Slight increase in producer sentiment despite rising costs and lower crop prices
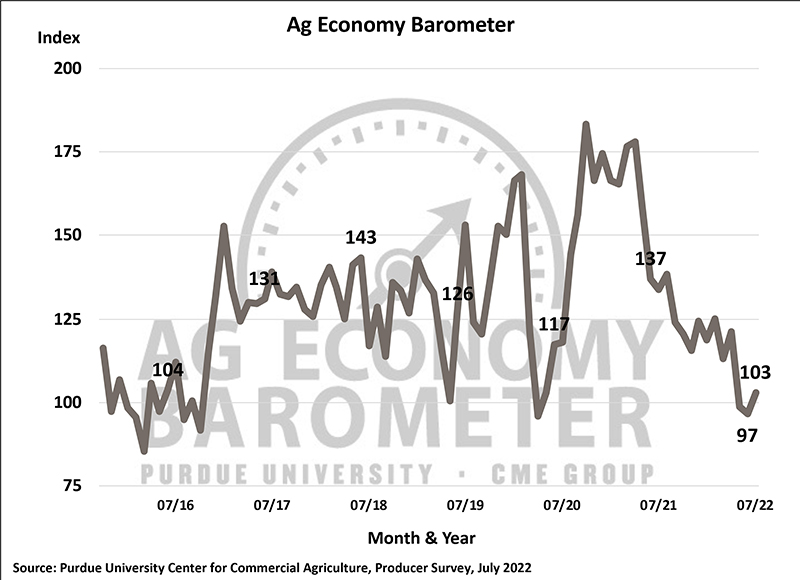
The Purdue University/CME Group Ag Economy Barometer farmer sentiment index rose 6 points in July to a reading of 103. Producers were somewhat more optimistic about both current and future economic conditions on their farms when compared to June. The Index of Current Conditions rose 10 points to a reading of 109, and the Index of Future Expectations rose 4 points to a reading of 100. Although all three indices rose this month, they were still 23% to 24% lower than a year earlier. The Ag Economy Barometer is calculated each month from 400 U.S. agricultural producers’ responses to a telephone survey. This month’s survey was conducted July 11-15.
“Even though we saw a slight uptick in sentiment this month, there is still a tremendous amount of uncertainty in the agricultural economy,” said James Mintert, the barometer’s principal investigator and director of Purdue University’s Center for Commercial Agriculture. “Key commodity prices, including wheat, corn and soybeans, all weakened during the month and producers remain concerned over rising input prices and input availability.”
Farm operators in this month’s survey voiced concerns about several key issues affecting their operation, including higher input prices (42% of respondents), lower crop prices (19% of respondents), rising interest rates (17% of respondents) and availability of inputs (15% of respondents).
The Farm Financial Performance Index, which is primarily reflective of income expectations for the current year, improved 5 points to a reading of 88 in June. However, this month, 49% of respondents said they expect their farm to be worse off financially a year from now, which compares to 51% who felt that way in June. This is a markedly more pessimistic outlook than producers provided a year ago when just 30% of respondents said they expect their financial condition to worsen in the upcoming year.
Producers remain uncertain over their expectations for crop input prices over the next 12 months. In July, 18% of crop producers said they expect 2023’s crop input prices to decline between 1% and 10% when compared to 2022’s prices, versus 12% who felt that way in June. Meanwhile, 26% of respondents in July said they expect 2023’s prices to rise by 10% or more, compared to 38% who expected a crop input price rise of that magnitude in June.
The rise in input costs is leading some producers to reassess their cropping plans for the upcoming year. In this month’s survey, nearly one out of four (24%) of crop producers said that as a result of the rise in input costs, they plan to change their farm’s crop mix in 2023. In a follow-up question, over half (53%) of respondents who said they plan to change their mix will increase the percentage of their cropland devoted to soybeans. In a separate set of questions, 26% of producers who said they planted winter wheat last year indicated they plan to increase their wheat acreage this fall.
