PFAS Publication Named Among Exceptional Papers of 2021
The article “Chronic Per-/Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Exposure Under Environmentally Relevant Conditions Delays Development in Northern Leopard Frog (Rana Pipiens) Larvae” was named as one of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (ET&C)’s Top 10 Exceptional Papers of 2021.
The publication was co-authored by Wes Flynn, research ecologist for the U.S. Geological Survey; Drs. Marisol Sepulveda and Jason Hoverman and former lab technician Michael Iacchetta from Purdue Forestry and Natural Resources; and Dr. Linda Lee and Chloe De Perre in the Purdue Department of Agronomy.
 This research aimed to assess the impact of Per-/polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) on amphibians under semirealistic conditions, rather than in a lab, to help determine whether environmental factors affect toxicity of PFAS on aquatic life by studying northern leopard frogs reared in outdoor mesocosms. Their results suggested that developmental delays were found in water concentrations as low as 0.06 parts per billion, which is considerably lower than levels associated with those in lab studies.
This research aimed to assess the impact of Per-/polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) on amphibians under semirealistic conditions, rather than in a lab, to help determine whether environmental factors affect toxicity of PFAS on aquatic life by studying northern leopard frogs reared in outdoor mesocosms. Their results suggested that developmental delays were found in water concentrations as low as 0.06 parts per billion, which is considerably lower than levels associated with those in lab studies.
“I think this work is important because it shows that exposure of PFAS under more realistic conditions (in this case in mesocosms) resulted in enhanced sensitivity to these chemicals compared to previous indoor lab experiments,” Sepulveda said. ”These studies are uncommon and are overall lacking in the PFAS ecotoxicity literature. This, and the fact that developmental delays were reported at much lower PFAS concentrations than previously reported, are the reasons why I think the paper was recognized by the scientific community. Our research team is thrilled that our work was recognized this way and hope to continue to advance the field of PFAS amphibian ecotoxicology."
One of the unique aspects of the research was that it utilized a simulated pond community that allowed for PFAS to distribute between water, sediments and algae (food for tadpoles) as it would in a natural environment, while most laboratory toxicity studies tend to focus on aquatic exposure (water) as the primary method of exposure. This may explain why researchers observed developmental effects at much lower PFAS water concentrations than those reported in laboratory investigations and also highlights how ecological interactions could influence outcomes of contaminant exposure in the environment. The data from this study as well as those found in food web studies, found that diet may be an important route of exposure that can influence toxicity.
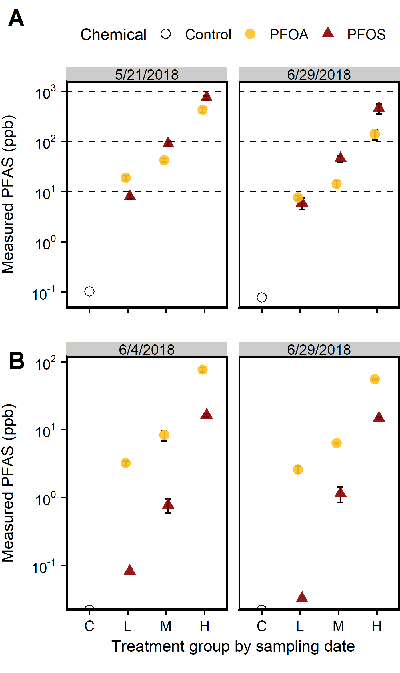 Graphic showing measured concentrations of PFOS and PFOA (± SD) in sediment (A) and water (B) at two sampling times. Dashed lines in Panel A show nominal PFAS sediment concentrations that were targeted for the three. The x-axis shows treatment levels, where C = control, L = low, M = medium, and H = high concentrations.
Graphic showing measured concentrations of PFOS and PFOA (± SD) in sediment (A) and water (B) at two sampling times. Dashed lines in Panel A show nominal PFAS sediment concentrations that were targeted for the three. The x-axis shows treatment levels, where C = control, L = low, M = medium, and H = high concentrations. Of more than 300 articles published in ET&C in 2021, 30 were nominated based on scientific impact, public and professional interest, comprehension and experimental design and quality. The Top 10 were selected and an overall Annual Best Paper Award was given out. The list of papers honored among the Top 10 Exceptional Papers were published in the July 2022 issue.
The recognized publication is part of a larger SERDP grant focusing on the Development of Amphibian PFAS Toxicity Reference Values for Use in Ecological Risk Assessment at Aqueous Film-Forming Foam (AFFF) Sites.






