Intro to Trees of Indiana: Boxelder
The classic and trusted book "Fifty Common Trees of Indiana" by T.E. Shaw was published in 1956 as a user-friendly guide to local species. Nearly 70 years later, the publication has been updated through a joint effort by the Purdue Department of Forestry and Natural Resources, Indiana 4-H, and the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, and reintroduced as "An Introduction to Trees of Indiana."
A printed copy of the full publication is available for purchase for $7 in the Purdue Extension Education Store. The field guide helps identify common Indiana woodlot trees.
Each week, the Intro to Trees of Indiana web series will offer a sneak peek at one species from the book, paired with an ID That Tree video from Purdue Extension forester Lenny Farlee to help visualize each species as it stands in the woods. Threats to species health as well as also insight into the wood provided by the species, will be provided through additional resources as well as the Hardwoods of the Central Midwest exhibit of the Purdue Arboretum, if available.
 This week, we introduce Boxelder or Acer negundo.
This week, we introduce Boxelder or Acer negundo.
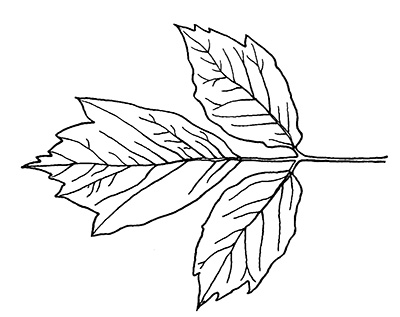
This member of the maple family has opposite leaf arrangement, but is the only maple that features compound leaves, often with three to five leaflets. The shape of the leaflets is extremely variable, but all held on green twigs, unlike any other native Indiana maples. Boxelder bark is a medium gray color with long flat ridges running up and down the trunk.
 The leaves of boxelder are often confused with poison ivy, however poison ivy features alternate leaf arrangement.
The leaves of boxelder are often confused with poison ivy, however poison ivy features alternate leaf arrangement.
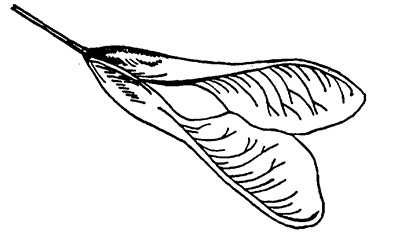
Boxelder flowers feature long strands of green or yellow green that hold the pollen. The fruit produced are paired winged seeds, which are often seen floating across the landscape.
Boxelder is frequently found growing in wet locations, such as bottomlands and forested sites near streams. They can help stabilize stream banks. Boxelder provides important habitat for many wildlife species and its seeds offer food for birds, squirrels and deer.
According to the U.S. Forest Service database, boxelder is not a desired timber species because its wood is light, soft, close grained and low in strength. The wood is occasionally used for cheap furniture and woodenware. It was once used for posts, fencing and fuel, but the soft, spongy wood generally makes poor firewood.
Other Resources:
Boxelder – Purdue Arboretum
Purdue Plant Doctor
Native Trees of the Midwest
Shrubs and Woody Vines of Indiana and the Midwest
ID That Tree YouTube playlist
Woodland Management Moment YouTube playlist
Investing in Indiana Woodlands
Forest Improvement Handbook






