Intro to Trees of Indiana: Chestnut Oak
The classic and trusted book "Fifty Common Trees of Indiana" by T.E. Shaw was published in 1956 as a user-friendly guide to local species. Nearly 70 years later, the publication has been updated through a joint effort by the Purdue Department of Forestry and Natural Resources, Indiana 4-H, and the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, and reintroduced as "An Introduction to Trees of Indiana."
A printed copy of the full publication is available for purchase for $7 in the Purdue Extension Education Store. The field guide helps identify common Indiana woodlot trees.
Each week, the Intro to Trees of Indiana web series will offer a sneak peek at one species from the book, paired with an ID That Tree video from Purdue Extension forester Lenny Farlee to help visualize each species as it stands in the woods. Threats to species health as well as also insight into the wood provided by the species, will be provided through additional resources as well as the Hardwoods of the Central Midwest exhibit of the Purdue Arboretum, if available. 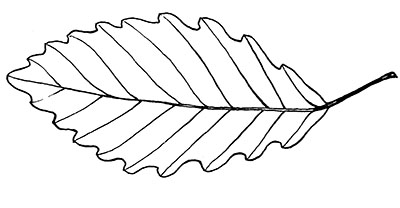
This week, we take a look at the fourth of our oak varieties in Indiana, the Chestnut Oak or Quercus montana.
The leaves of the chestnut oak have small, evenly lobed rounded margins. The upper leaf surface is leathery in appearance and is dark green in color, while the lower surface is a duller green. In the fall, the leaves can range from red and orange to yellow and brown.
The bark may be its tell-tale characteristic. Unlike other members of the white oak group, the bark of chestnut oak is dark and deeply ridged.
chestnut oak is dark and deeply ridged.
The fruit of the chestnut oak is a relatively-large dark brown acorn with a smooth edge on the outer margin of the cap.
Chestnut oaks, which grow to 60 to 70 feet tall, are often found on high, dry sites in Indiana. The natural range of chestnut oak is across the northeastern United States, extending south to the northern parts of Alabama and Georgia and west to the southern tip of Illinois.
The Morton Arboretum warns that chestnut oak is a difficult to transplant due to a deep taproot, but that it can tolerate most soils except those that drain poorly. It also notes that oaks should be pruned in the dormant season to avoid attracting beetles that may carry oak wilt. Chestnut oak can be affected by pests such as scale insects and two-lined chestnut borer. 
In general, lumber from the white oak group is among the heaviest next to hickory, weighing in at 47 pounds per cubic foot. It is very resistant to decay and is one of the best woods for steam bending. Chestnut oak, however, is considered a poor lumber species.
White oak lumber has been used for a variety of purposes including log cabins, ships, wagon wheels and furniture. It also is preferred for indoor decorative applications ranging from furniture, especially in churches, to cabinets, interior trim, millwork and hardwood flooring and veneers. It also may be used for barrel making.
Its density and durability make white oak a favorite for industrial applications such as railroad ties, mine timbers, sill plates, fence posts and boards, pallets, and blocking, as well as industrial, agricultural and truck flooring.
ID That Tree: Chestnut Oak
ID That Tree: White Oak Group
Hardwood Lumber and Veneer Series: White Oak Group
Morton Arboretum: Chestnut Oak
Purdue Plant Doctor
Native Trees of the Midwest, The Education Store
Shrubs and Woody Vines of Indiana and the Midwest, The Education Store
Investing in Indiana Woodlands, The Education Store
Forest Improvement Handbook, The Education Store
ID That Tree, Purdue Extension-Forestry & Natural Resources (FNR) YouTube playlist
Woodland Management Moment , Purdue Extension-FNR YouTube playlist






