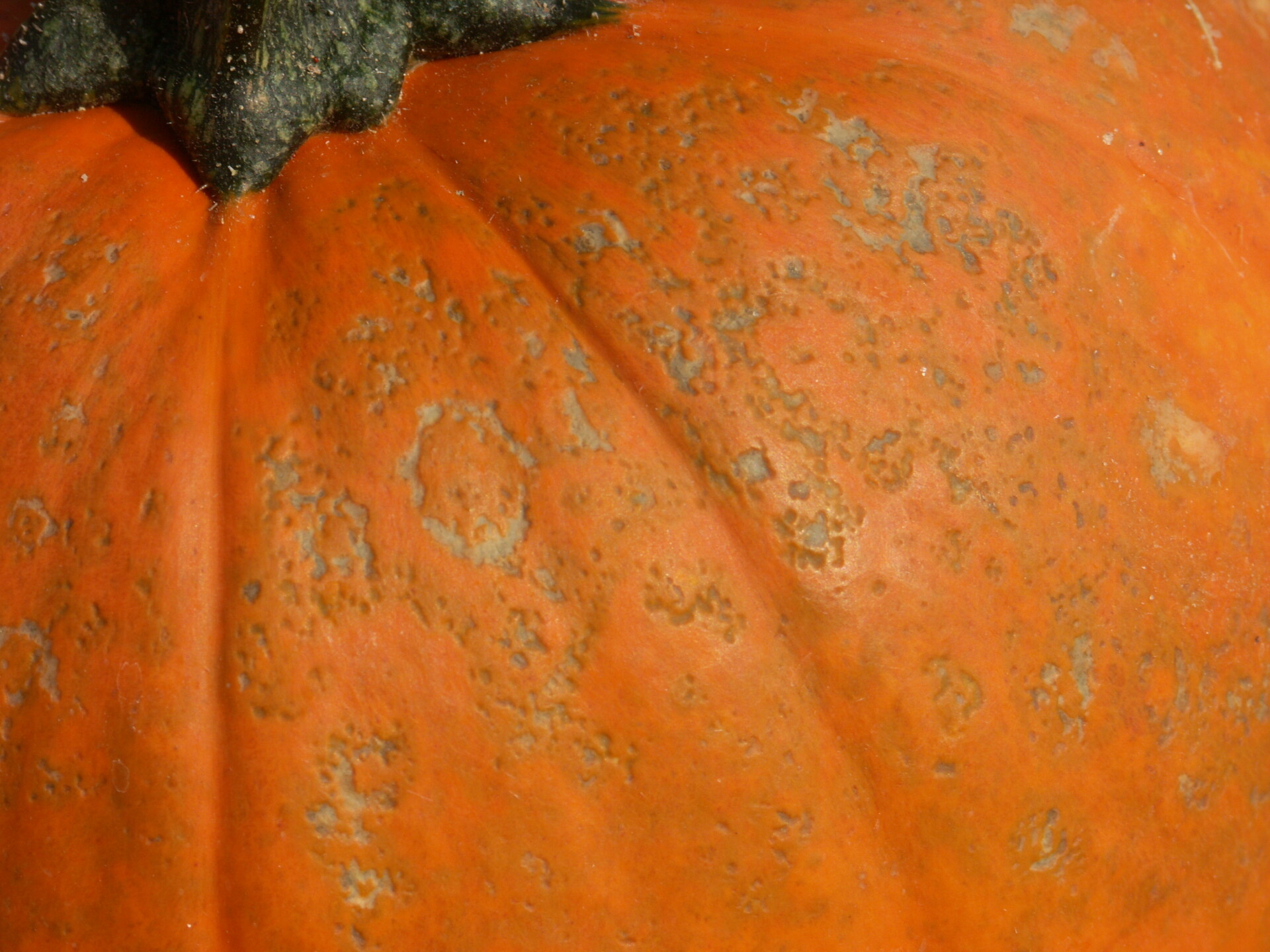
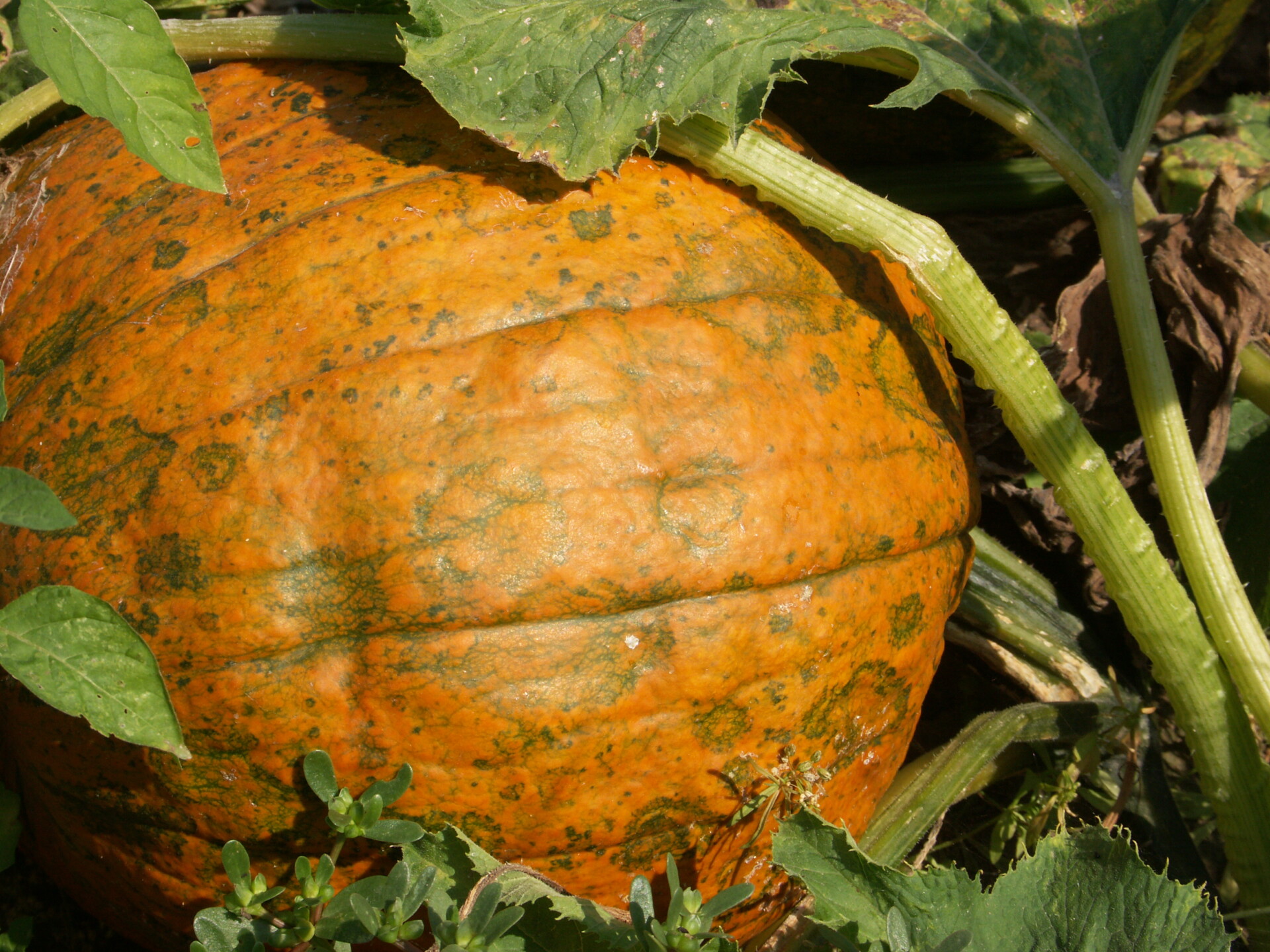
Figure 4. A specialty pumpkin with lesions of bacterial leaf spot of pumpkin. Note that lesions may have a water-soaked appearance. Older lesions may have a light necrotic center.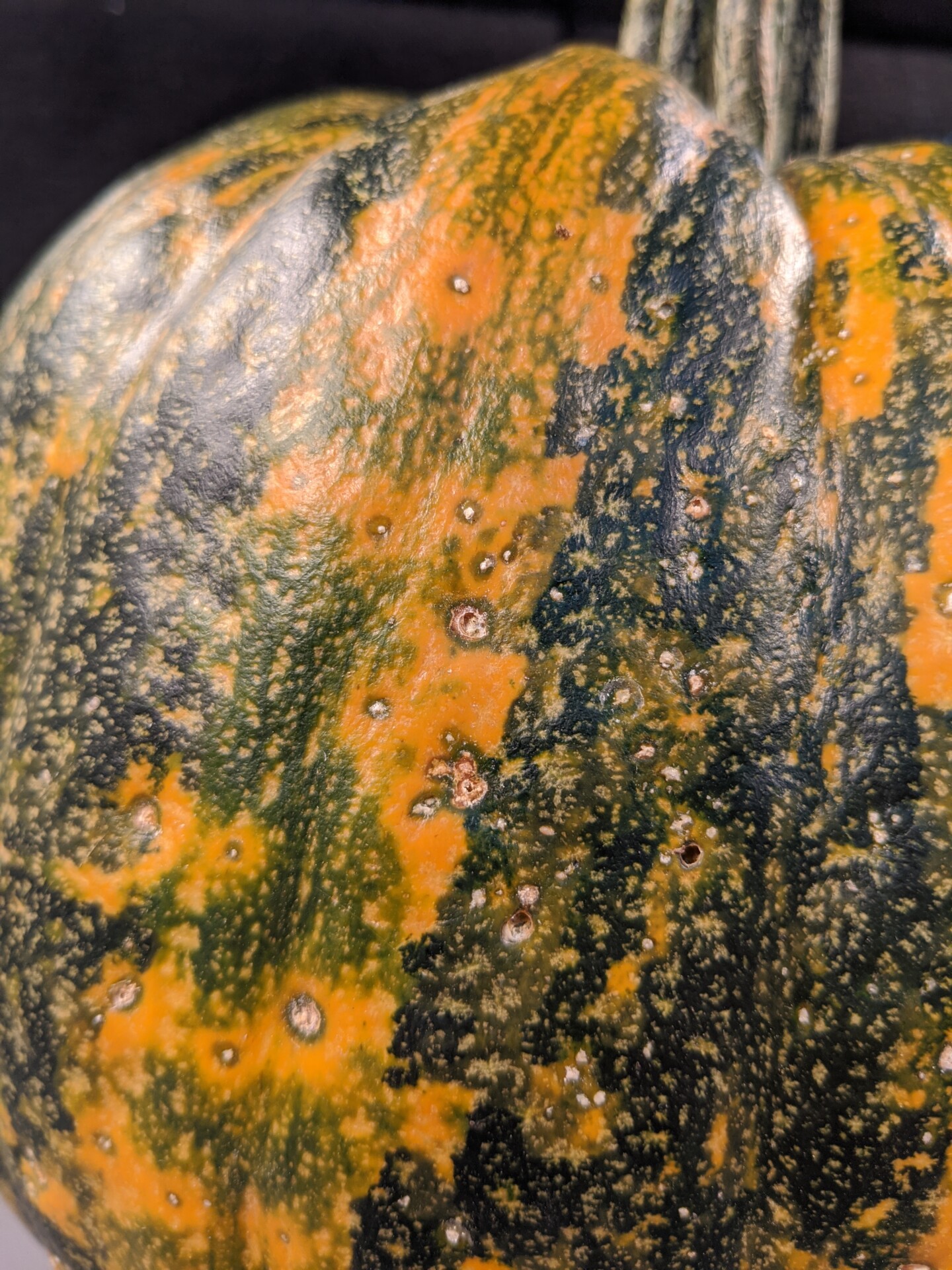  Figure 5. Lesions of bacterial spot on this pumpkin appear necrotic and may have small depressions in the center.
