Intro to Trees of Indiana: River Birch
The classic and trusted book "Fifty Common Trees of Indiana" by T.E. Shaw was published in 1956 as a user-friendly guide to local species. Nearly 70 years later, the publication has been updated through a joint effort by the Purdue Department of Forestry and Natural Resources, Indiana 4-H, and the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, and reintroduced as "An Introduction to Trees of Indiana."
A printed copy of the full publication is available for purchase for $7 in the Purdue Extension Education Store. The field guide helps identify common Indiana woodlot trees.
Each week, the Intro to Trees of Indiana web series will offer a sneak peek at one species from the book, paired with an ID That Tree video from Purdue Extension forester Lenny Farlee to help visualize each species as it stands in the woods. Threats to species health as well as also insight into the wood provided by the species, will be provided through additional resources as well as the Hardwoods of the Central Midwest exhibit of the Purdue Arboretum, if available.
 This week, we introduce River Birch or Betula nigra, which is also known as red birch.
This week, we introduce River Birch or Betula nigra, which is also known as red birch.
As its name implies, it is found frequently in wet situations. It is often found need waterways and in moist soil areas across the state.
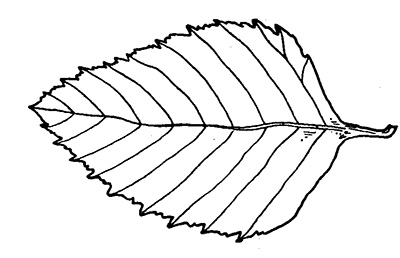
River birch is identifiable by its simple, triangular-shaped leaves with doubly-serrated or toothed margins, which are held on fine twigs, as well as its  flaking or peeling bark. The bark of young trees and the upper bark on older trees peels off in thin, papery strips with a pink to reddish tinge. In younger trees, the bark peels more and can range from chalky white to reddish brown. Bark on older trees is darker gray/brown and peeling is less prominent.
flaking or peeling bark. The bark of young trees and the upper bark on older trees peels off in thin, papery strips with a pink to reddish tinge. In younger trees, the bark peels more and can range from chalky white to reddish brown. Bark on older trees is darker gray/brown and peeling is less prominent.
This species can be either single stemmed, often in woodlands and bottomlands, or multi-stemmed, often in landscaping. River birch typically will reach a height of 70 to 80 feet and a diameter of two to three feet. The tree often divides into several trunks, which makes utilization for lumber or veneer difficult.
The river birch produces a small cone-like fruit, which matures in the spring.
River birch ranges from New Hampshire west to southeastern Minnesota, south to east Texas and back east to northern Florida. In Indiana, river birch is found mostly in the western half and south/central parts of the state.
Unlike its sister birch species white, paper and yellow birch trees, river birch is plant borer resistant to the native insect pest, the bronze birch borer.
Other Resources:
Birch - Hardwood Lumber and Veneer Series
Purdue Plant Doctor
Native Trees of the Midwest
Shrubs and Woody Vines of Indiana and the Midwest
ID That Tree YouTube playlist
Woodland Management Moment YouTube playlist
Investing in Indiana Woodlands
Forest Improvement Handbook






