LiDAR-based tree inventory – not Sci-Fi anymore
Drs. Gang Shao, Guofan Shao, & Songlin Fei of Purdue Forestry and Natural Resources recently published the article - Delineation of individual deciduous trees in plantations with low-density LiDAR data - in the International Journal of Remote Sensing.
In this work, Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) data was used to delineate individual deciduous trees using a point-density-based algorithm. First a high-resolution point density model (PDM) was developed from low-density LiDAR point cloud to locate individual trees through the horizontal spatial distribution of LiDAR points. Then, individual tree crowns and associated attributes were delineated with a 2D marker-controlled watershed segmentation. Additionally, the PDM-based approach was compared with a conventional canopy height model (CHM) based delineation. The PDM-based approach produced an 89% detection accuracy to identify deciduous trees and tree attributes derived from the PDM-based algorithm explained 81% and 83% of tree height and crown width variations of forest stands, respectively.
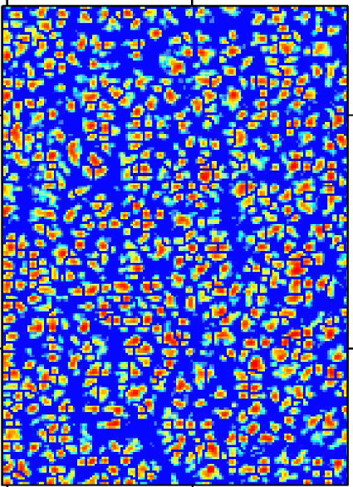
Light Detection And Ranging (LiDAR) crown detection predicts tree diameter with a correlation coefficient of 0.83.





