How a diagnostic tool used on cows might unlock a key to COVID-19 testing
What do cows and COVID-19 have in common? Unless you’re Mohit Verma, assistant professor in Purdue University’s Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, the answer is probably not much.
Verma’s research focuses on developing biosensors to monitor infectious diseases in bovines. Specifically, he studies how to diagnose Bovine Respiratory Disease (BRD), the most common bovine disease in beef cattle in the world. Detection of the disease can be difficult and costly. Verma’s lab develops methods for testing that are accurate, safe and less expensive for farmers and veterinarians.
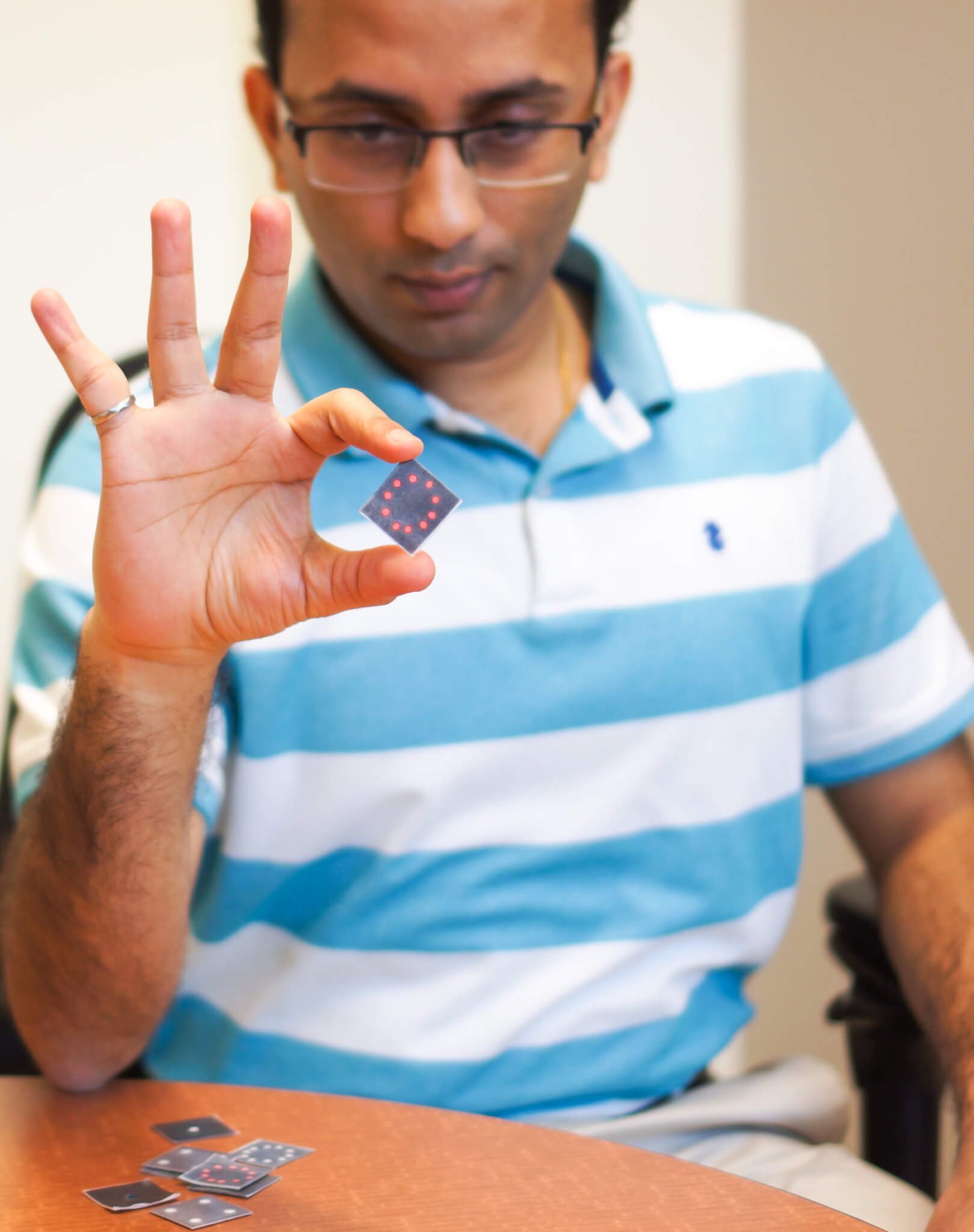
“The technique we use is based on the identification of nucleic acids specific to that virus,” Verma said. “The test will show us what pathogen is causing the infection. This helps determine which antibiotic to prescribe.” The tests are small sensors, cheap and easy to produce that provide test results in a matter of minutes.
“That’s exactly what is needed right now for COVID-19 testing,” Verma said. “So, back in February, we began looking at ways to adapt the biosensor used for BRD to a cheap, reliable test for COVID-19 and other SARS diseases.”
The tests have performed well in the lab setting, and Verma said he is working with external partners (Raytheon BBN, PortaScience, Laduca RCA) to fast-track the approval of the device when the time is appropriate. Several challenges remain.

The main hurdle: logistics.
The project is being accelerated, attempting to accomplish a goal in months that would typically take years. There are technical challenges in the lab. And Verma faces challenges with purchasing, personnel, and facilities. He is working with administrative leaders to overcome these challenges and minimize delays. His target is for the device to be submitted to the FDA for emergency use within three months.
Verma knows many other researchers are working on COVID-19 testing devices around the world, and even some at Purdue. That’s an entirely positive thing, he explains. A likely and ideal scenario, he continued, is that many of these tests are approved for usage and flood the market, addressing the severe shortage of diagnostic equipment currently stymieing efforts to eradicate COVID-19 globally.
Long-term, Verma hopes this same kind of technology can be used for other kinds of viruses, including influenza. Ideally, one device could detect multiple targets, which would improve diagnostic accuracy, cut down on healthcare cost and save time for healthcare professionals.
“This is a great example of how the technology developed in agriculture can have implications far beyond that sphere,” Verma said.