Intro to Trees of Indiana: Sweetgum
The classic and trusted book "Fifty Common Trees of Indiana" by T.E. Shaw was published in 1956 as a user-friendly guide to local species. Nearly 70 years later, the publication has been updated through a joint effort by the Purdue Department of Forestry and Natural Resources, Indiana 4-H, and the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, and reintroduced as "An Introduction to Trees of Indiana."
A printed copy of the full publication is available for purchase for $7 in the Purdue Extension Education Store. The field guide helps identify common Indiana woodlot trees.
Each week, the Intro to Trees of Indiana web series will offer a sneak peek at one species from the book, paired with an ID That Tree video from Purdue Extension forester Lenny Farlee to help visualize each species as it stands in the woods. Threats to species health as well as also insight into the wood provided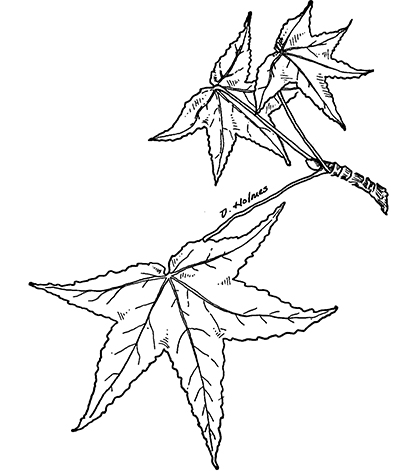 by the species, will be provided through additional resources as well as the Hardwoods of the Central Midwest exhibit of the Purdue Arboretum, if available.
by the species, will be provided through additional resources as well as the Hardwoods of the Central Midwest exhibit of the Purdue Arboretum, if available.
This week, we introduce the sweetgum or Liquidambar styraciflua.
This species is easily identified by its leaves, which are shaped like a five-pointed star and held alternately near the end of the twigs on long leaf stems. The leaves change from bright green in the summer to fall colors ranging from yellow to orange, red and purple. The twigs of sweetgum may be smooth or feature corky winged projections. The fruit of the sweetgum are spiny spherical balls that hold tiny winged seeds inside, which are released in the fall.
Sweetgum is found natively in the low, wet bottomland woods of southern Indiana, but is planted ornamentally through the state. This species grows as far north as coastal New York, as far south as central Florida, as far west as eastern Texas as well as throughout the Midwest with the exception of the Appalachian Mountains.
According to Morton Arboretum, the sweetgum grows to between 60 and 75 feet tall.
 Sweetgum is sometimes call red gum in the wood products industry due to its reddish brown heartwood. Historically, it was exported to Europe and sold as “satin walnut.” It also was used to make furniture, millwork, doors and paneling where a decorative effect was desired, but much of that has been replaced with reconstituted wood products.
Sweetgum is sometimes call red gum in the wood products industry due to its reddish brown heartwood. Historically, it was exported to Europe and sold as “satin walnut.” It also was used to make furniture, millwork, doors and paneling where a decorative effect was desired, but much of that has been replaced with reconstituted wood products.
Sweetgum is easily rotary cut into veneer and used in baskets and plywood core. Lower grade stock can be used for pallets, boxes, crates, railroad ties and pulp. Sweetgum has a 12 percent moisture content and weighs 36 pounds per cubic foot.
Other Resources:
Sweetgum in Hardwoods of the Midwest
Sweetgum in the Hardwood Lumber and Veneer Series
Purdue Plant Doctor
Native Trees of the Midwest
Shrubs and Woody Vines of Indiana and the Midwest
ID That Tree YouTube playlist
Woodland Management Moment YouTube playlist
Investing in Indiana Woodlands
Forest Improvement Handbook