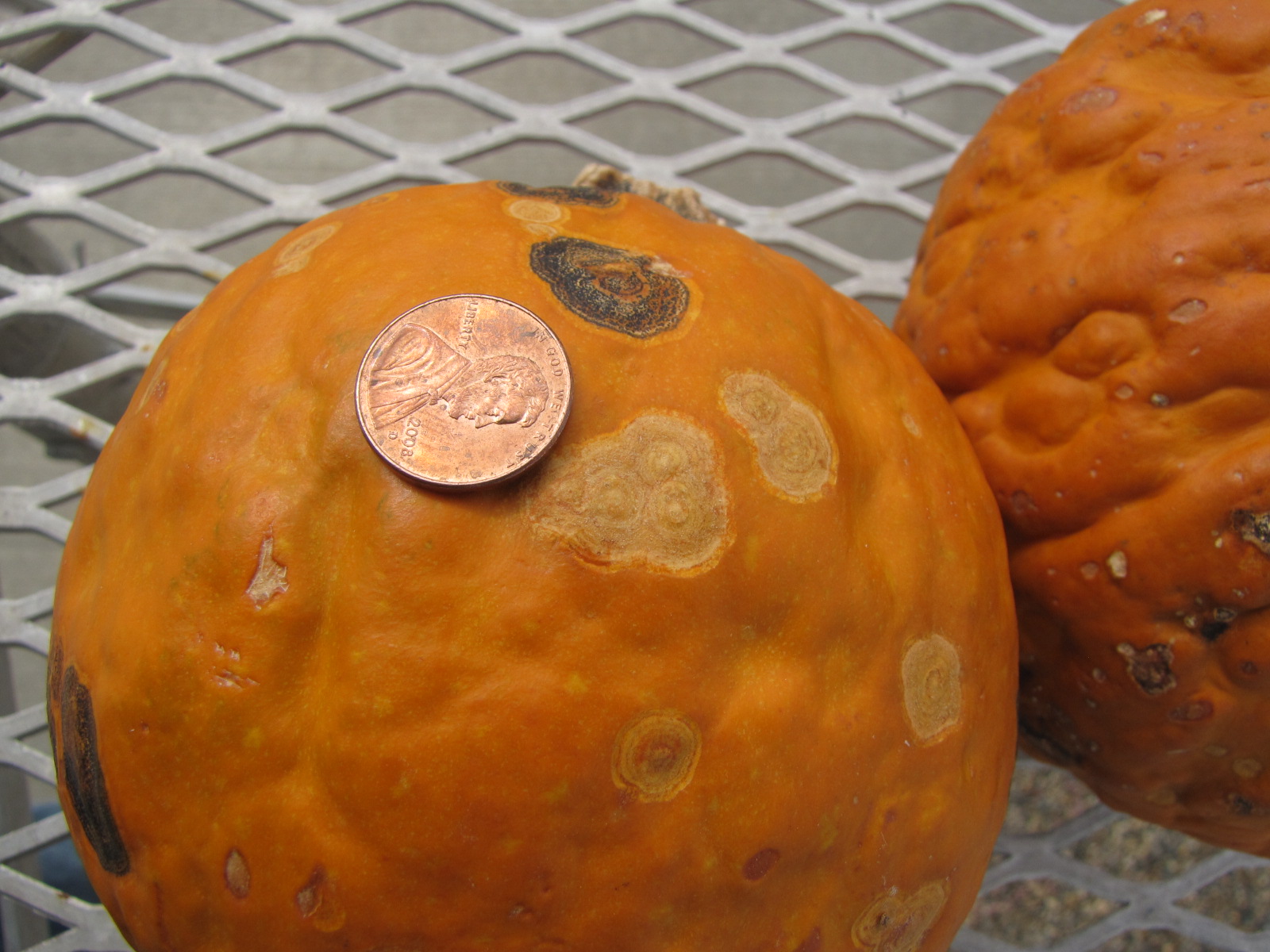
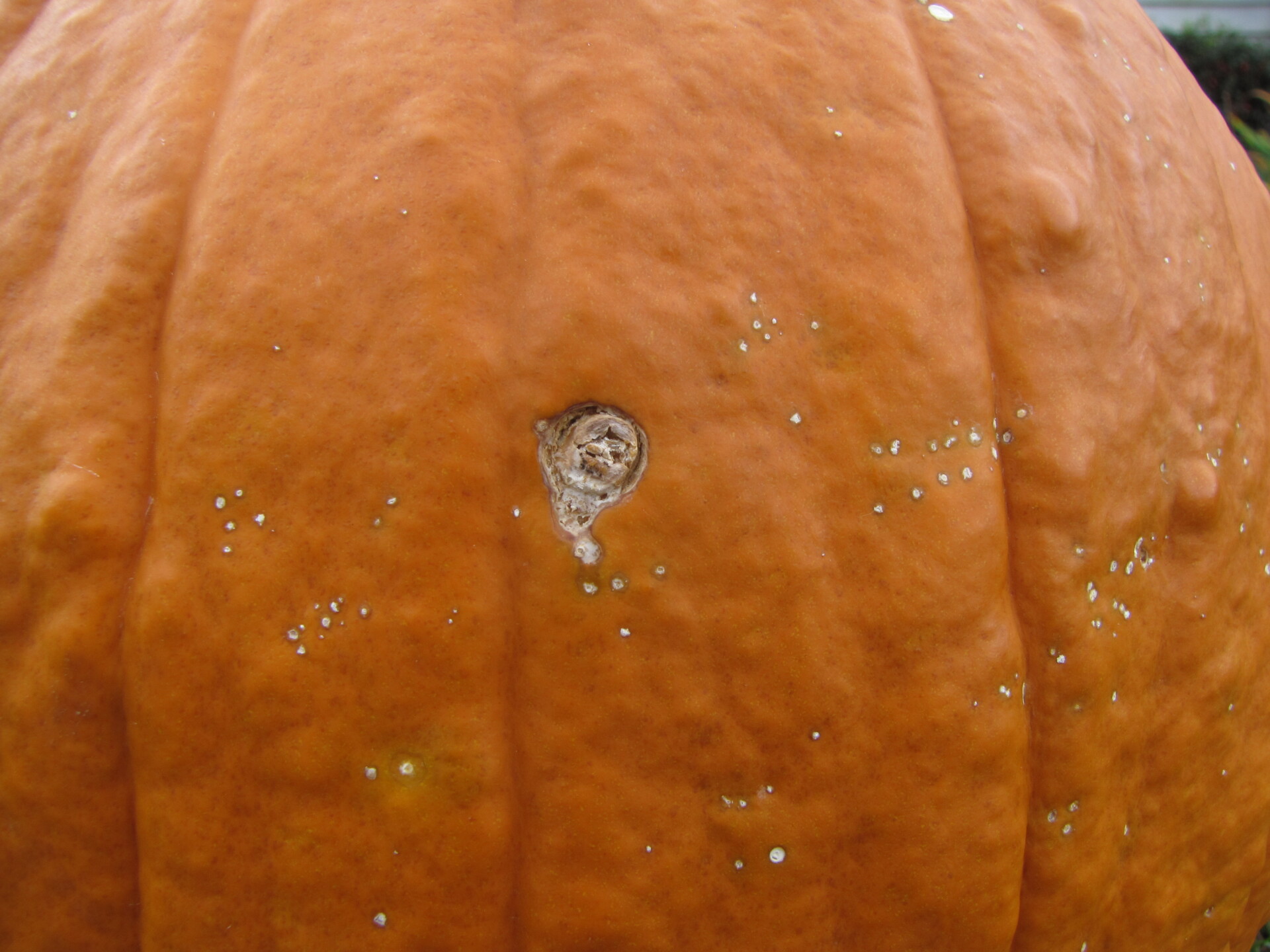
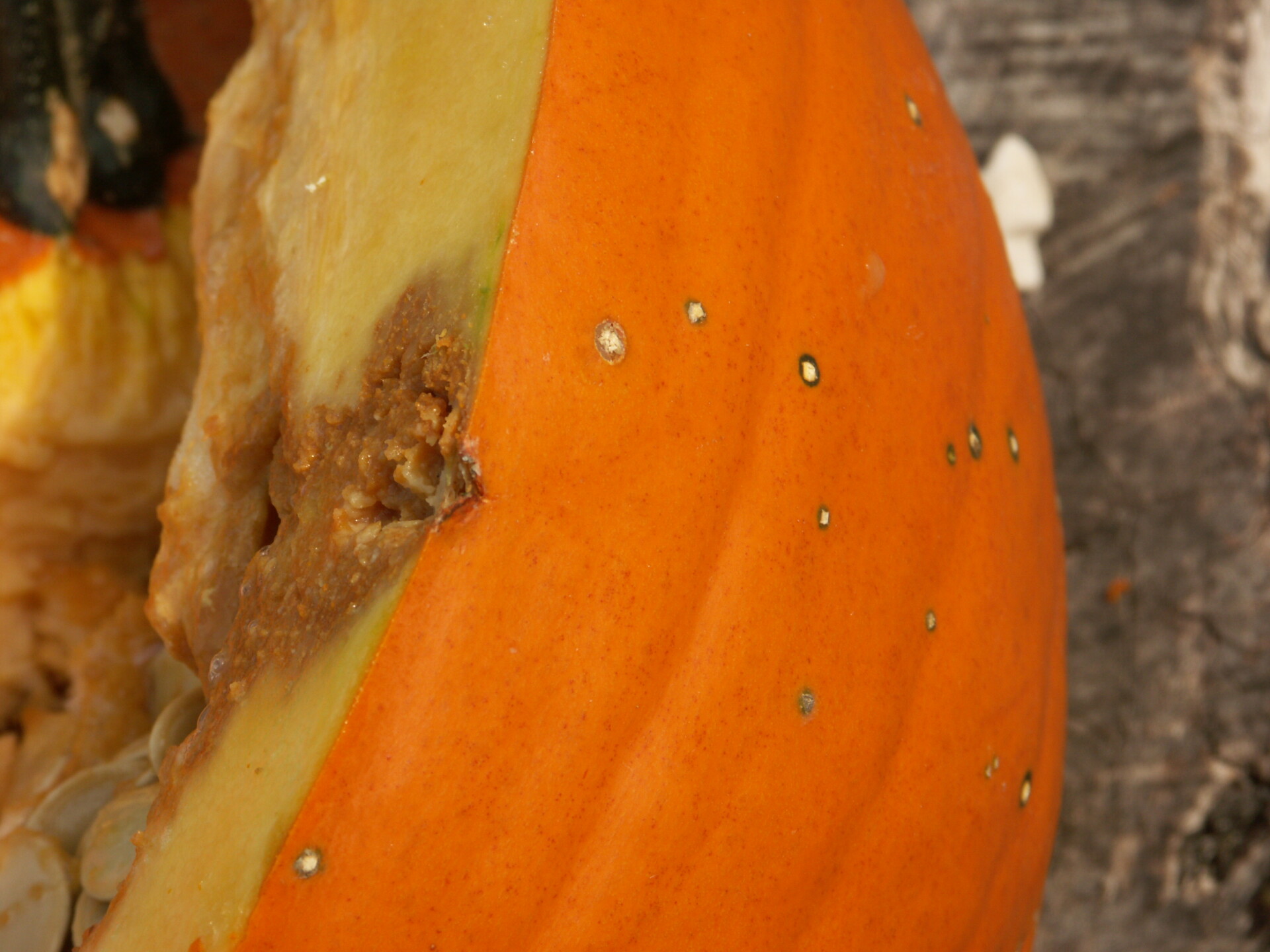
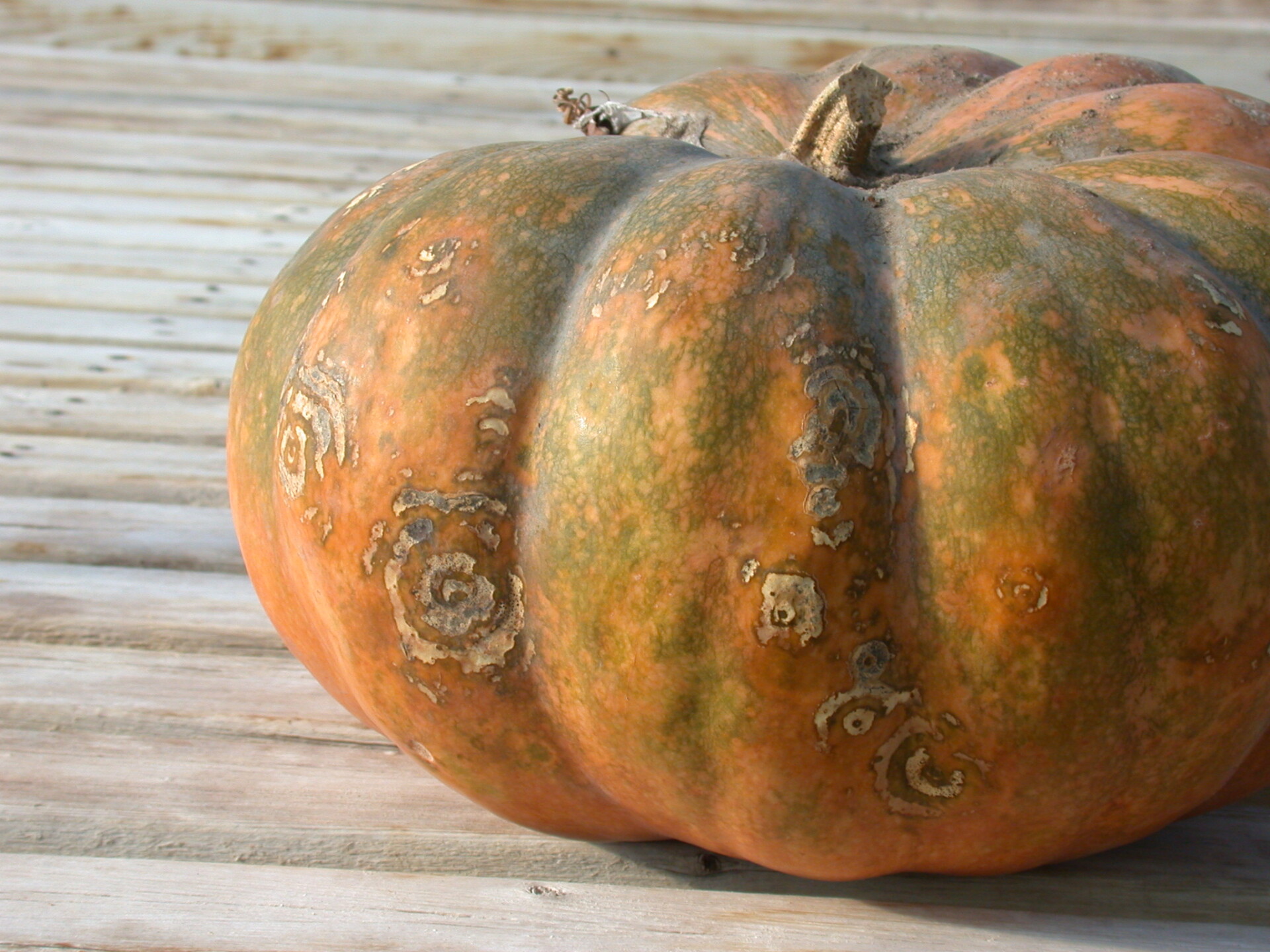
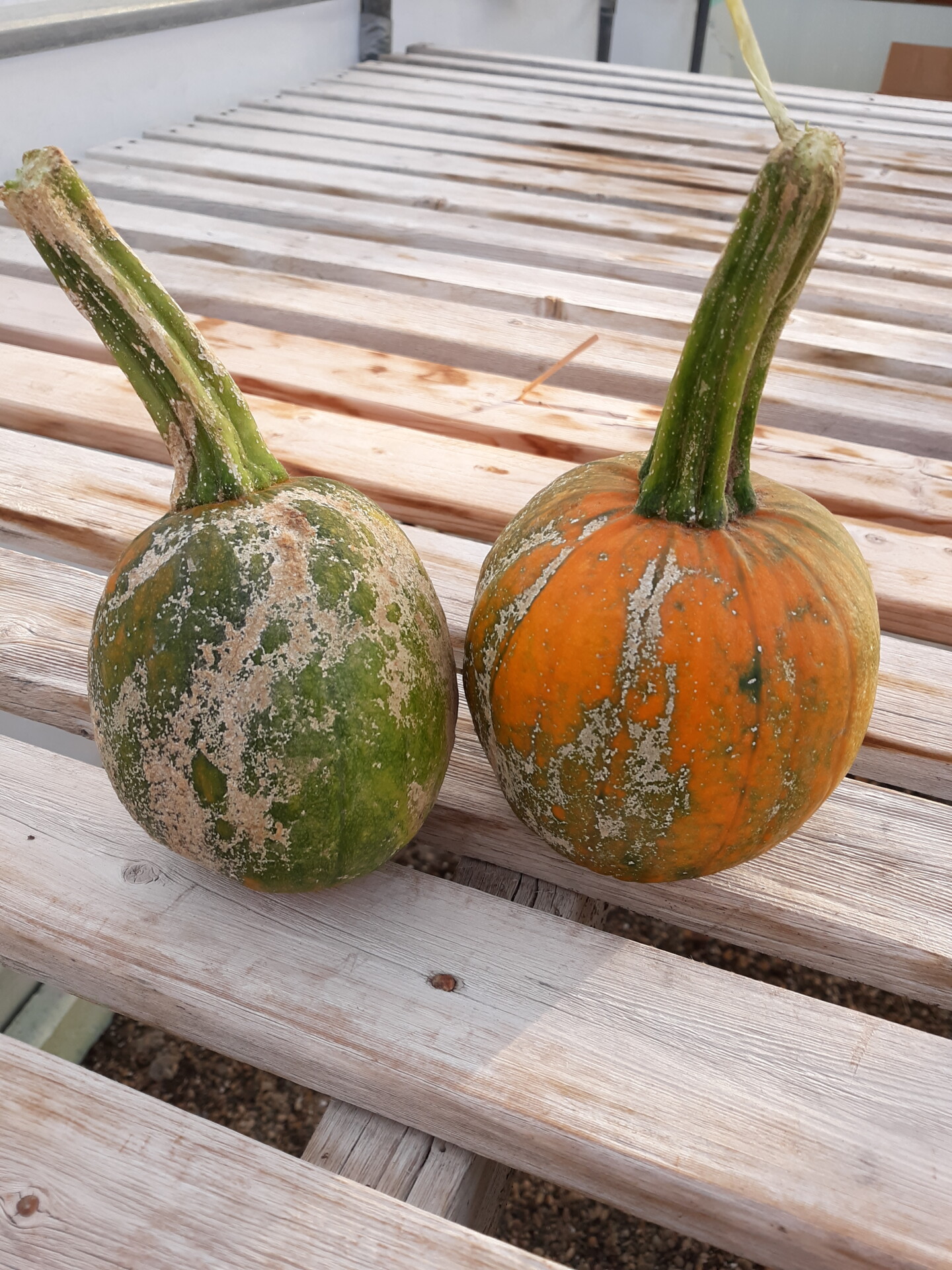
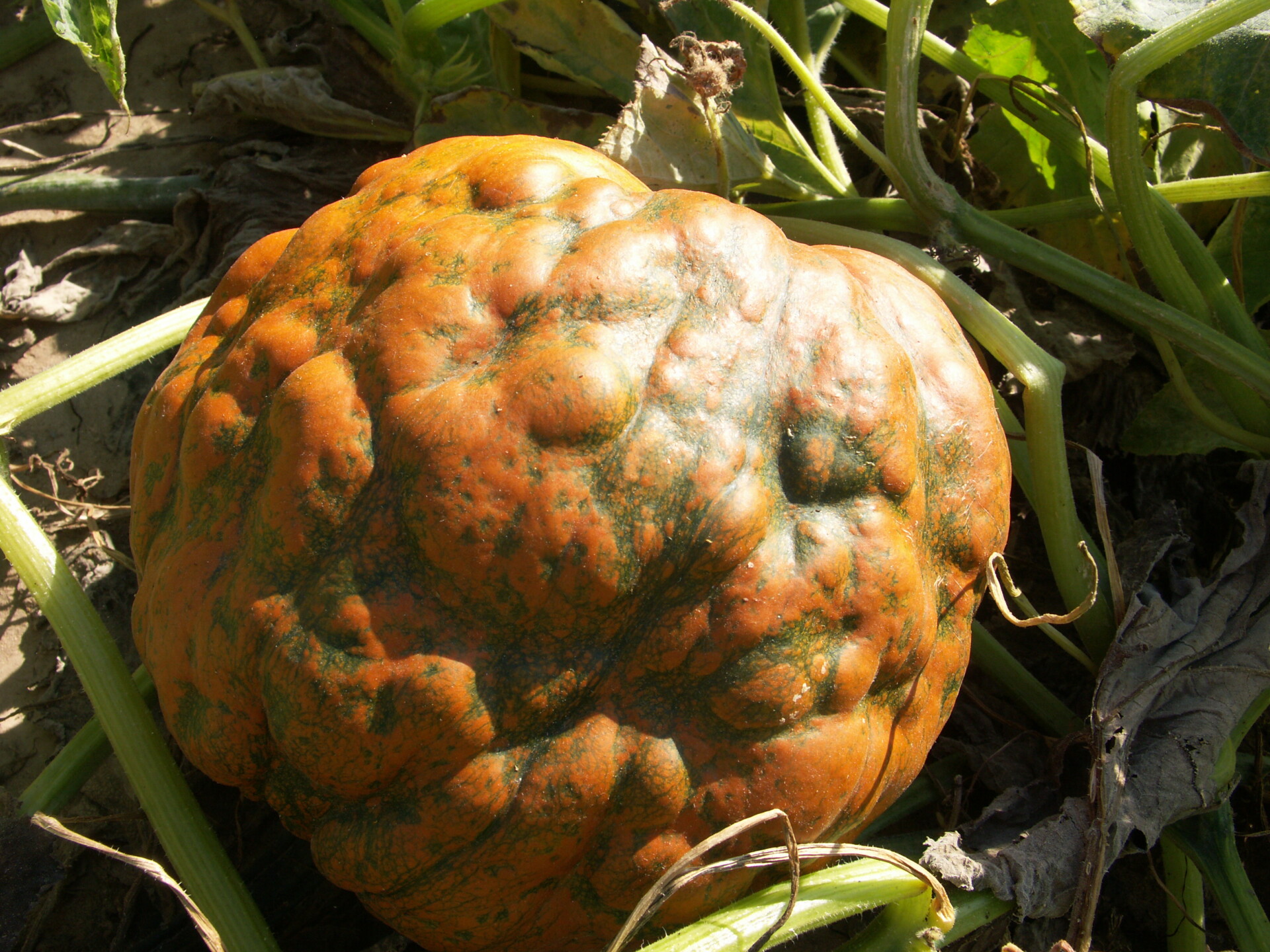
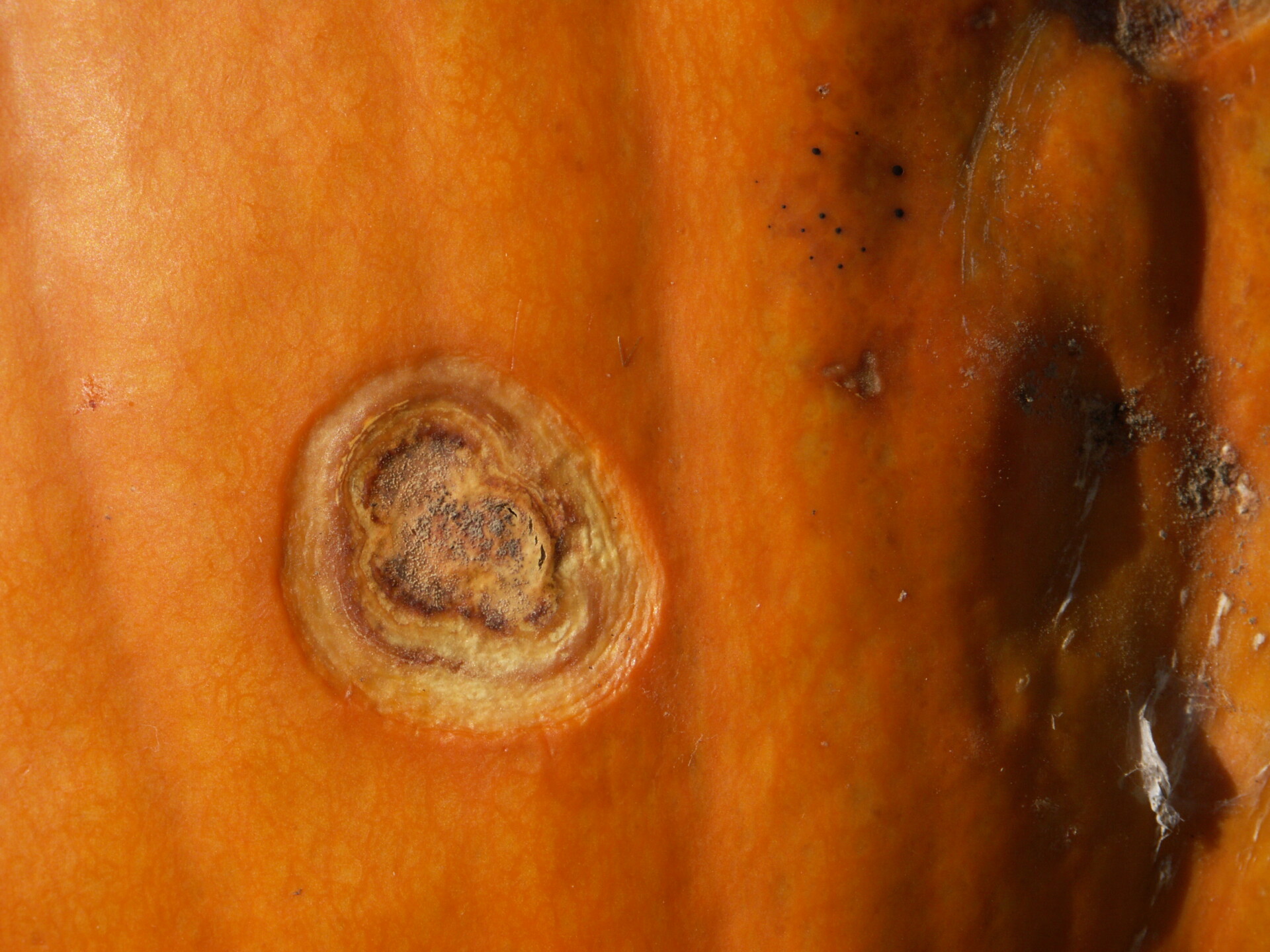
Figure 5. Lesions of bacterial spot on this pumpkin appear necrotic and may have small depressions in the center.