Invasive Plants Impacting Forest Ecosystems
A regional scale study of invasive plant impacts of forest ecosystem
 The Central Hardwood Forest is one of the most important forest ecosystems in the eastern United States, providing valuable economic and recreational opportunities to the citizens of the region.
The Central Hardwood Forest is one of the most important forest ecosystems in the eastern United States, providing valuable economic and recreational opportunities to the citizens of the region.
Invasive exotic plants are moving into these ecosystems, in some places reaching epidemic proportions. The long-term invasion of these plants and other pests can alter the composition and reduce the diversity of these ecosystems, resulting in dramatic declines in the wildlife habitat and diminished economic opportunities for the human inhabitants of these mostly rural regions.
This project seeks to provide understanding of these invasives and their impact on forest ecosystems and on soil organic carbon pools and temperature sensitivity.
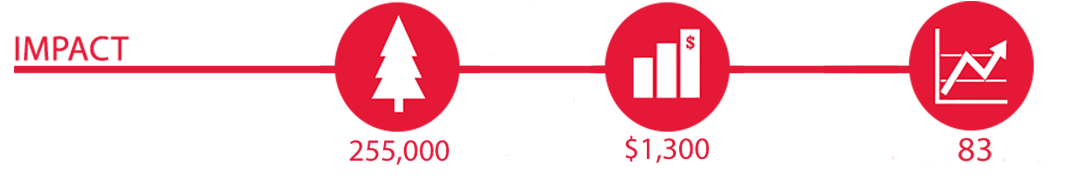
Results include the identification of interactions between pests and tree diversity, the impact of forest structural diversity on the prevalence of invasives, and a model predicting invasives impact on a continental scale. This information is being shared with the public as well as the scientific community and natural resources professionals.
Project Director: Dr. Songlin Fei
10/01/2016 - 09/30/2021
Print/Research