Study suggests new targets for improving soybean oil content
Scientists working to increase soybean oil content tend to focus their efforts on genes known to impact the plant’s seeds, but a Purdue University study shows that genes affecting other plant parts deserve more attention.
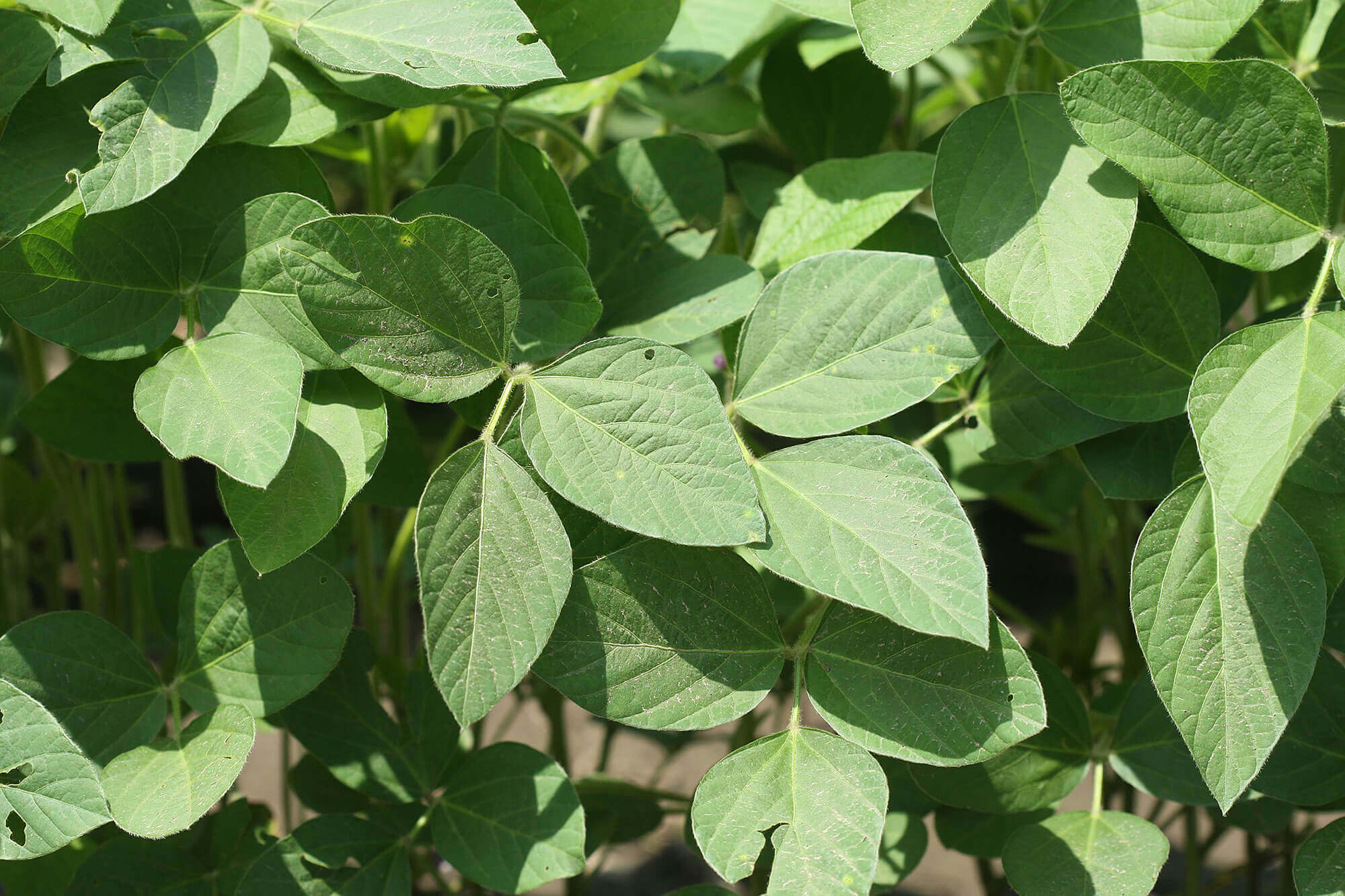
Wild-type soybeans contain bloom, a powdery substance originating in the pod that can coat seeds. This trait makes the seeds less visible and is believed to be advantageous for their long-term survival in natural environments. But the bloom is enriched with allergens and can be harmful for animals and people if ingested. People domesticating soybeans selected a naturally occurring mutation that makes soybean seeds shiny through eliminating bloom.
“This mutation was selected by ancient farmers approximately 5,000 years ago,” said Jianxin Ma, professor in Purdue’s Department of Agronomy. “That could have been a key step for domesticating soybean for agricultural production and human consumption.”
Ma and his colleagues wanted to know more about the genetic control of bloom in wild soybeans. They found that a single nucleotide polymorphism - a change from a single cytosine (C) to a thymine (T) within a gene called B1 eliminates bloom from wild soybeans.
Surprisingly, that’s not all the mutation did for soybeans.
“We found that the mutation within the B1 gene resulted in substantial increases of seed oil content in cultivated soybeans compared with the wild type,” said Ma, whose findings were published in the journal Nature Plants. “It seems like the selection of this mutation by farmers was essential for making soybean an important oilseed crop that we have now.”
The B1 gene does not seem to affect oil biosynthesis within seeds. However, the mutation that leads to loss of bloom heightens the activity of master regulators of oil biosynthesis in the endocarp of pods that appears to result in enhanced oil accumulation in seeds.
The findings show that there may be genetic targets outside those responsible for seed traits that could affect soybean seed oil content.
Ma will continue studying the genetic control of seed oil content mediated by the B1 gene, in particular the ways in which it interacts with other genes in a network to affect the pod and seed traits.
Funding for this work came from the North Central Soybean Research Program, the Indiana Soybean Alliance, the Agriculture and Food Research Initiative of the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture, the Republic of Korea Rural Development Administration (RDA) Research Program, Qingdao Agricultural University, and the Purdue University AgSEED Program.