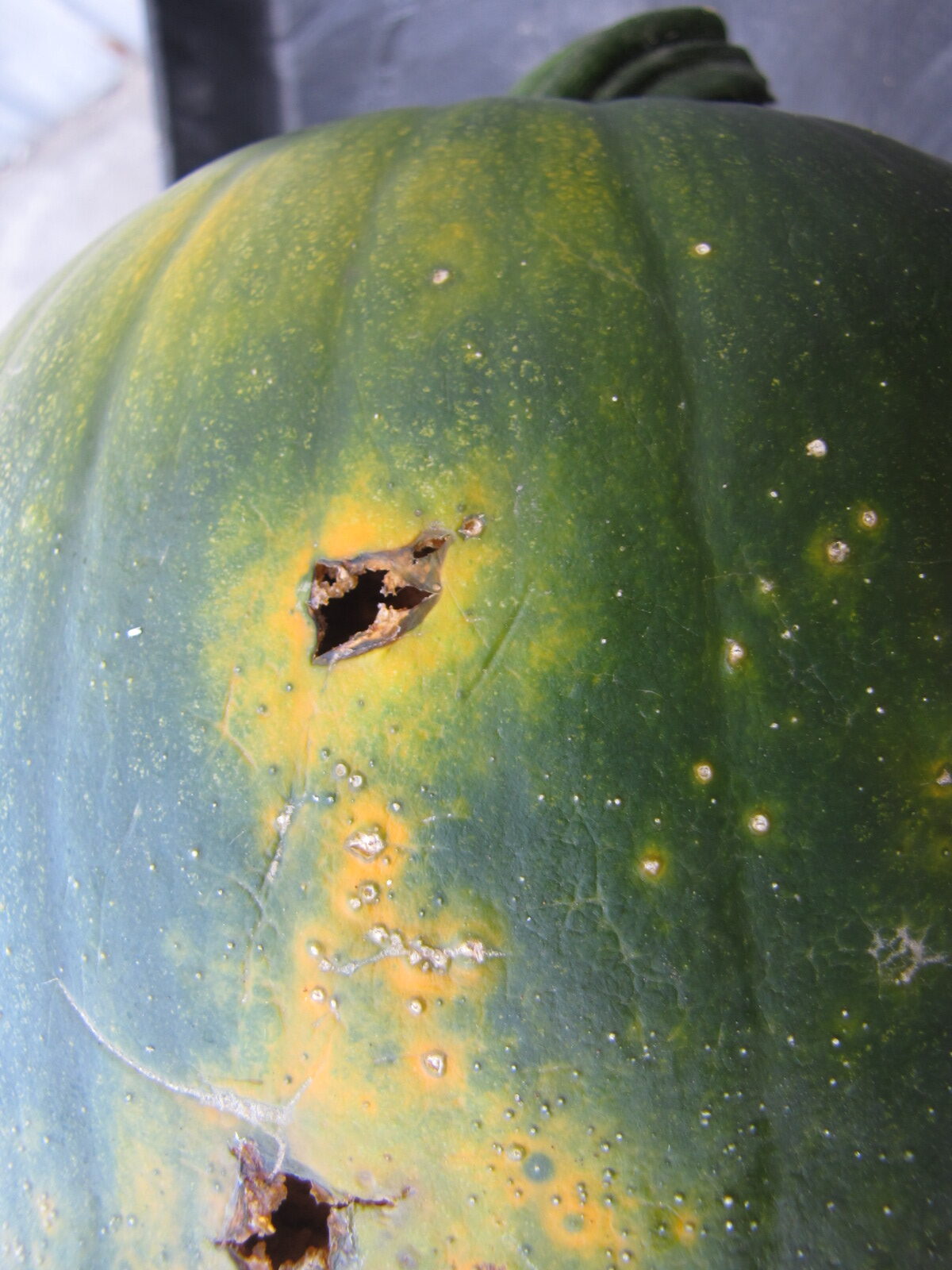  Figure 6. This immature pumpkin has lesions of bacterial spot of pumpkin. The lesions have the appearance of light necrotic scabs. The larger lesions are probably where one of the bacterial spot lesions became infected with a fungus that started in one of the bacterial spot lesions.
