Intro to Trees of Indiana: Butternut
The classic and trusted book "Fifty Common Trees of Indiana" by T.E. Shaw was published in 1956 as a user-friendly guide to local species. Nearly 70 years later, the publication has been updated through a joint effort by the Purdue Department of Forestry and Natural Resources, Indiana 4-H, and the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, and reintroduced as "An Introduction to Trees of Indiana."
A printed copy of the full publication is available for purchase for $7 in the Purdue Extension Education Store. The field guide helps identify common Indiana woodlot trees.
Each week, the Intro to Trees of Indiana web series will offer a sneak peek at one species from the book,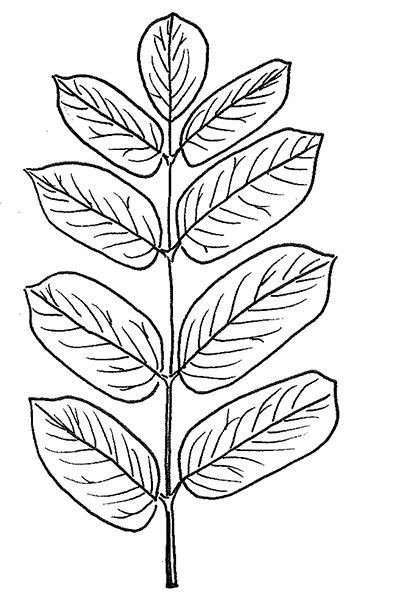 paired with an ID That Tree video from Purdue Extension forester Lenny Farlee to help visualize each species as it stands in the woods. Threats to species health as well as also insight into the wood provided by the species, will be provided through additional resources as well as the Hardwoods of the Central Midwest exhibit of the Purdue Arboretum, if available.
paired with an ID That Tree video from Purdue Extension forester Lenny Farlee to help visualize each species as it stands in the woods. Threats to species health as well as also insight into the wood provided by the species, will be provided through additional resources as well as the Hardwoods of the Central Midwest exhibit of the Purdue Arboretum, if available.
This week, we meet Butternut or Juglans cinerea.
Also known as white walnut, this species has slowly disappeared from the landscape due to a fungal disease. Butternut canker can cause large dead spots on the tree and can even girdle the tree and kill it before it can produce fruit.
Butternut has alternately held compound leaves that can be between one and two feet long, resembling a black walnut leaf with pairs of leaflets, but butternut often has a terminal leaflet. The toothed leaflets are green in the summer and yellow in the fall.
The bark is light gray and relatively smooth, but it may become furrowed with age, silver on top and darker between the fissures. Butternut twigs are light tan in color and have an elongated terminal bud. The leaf scar resembles the face of a monkey and it has a “hairy eyebrow” above the leaf scar/below the bud.
between the fissures. Butternut twigs are light tan in color and have an elongated terminal bud. The leaf scar resembles the face of a monkey and it has a “hairy eyebrow” above the leaf scar/below the bud.
The fruit is a lemon-shaped edible nut approximately two inches in diameter with sharp ridges on the nut inside the husk. When they are green, the husk is sticky and clammy to the touch, unlike the smooth, thick skin of its cousin black walnut.
Butternuts, which grow 40 to 60 feet tall, prefer moist, well-drained, loamy soils, found in ravines and coves, but it can also grow on drier, rocky soil, especially that of limestone origin. It is usually scattered in the forest and associated with other species that prefer upland sites.
The natural range of the butternut extends from central Minnesota, Iowa and Missouri to the west, and south across Tennessee, Kentucky, West Virginia and Virginia. The range extends north across Minnesota, Wisconsin, Michigan, New York, New Hampshire, Vermont and Maine.
The Morton Arboretum warns that butternut canker is a serious problem of butternut, limiting its usefulness as a landscape tree. It also states that the species produces juglone, a chemical which is toxic to many plants. Butternuts also are difficult to transplant due to a deep taproot.
At 12 percent moisture content, butternut wood weighs 27 pounds per cubic foot. As with other light-weight woods, butternut has a lower strength value. The wood is soft, but rated good for machining properties. When stained dark, butternut can be used a substitute for walnut, but butternut is rated as a nondurable wood.
When stained dark, butternut can be used a substitute for walnut, but butternut is rated as a nondurable wood.
In the past, butternut wood has been used for furniture, cabinets, paneling and other millwork in the past as well as for fancy face veneers. The wood is easily chopped for bowls. The fruit produces a yellow die that was used in the Civil War to color uniforms.
With the scarcity of the tree due to canker disease, commercial interest in the wood is limited. It is primarily used for carving, architectural veneer, internal furniture components, interior trim, boxes and crates.
Other Resources:
ID That Tree: Butternut
Hardwoods of the Central Midwest: Butternut
Hardwood Lumber and Veneer Series: Butternut
Morton Arboretum: Butternut
Identification of Butternuts and Butternut Hybrids, The Education Store
Conservation and Management of Butternut Trees, The Education Store
The Plight of the Butternut
HTIRC Seed Propagation Protocol for Purdue and Hybrid Butternut
Purdue Arboretum Explorer
The Woody Plant Seed Manual, U.S. Forest Service
Purdue Plant Doctor
Native Trees of the Midwest, The Education Store
Shrubs and Woody Vines of Indiana and the Midwest, The Education Store
Investing in Indiana Woodlands, The Education Store
Forest Improvement Handbook, The Education Store
ID That Tree, Purdue Extension-Forestry & Natural Resources (FNR) YouTube playlist
Woodland Management Moment , Purdue Extension-FNR YouTube playlist