The Farm Capital Investment Index remains near its record low, up one point to a reading of 36 in July. To shed light on why, respondents who said now is a bad time for large investments were asked for the primary reason they felt that way. Of those respondents, 44% indicated an “increase in prices for farm machinery and new construction,” 15% said “uncertainty about farm profitability,” and 14% chose “rising interest rates” as the primary reason they viewed now as a bad time for large investments. Somewhat surprisingly, only 7% of respondents chose “tight farm machinery inventories at dealers” as their primary reason for responding negatively to the investment question.
Producers’ views on farmland values diverged this month as the Short-Term Farmland Value Index declined 9 points to 127, while the long-term index rose 9 points to 150. The short-term index is down 20% from its peak reading in 2021, while the long-term index is only 6% lower than the peak reached last year. Short-term, there was a shift away from expectations that farmland values will go higher, with more producers in July expecting values to remain about the same. The long-term change was attributable to more respondents this month expecting values to rise with fewer expecting a decline over the next five years.
“The short-run and long-term farmland indices don’t always move in tandem, but the magnitude of this month’s divergence between the short and long-term indices is unusual,” Mintert said. “Producers who expect values to rise over the upcoming five years continue to say that nonfarm investor demand and inflation are the two primary reasons they expect values to rise.”
Read the full Ag Economy Barometer report at https://purdue.ag/agbarometer. The site also offers additional resources – such as past reports, charts and survey methodology – and a form to sign up for monthly barometer email updates and webinars.
Each month, the Purdue Center for Commercial Agriculture provides a short video analysis of the barometer results, available at https://purdue.ag/barometervideo. For even more information, check out the Purdue Commercial AgCast podcast. It includes a detailed breakdown of each month’s barometer, in addition to a discussion of recent agricultural news that affects farmers. Available now at https://purdue.ag/agcast.
The Ag Economy Barometer, Index of Current Conditions and Index of Future Expectations are available on the Bloomberg Terminal under the following ticker symbols: AGECBARO, AGECCURC and AGECFTEX.
About the Purdue University Center for Commercial Agriculture
The Center for Commercial Agriculture was founded in 2011 to provide professional development and educational programs for farmers. Housed within Purdue University’s Department of Agricultural Economics, the center’s faculty and staff develop and execute research and educational programs that address the different needs of managing in today’s business environment.
About CME Group
As the world’s leading and most diverse derivatives marketplace, CME Group (www.cmegroup.com) enables clients to trade futures, options, cash and OTC markets, optimize portfolios, and analyze data – empowering market participants worldwide to efficiently manage risk and capture opportunities. CME Group exchanges offer the widest range of global benchmark products across all major asset classes based on interest rates, equity indexes, foreign exchange, energy, agricultural products and metals. The company offers futures and options on futures trading through the CME Globex® platform, fixed income trading via BrokerTec and foreign exchange trading on the EBS platform. In addition, it operates one of the world’s leading central counterparty clearing providers, CME Clearing. With a range of pre- and post-trade products and services underpinning the entire lifecycle of a trade, CME Group also offers optimization and reconciliation services through TriOptima, and trade processing services through Traiana.
CME Group, the Globe logo, CME, Chicago Mercantile Exchange, Globex, and E-mini are trademarks of Chicago Mercantile Exchange Inc. CBOT and Chicago Board of Trade are trademarks of Board of Trade of the City of Chicago, Inc. NYMEX, New York Mercantile Exchange and ClearPort are trademarks of New York Mercantile Exchange, Inc. COMEX is a trademark of Commodity Exchange, Inc. BrokerTec, EBS, TriOptima, and Traiana are trademarks of BrokerTec Europe LTD, EBS Group LTD, TriOptima AB, and Traiana, Inc., respectively. Dow Jones, Dow Jones Industrial Average, S&P 500, and S&P are service and/or trademarks of Dow Jones Trademark Holdings LLC, Standard & Poor’s Financial Services LLC and S&P/Dow Jones Indices LLC, as the case may be, and have been licensed for use by Chicago Mercantile Exchange Inc. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.