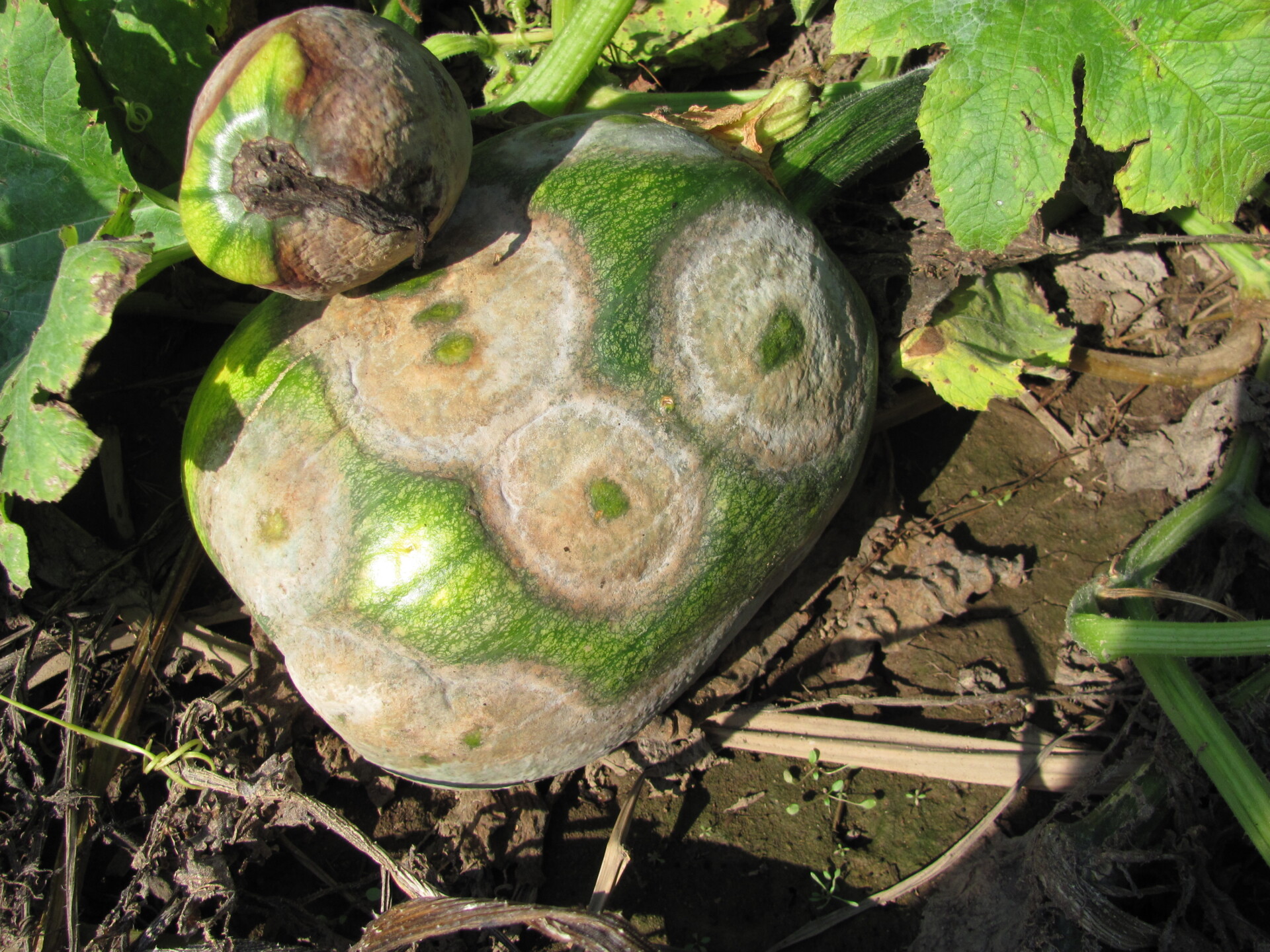
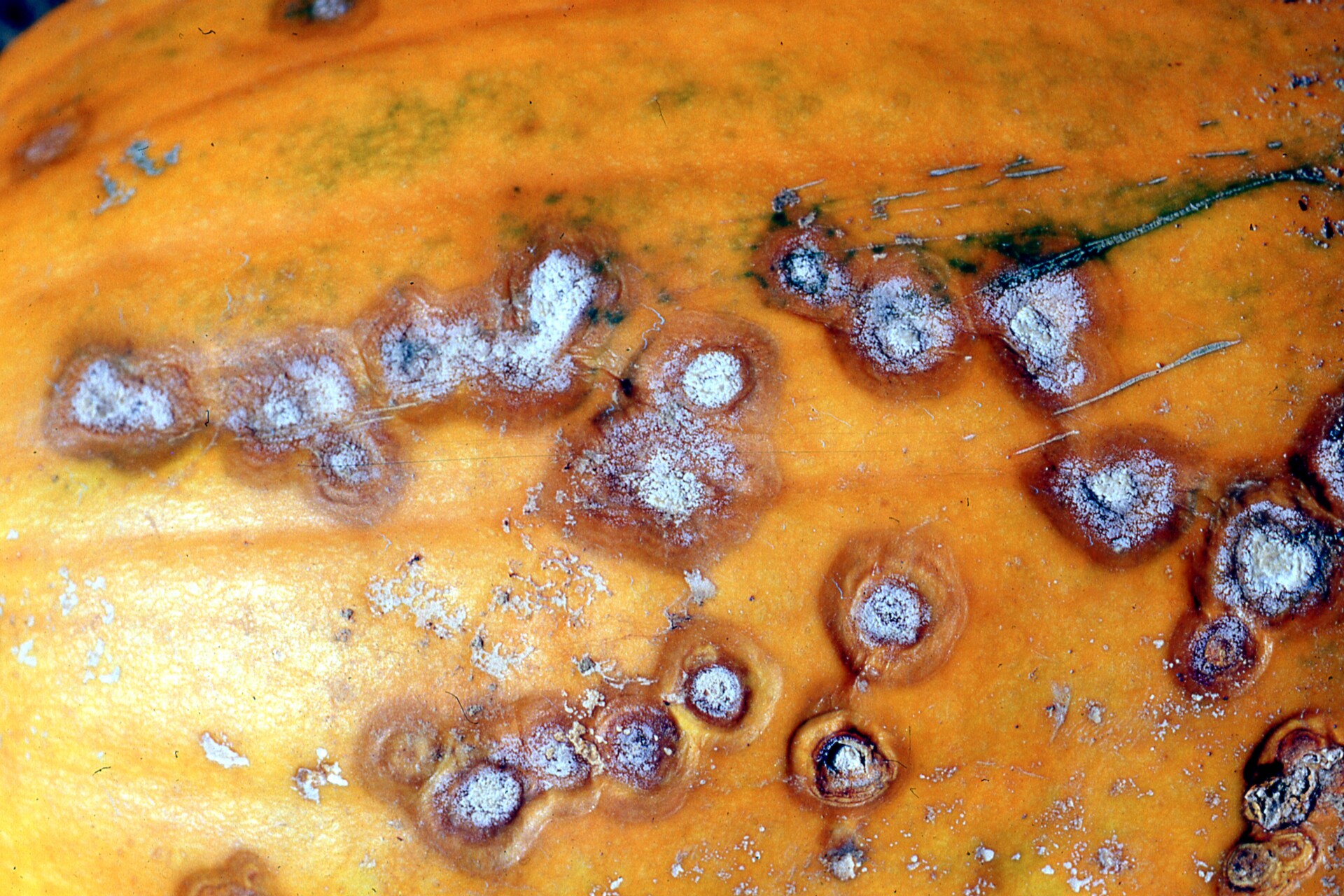
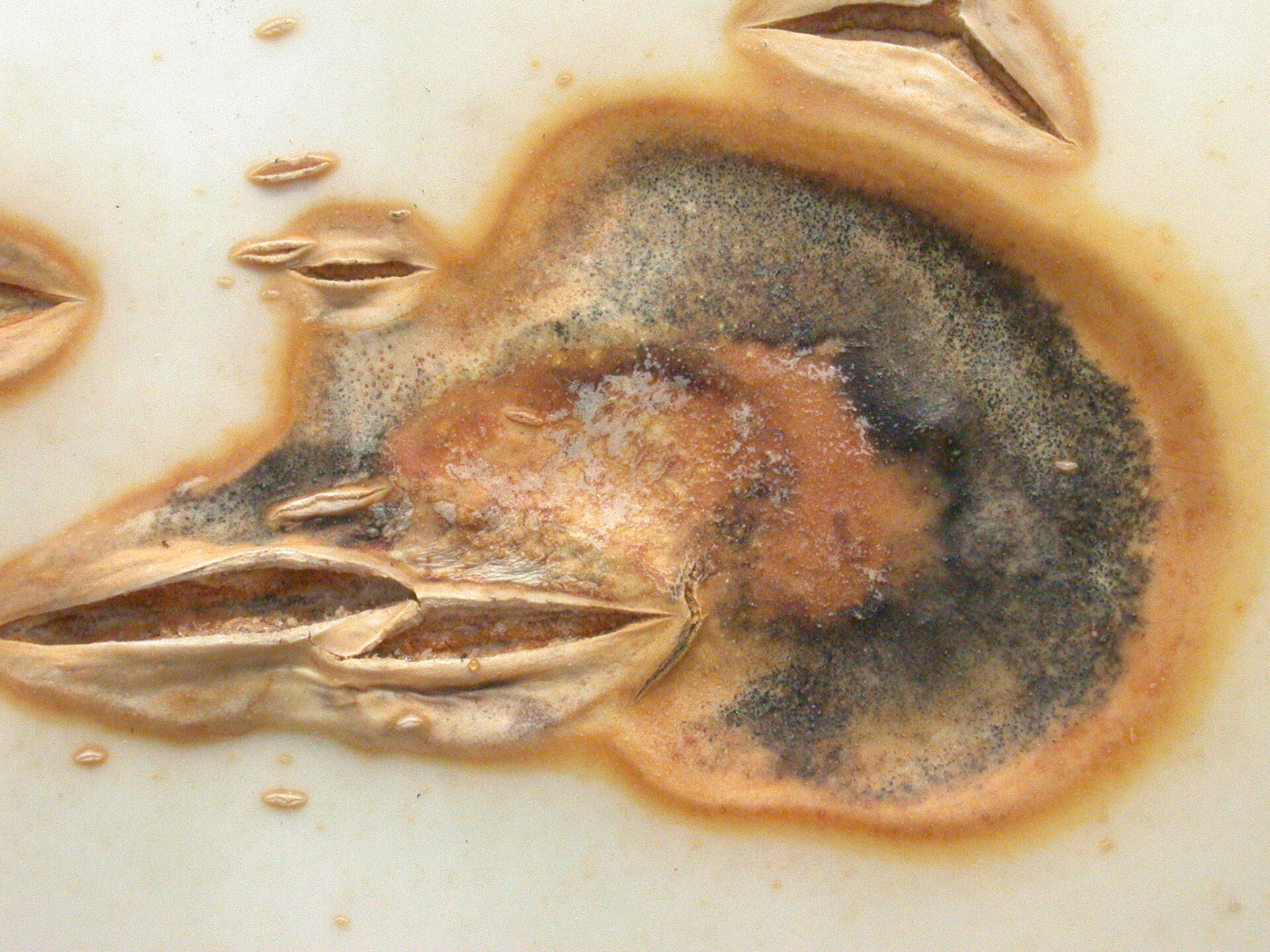
Figure 6. This immature pumpkin has lesions of bacterial spot of pumpkin. The lesions have the appearance of light necrotic