Intro to Trees of Indiana: Quaking Aspen
A printed copy of the full publication is available for purchase for $7 in the Purdue Extension Education Store. The field guide helps identify common Indiana woodlot trees.
Each week, the Intro to Trees of Indiana web series will offer a sneak peek at one species from the book, paired with an ID That Tree video from Purdue Extension forester Lenny Farlee to help visualize each species as it stands in the woods. Threats to species health as well as insight into the wood provided by the species, will be provided through additional resources as well as the Hardwoods of the Central Midwest exhibit of the Purdue Arboretum, if available.
This week, we introduce the quaking aspen or populus tremuloides.
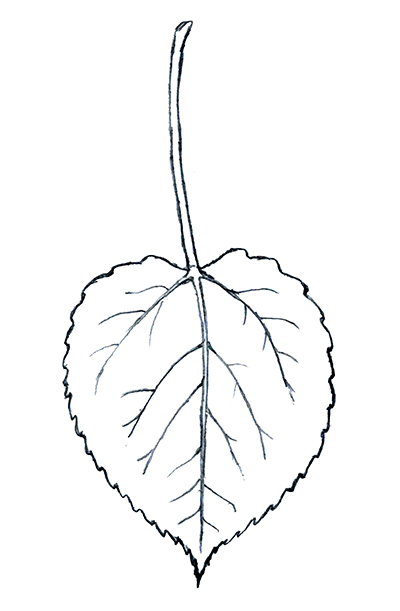 The quaking aspen, also known as the trembling aspen, is adaptable to a variety of soils, ranging from moist, loamy sands to clay, but it is shade intolerant. It is often found on the edge of woodlands or where the site has been disturbed, giving it access to full sunlight.
The quaking aspen, also known as the trembling aspen, is adaptable to a variety of soils, ranging from moist, loamy sands to clay, but it is shade intolerant. It is often found on the edge of woodlands or where the site has been disturbed, giving it access to full sunlight.
This species is identifiable by its whitish to grayish bark with dark spots where the branches come out of the trunk. It has small rounded leaves with very small teeth along the margin. Like most aspens, it has long flat leaf stems that are known to flutter in the wind.
Quaking aspen is found in the northern part of the state of Indiana. This species is found from Newfoundland through Alaska in the West, and as far south as Arizona. In the Midwest, it ranges south to northeastern Iowa, northern Illinois and Pennsylvania. It is also found in some scattered areas in the Appalachian Mountains. It is the most widely distributed tree in the United States.
According to the Hardwood Lumber and Veneer Series, aspen is one of our lightest woods with a 12 percent moisture content and a weight of 26 to 27 pounds per cubic foot. It was at one time relegated to the pulp and paper industry as a weed tree, however it is now a favored species for the manufacturer of panel boards.
Aspen - Hardwood Lumber and Veneer Series
Why Fall Color Is Sometimes a Dud – Purdue Landscape Report
Purdue Plant Doctor
Native Trees of the Midwest
Shrubs and Woody Vines of Indiana and the Midwest
ID That Tree YouTube playlist
Woodland Management Moment YouTube playlist
Investing in Indiana Woodlands
Forest Improvement Handbook






