Americans planning frugal uses for their 2023 tax refunds
Americans likely are receiving smaller tax refunds than they have in recent years, and most people will not be going out to spend this money, according to the February 2023 Consumer Food Insights Report. This month’s report also looks closer at religious demographics and includes new data on frozen food preferences.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainability assesses food spending, consumer satisfaction and values, support of agricultural and food policies and trust in information sources. Purdue experts conducted and evaluated the survey, which included 1,200 consumers across the U.S.
“Of those who will be spending their tax refunds, improving food purchases is top of mind, which suggests that refunds are a part of reinforcing some households’ food situation,” said Jayson Lusk, the head and Distinguished Professor of Agricultural Economics at Purdue, who leads the center. Americans expect to receive a tax refund of $1,940, on average. They plan to use most of it for savings, investment or to reduce debt.
In food spending, American consumers appear to be in a holding pattern.
“There seems to be some optimism about food inflation improving, but consumers are not willing or able to spend more on food than they are currently,” Lusk said. “I would also not expect food spending to start falling unless economic conditions worsen, which is a real possibility.”
This month’s report highlights the role that frozen foods play in many consumer diets. Frozen vegetables are the most common item that people select from the freezer aisle. It appears that price is a key part of that decision, Lusk noted.
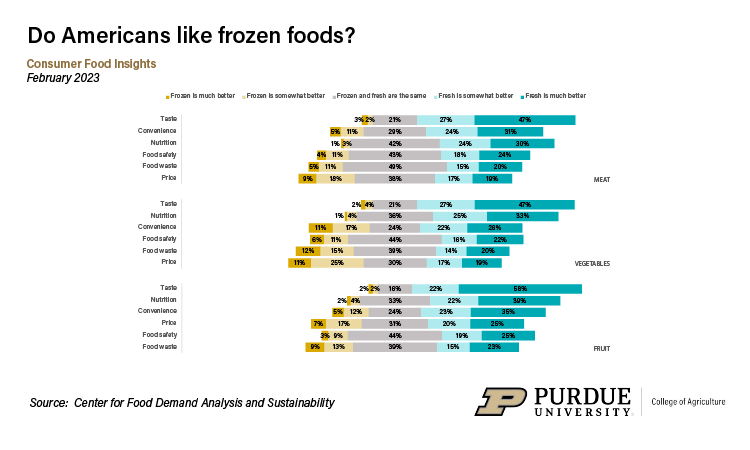 Consumer Preferences for Fresh vs. Frozen Foods, Feb. 2023
Consumer Preferences for Fresh vs. Frozen Foods, Feb. 2023 More than 60% of surveyed consumers assess fresh food as somewhat better or much better nutritionally than frozen food. “For most foods, the science does not support this belief or the difference in nutrition is not big enough to matter,” Lusk said.
Additional key results include:
- Religious consumers, namely Protestants, Catholics and Jews, tend to be happier with both their diets and lives.
- Religious affiliation correlates with some food behaviors like vegetarianism, but few generalizable trends emerge.
- Consumers largely think fresh food is better than frozen food, although frozen foods compete better on price.
- The average length of time that households are staying on SNAP has continued to increase over 13 months.
- Reported food spending remains flat on a monthly basis even though consumers feel that food inflation is easing.
The survey found no change in the food insecurity rate, a sign that most people are managing under current conditions, said Sam Polzin, a food and agriculture survey scientist for the center and co-author of the report.
Polzin noted, however, that the portion of Americans who are food insecure and who rely on SNAP benefits have now seen their increased SNAP benefits end along with the public health response to COVID-19.
This month’s closer look at religious demographics revealed few clear patterns except that Protestant, Catholic and Jewish people report experiencing higher rates of diet satisfaction and life happiness compared to other groups.
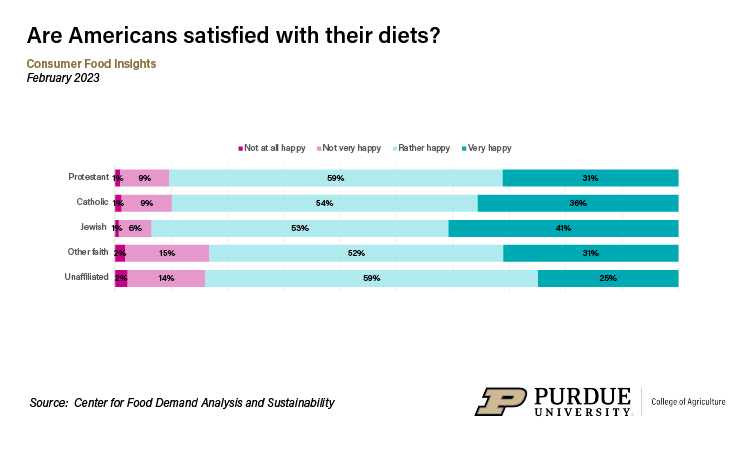 Rate of Consumer Diet Happiness by Religious Affiliation, Jan. 2022 - Feb. 2023
Rate of Consumer Diet Happiness by Religious Affiliation, Jan. 2022 - Feb. 2023 “Other research similarly shows that religious people are happier than those who are unaffiliated with a religious tradition, so these results are relatively unsurprising,” Polzin noted. “However, the fact that people who we have grouped under other faiths are not doing as well is notable.”
As to why, “I might guess that more people who are inactive members of a religious group or who broadly identify as spiritual selected the “other” option, which might relate to their happiness.
Polzin further observed that religion was an inexact social indicator when it came to food-related behaviors, beliefs and trust.
“Our takeaway from many of these sections should be that religious affiliation does not provide a very coherent lens for understanding most food behaviors,” Polzin said. “We would have more success identifying the influence of religion in the context of other socioeconomic and demographic variables.”
Lusk further discusses the report in his blog.
The Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainability is part of Purdue’s Next Moves in agriculture and food systems and uses innovative data analysis shared through user-friendly platforms to improve the food system. In addition to the Consumer Food Insights Report, the center offers a portfolio of online dashboards.