scabs. The larger lesions are probably where one of the bacterial spot lesions became infected with a fungus that started in one of the bacterial spot lesions. Phytophthora fruit rot
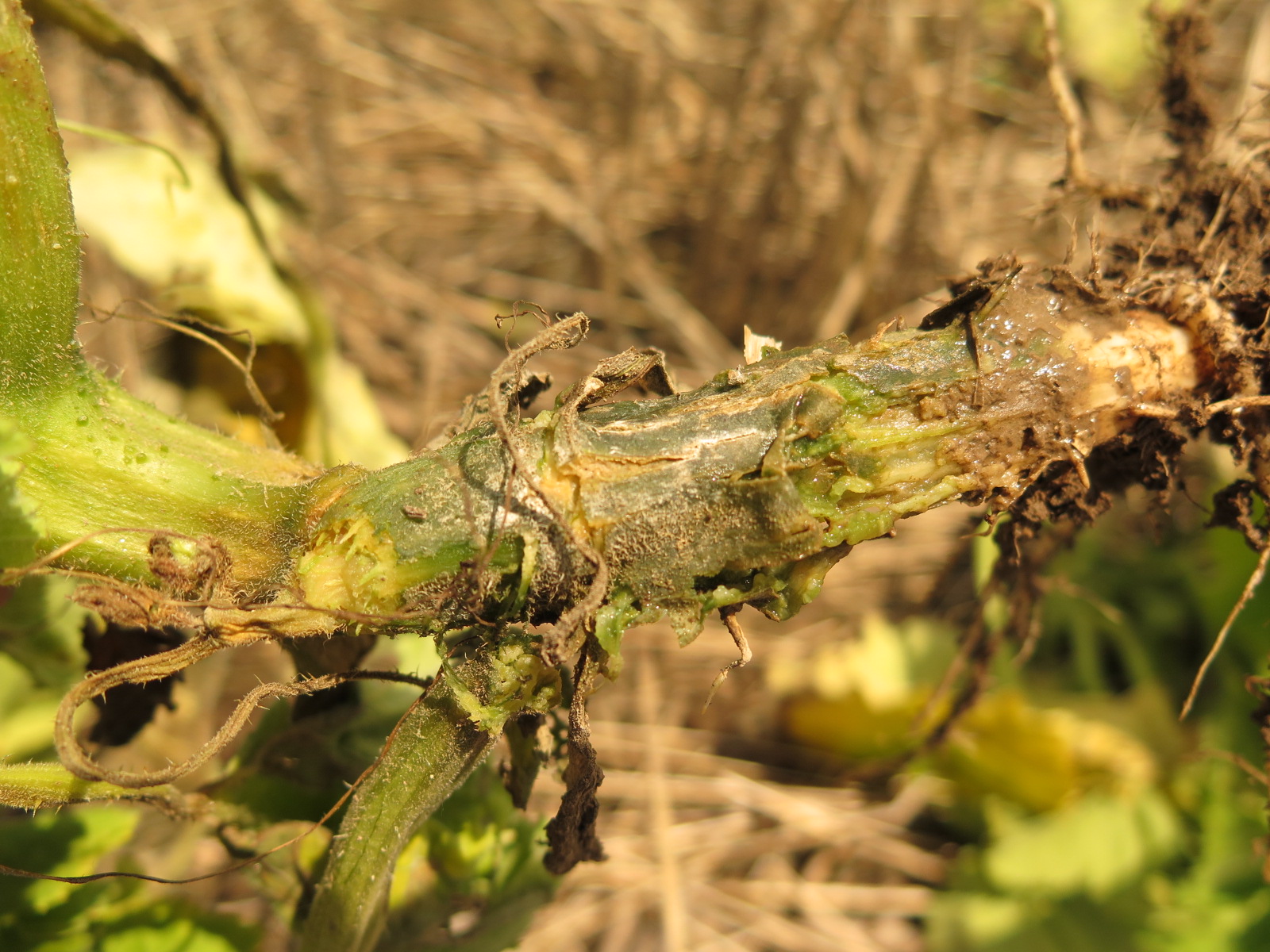
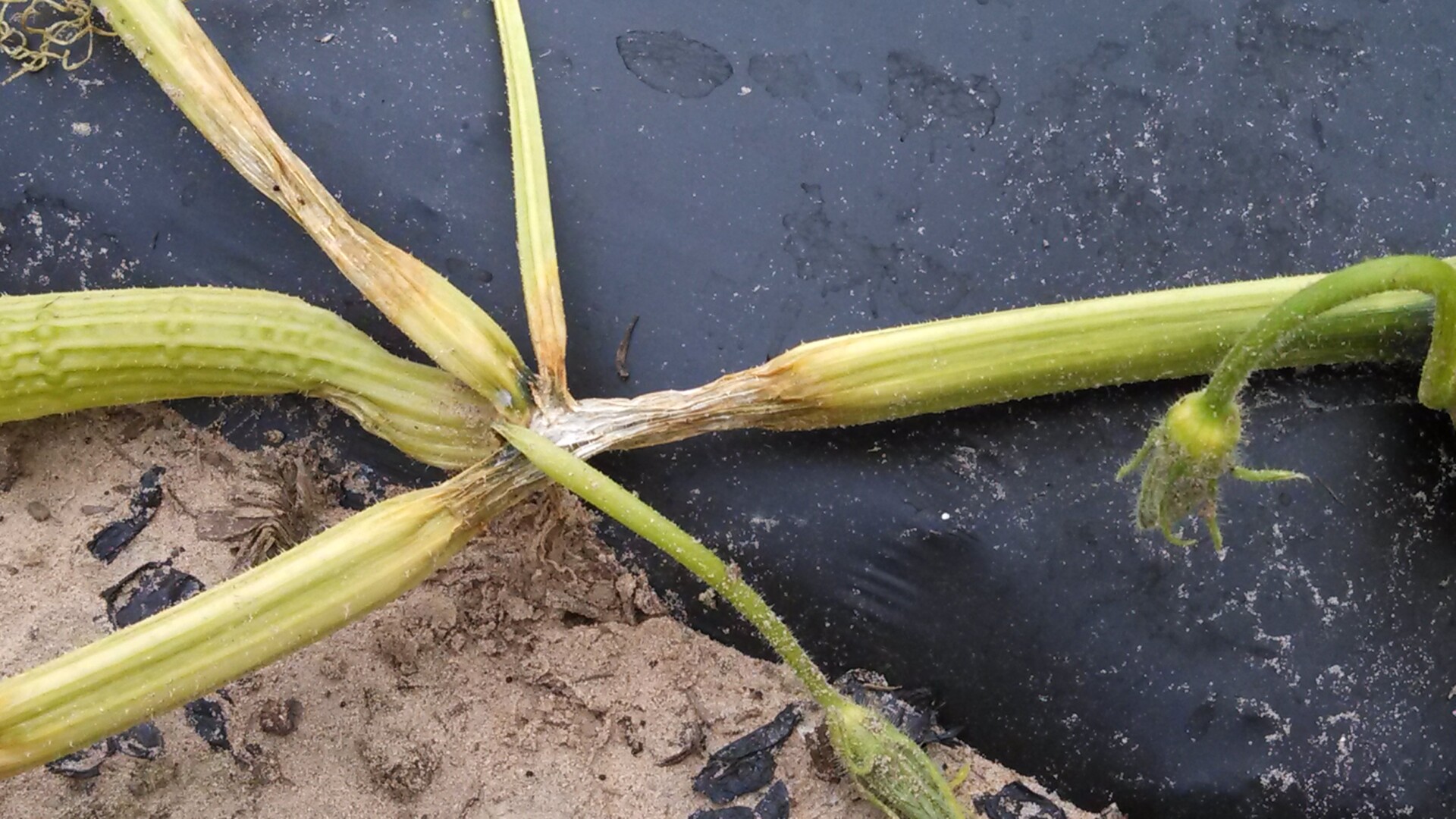
Plectosporium blight
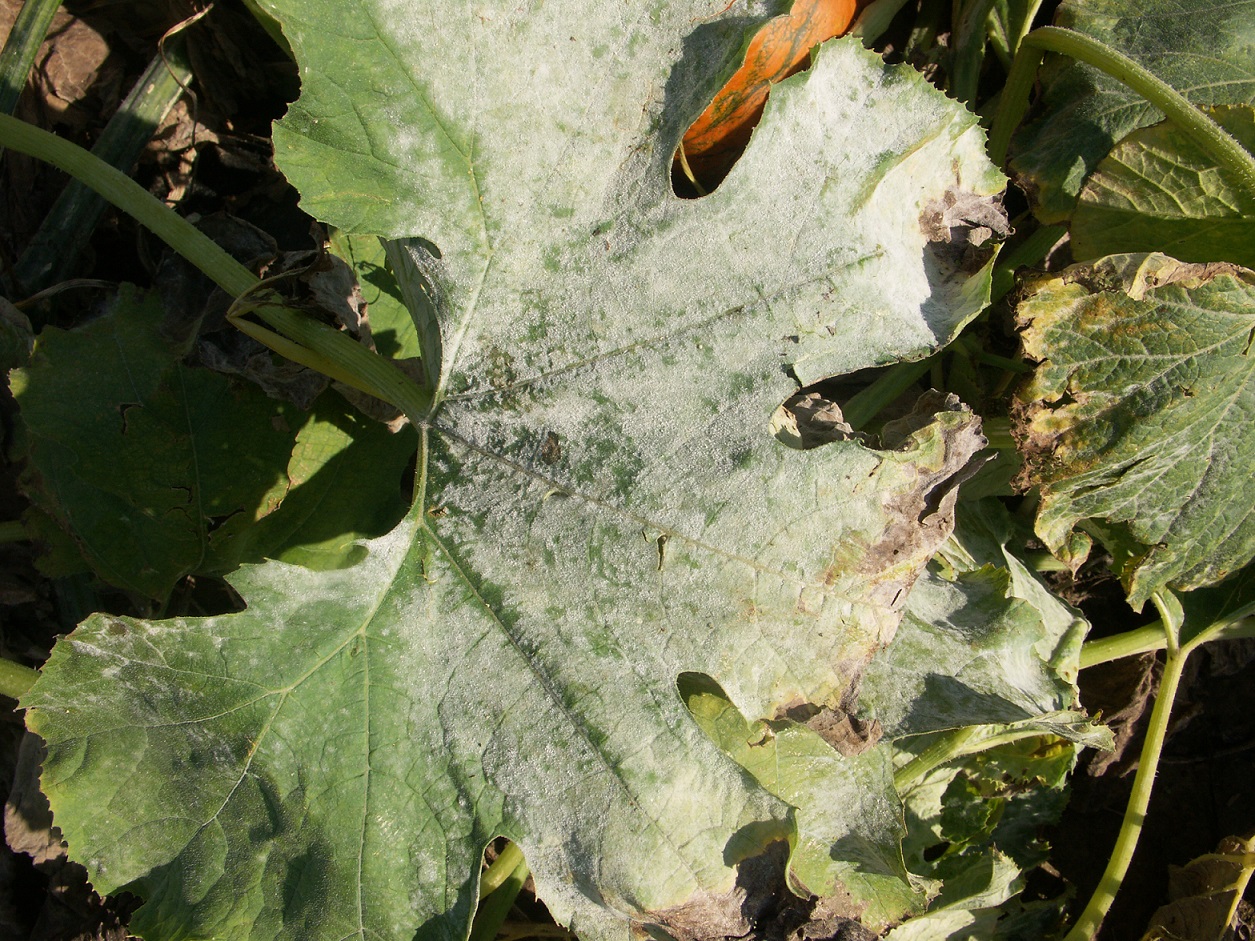
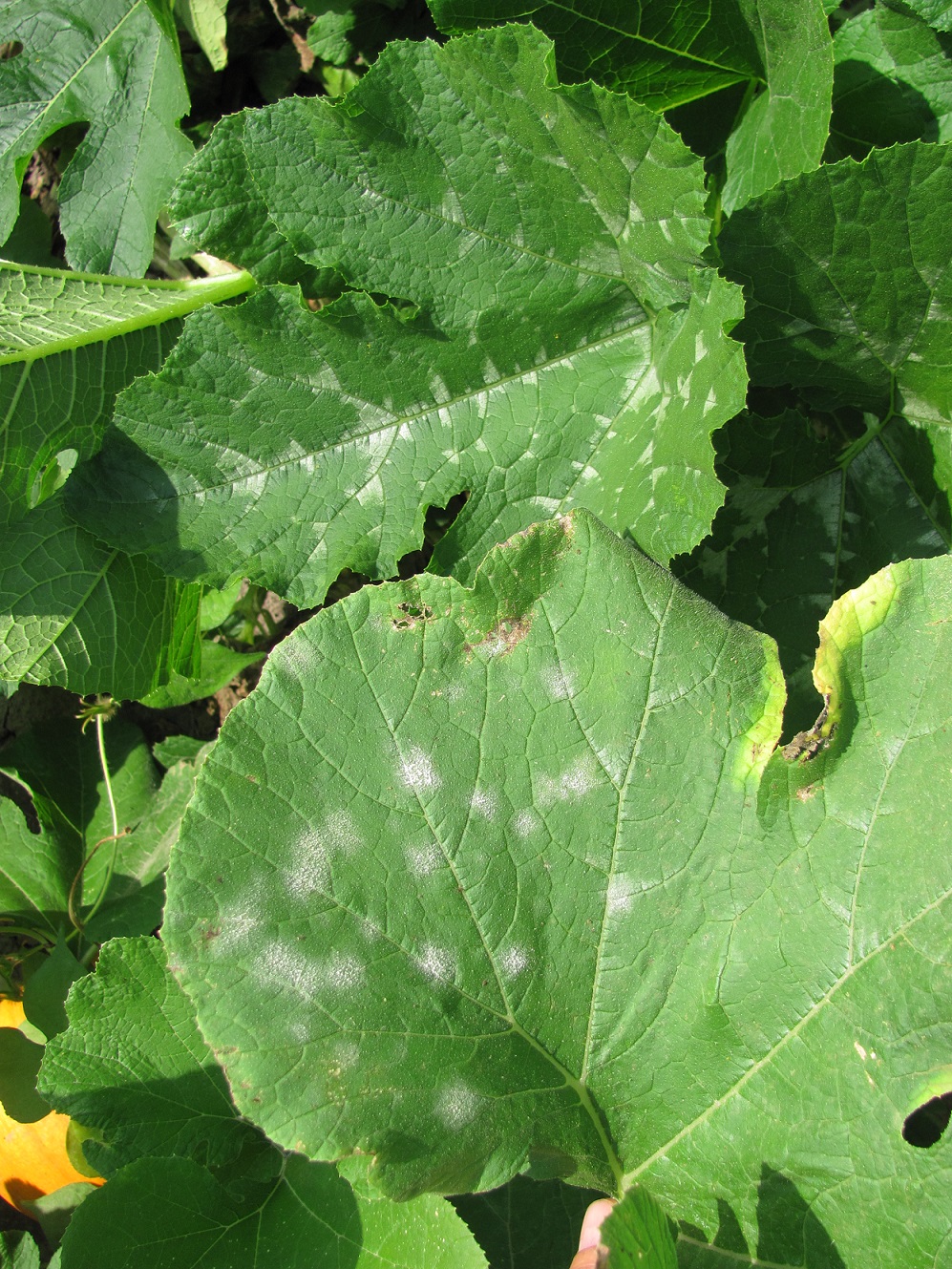
Powdery mildew
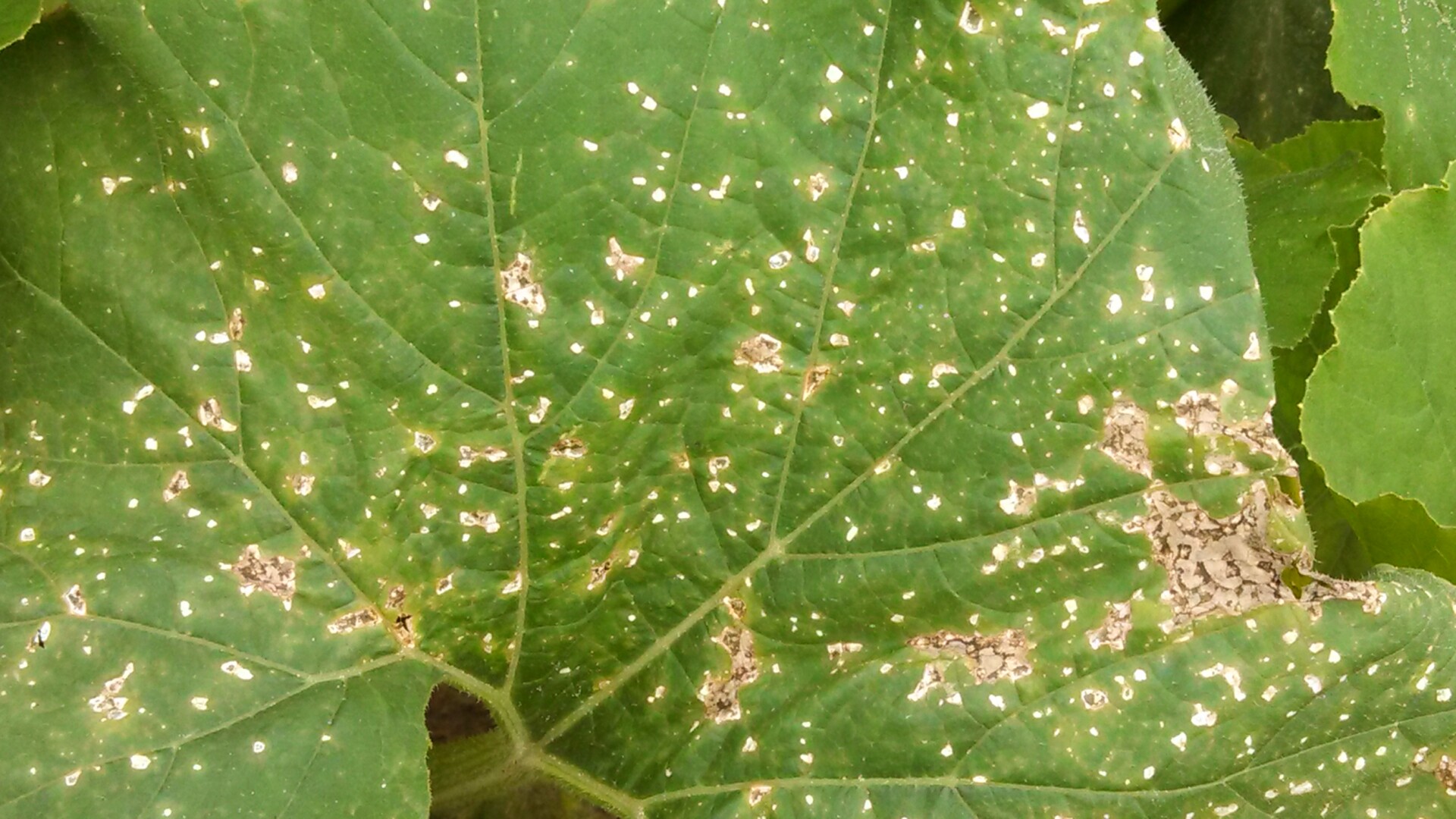
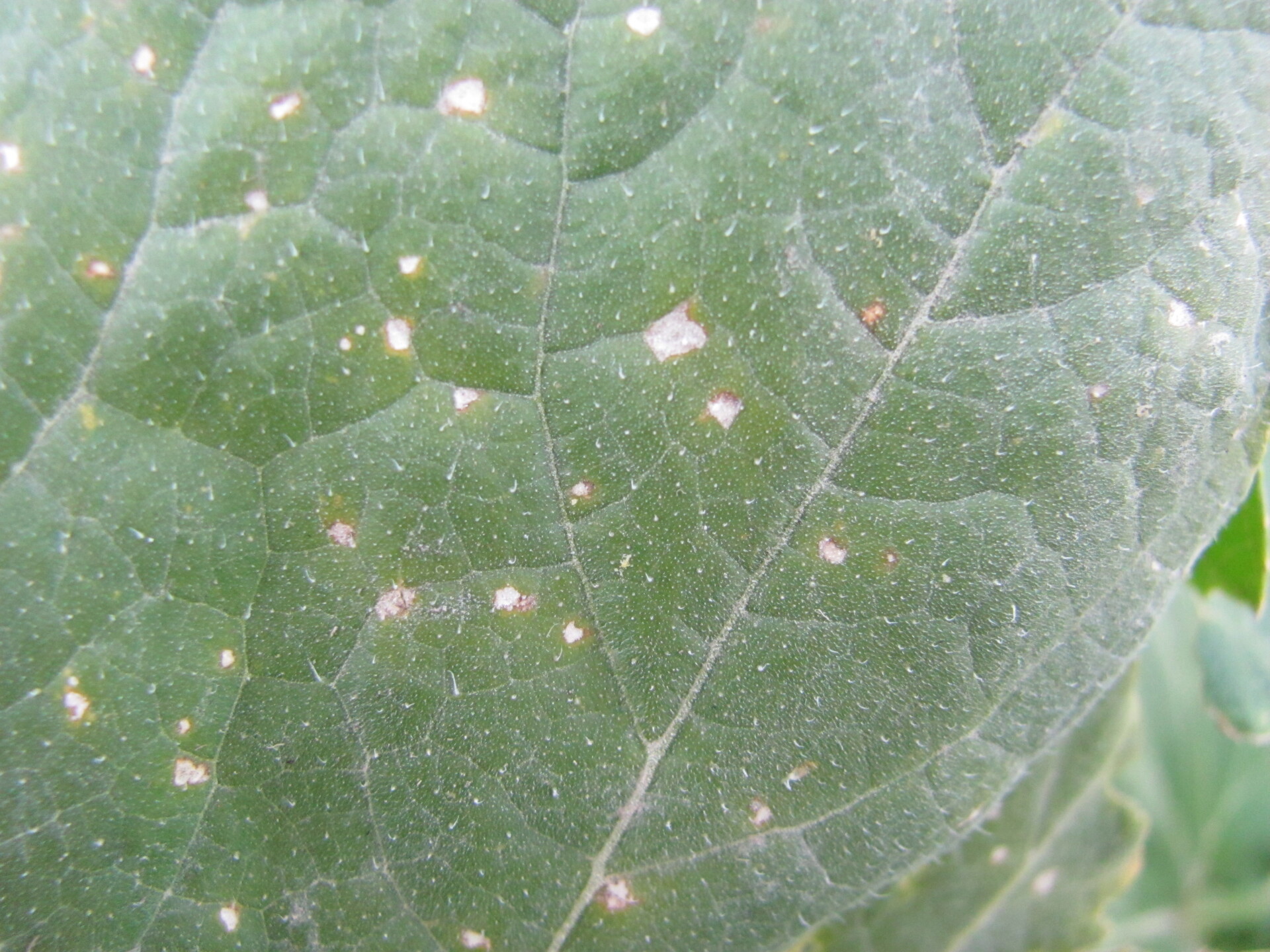
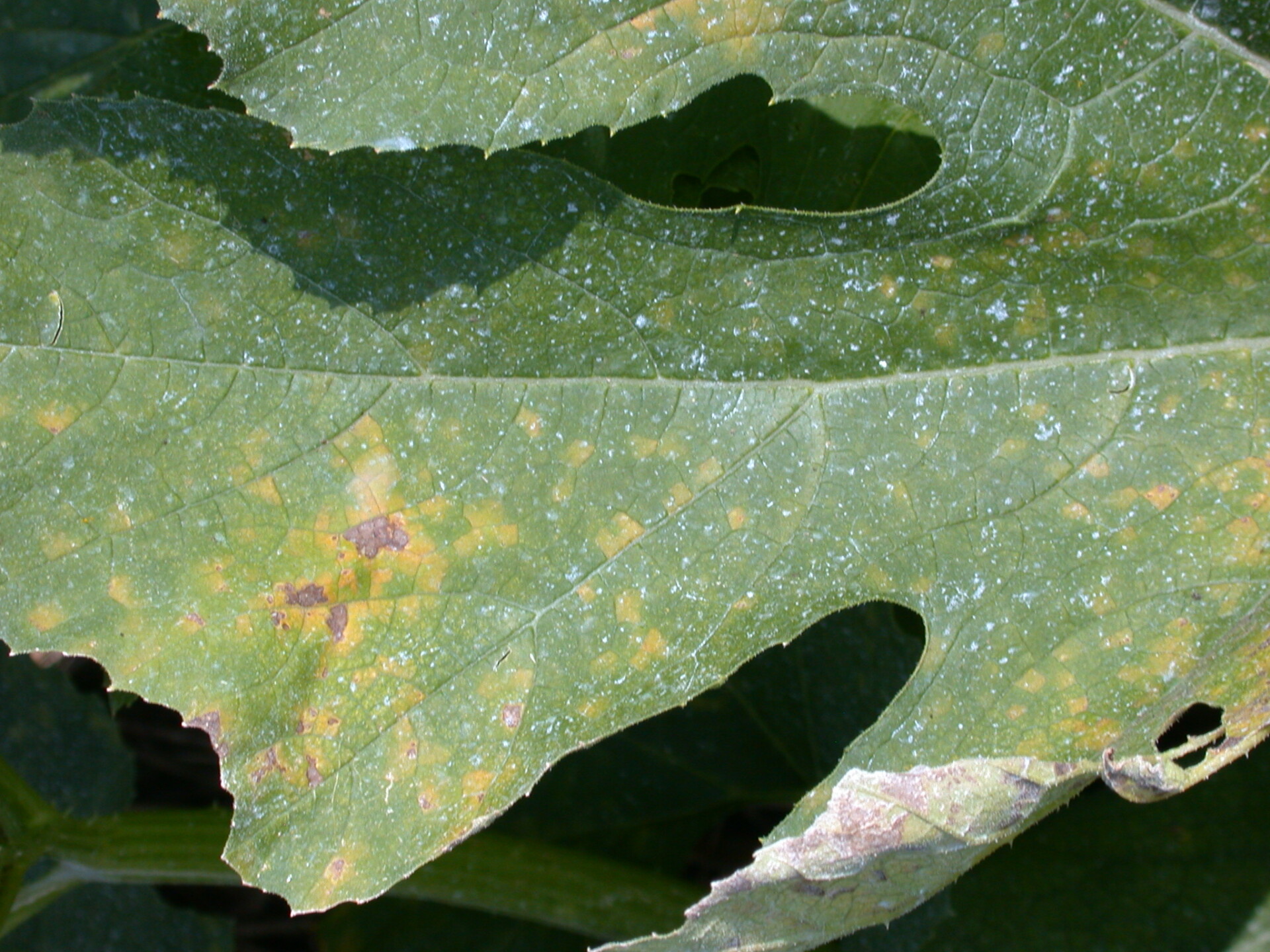
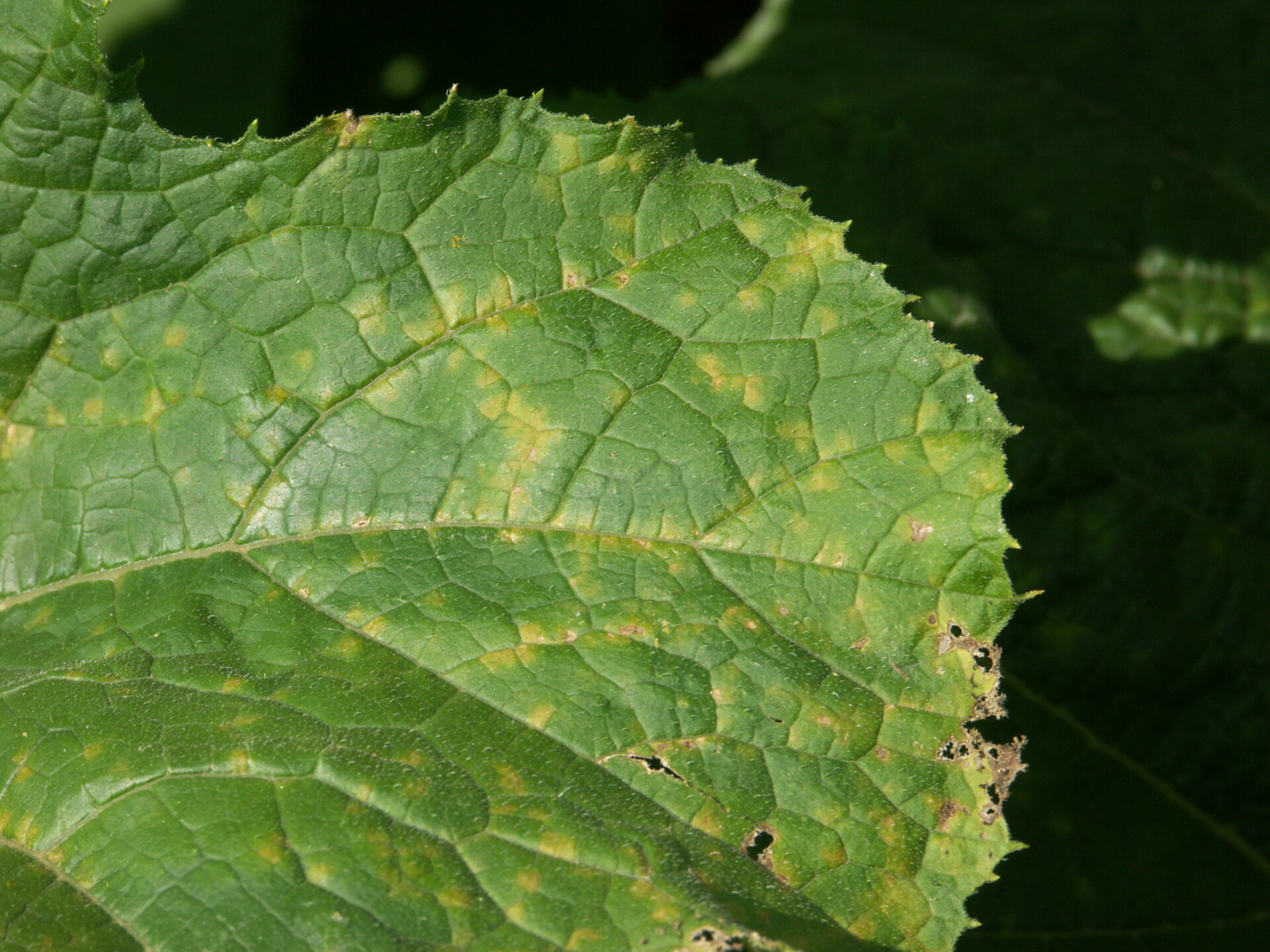
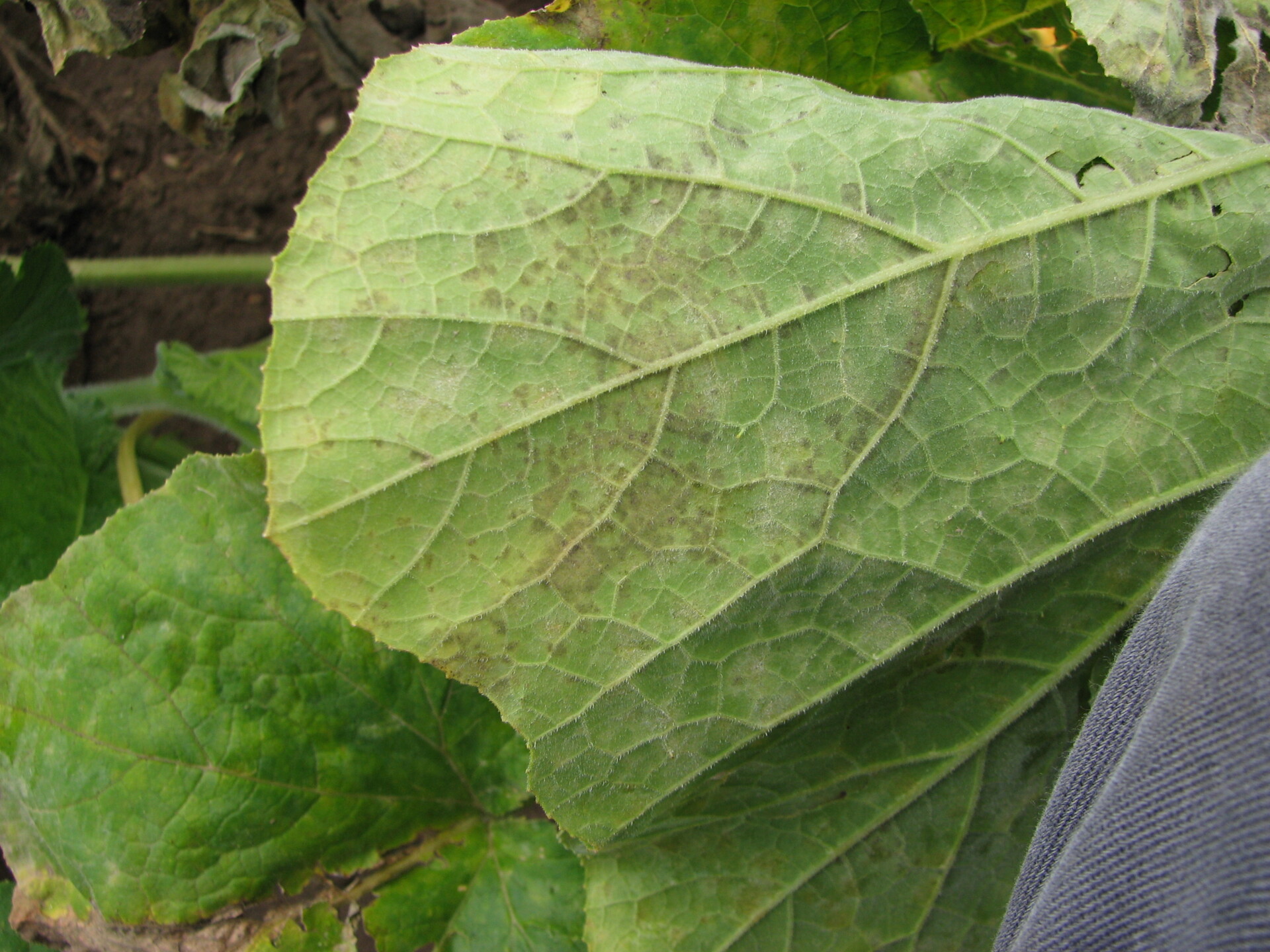
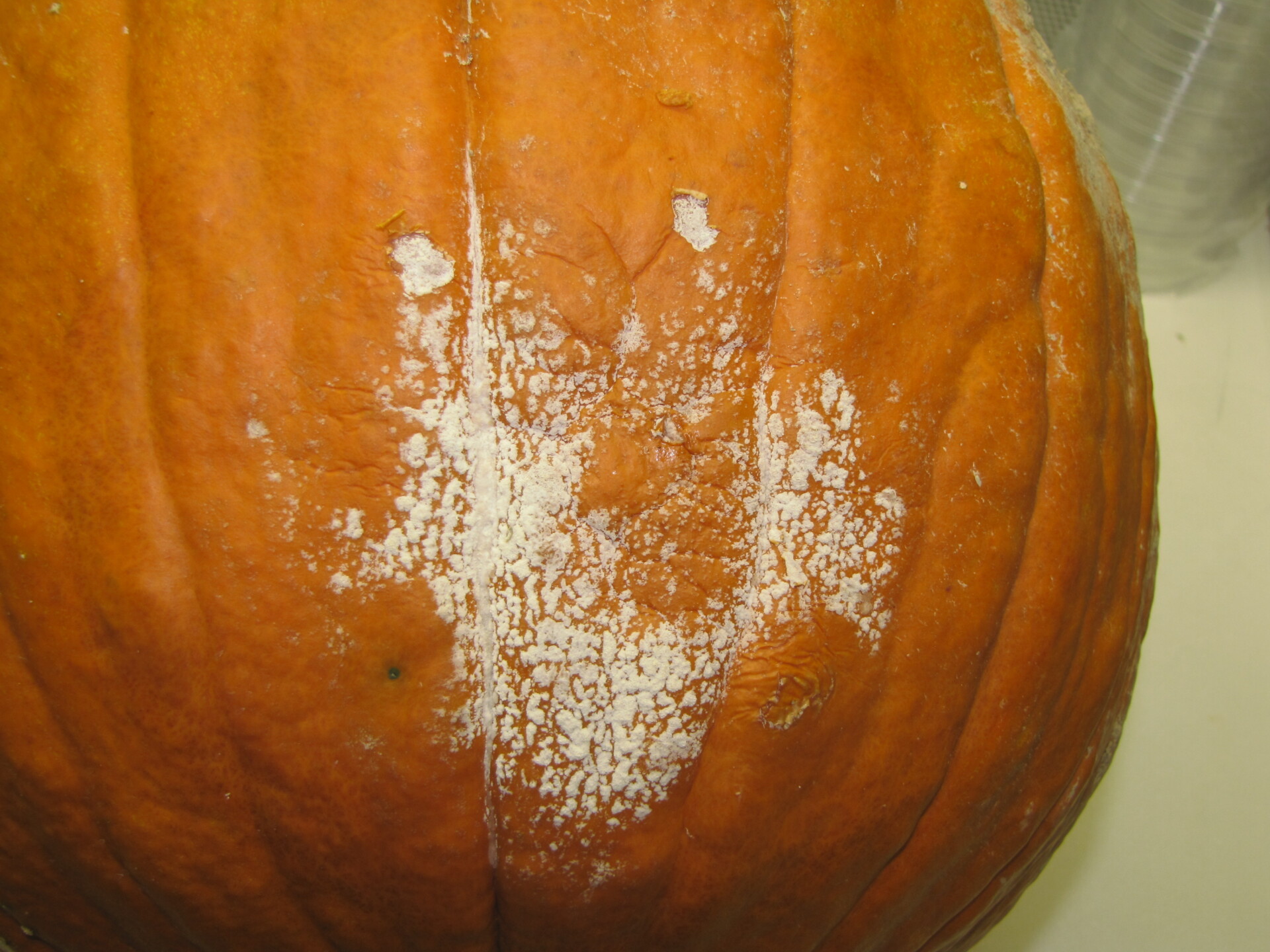
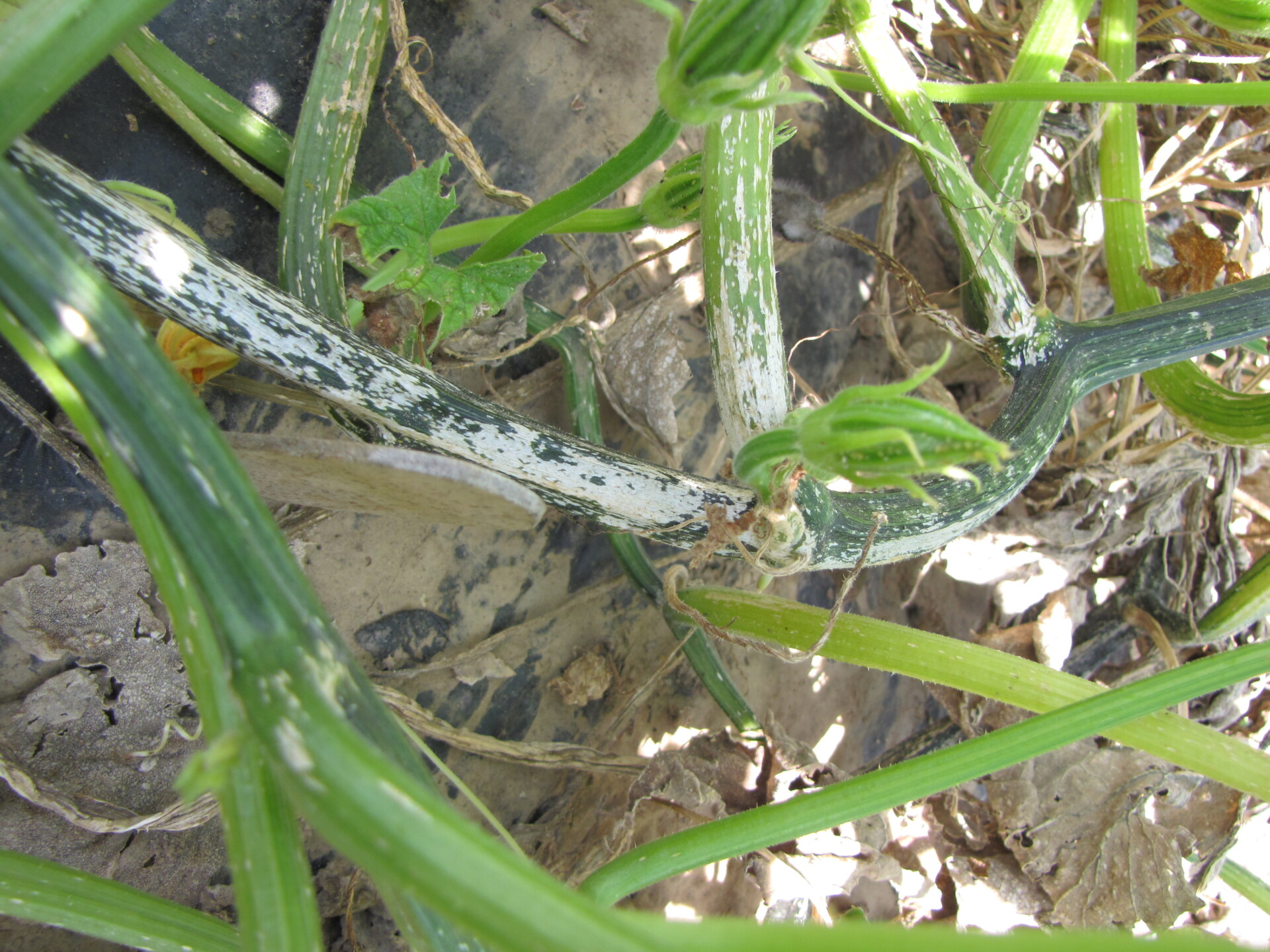
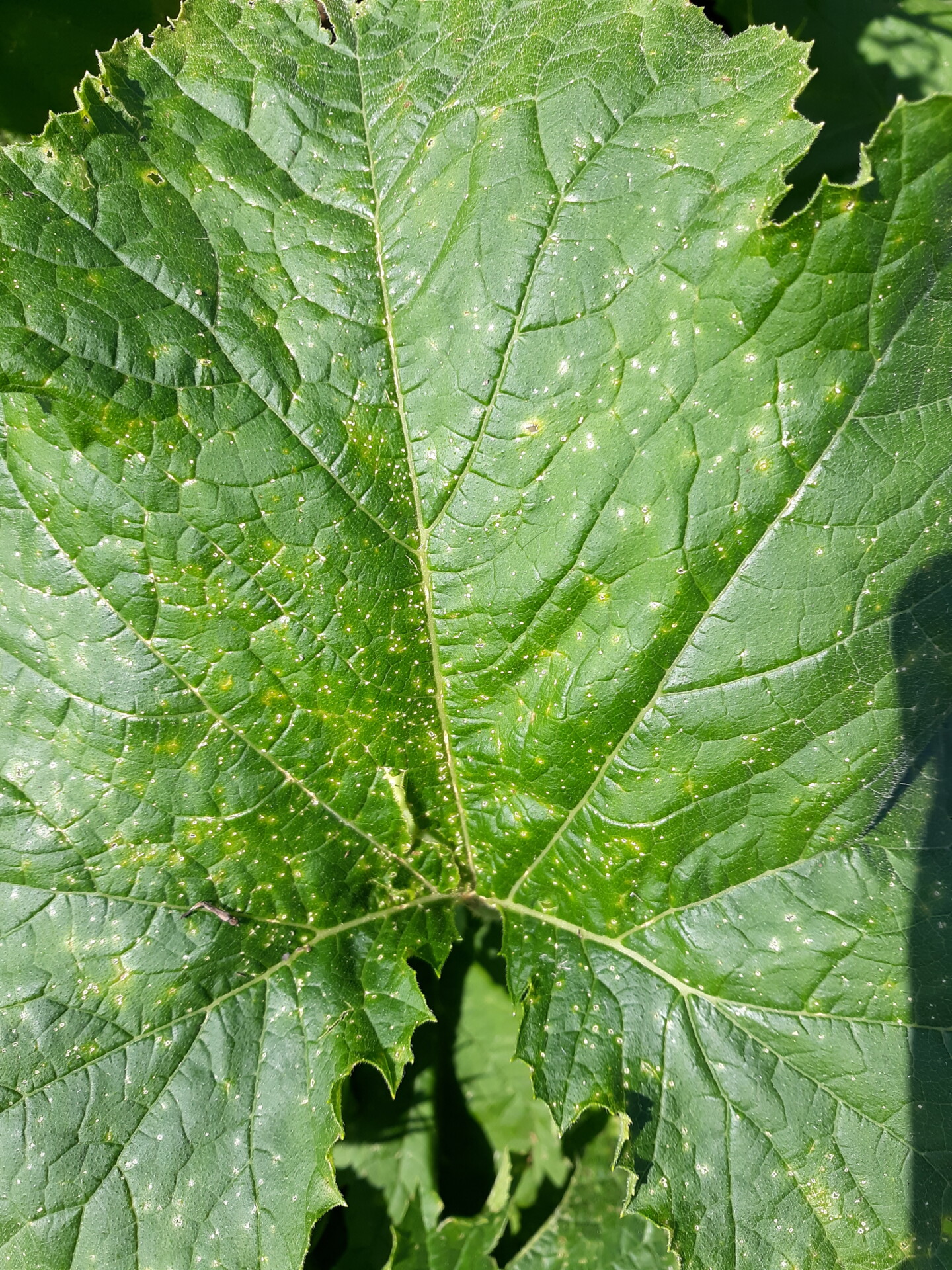
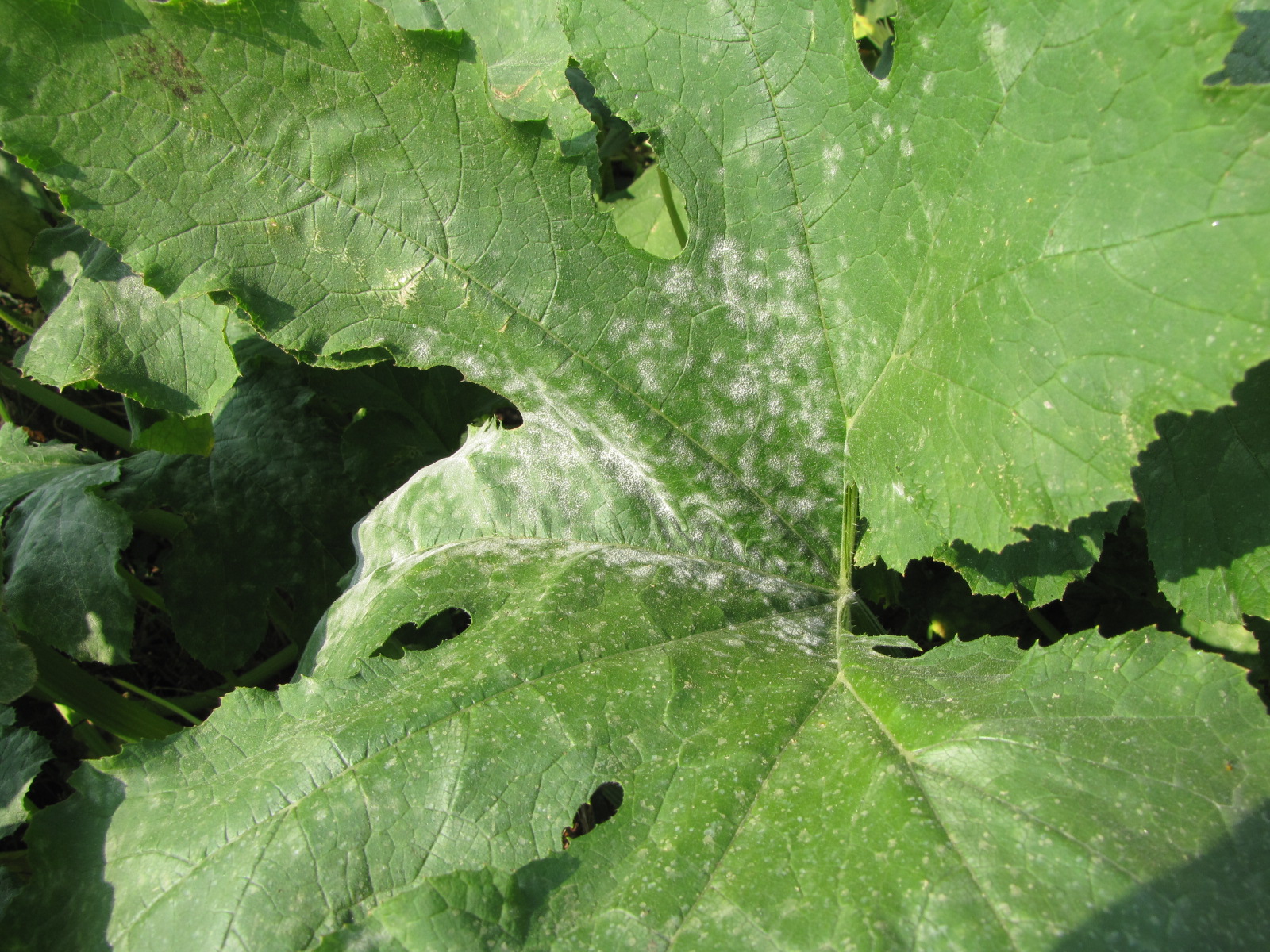 Figure 1. Powdery mildew of pumpkins can be easily recognized by the talc-like lesion on the upper and lower surface of leaves.
Figure 1. Powdery mildew of pumpkins can be easily recognized by the talc-like lesion on the upper and lower surface of leaves.