Intro to Trees of Indiana: Sycamore
The classic and trusted book "Fifty Common Trees of Indiana" by T.E. Shaw was published in 1956 as a user-friendly guide to local species. Nearly 70 years later, the publication has been updated through a joint effort by the Purdue Department of Forestry and Natural Resources, Indiana 4-H, and the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, and reintroduced as "An Introduction to Trees of Indiana."
A printed copy of the full publication is available for purchase for $7 in the Purdue Extension Education Store. The field guide helps identify common Indiana woodlot trees.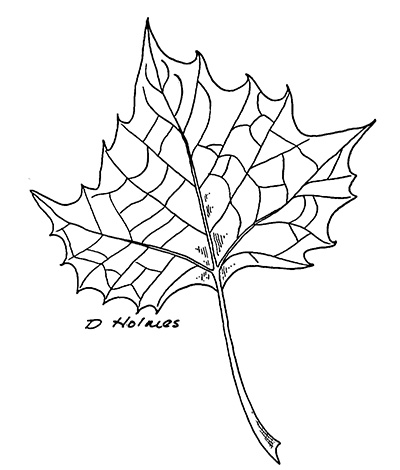
Each week, the Intro to Trees of Indiana web series will offer a sneak peek at one species from the book, paired with an ID That Tree video from Purdue Extension forester Lenny Farlee to help visualize each species as it stands in the woods. Threats to species health as well as also insight into the wood provided by the species, will be provided through additional resources as well as the Hardwoods of the Central Midwest exhibit of the Purdue Arboretum, if available.
This week, we meet Sycamore or Platanus occidentalis
The large leaves of this species have three to five lobes and loosely resemble that of maples, but are significantly larger and are alternately held, versus the opposite leaf arrangement of maples. The bright green, broadly toothed leaves and stems are slightly fuzzy to the touch.
The bark on the lower part of the tree is scaly and brown, while the upper trunk and limbs are smooth, shiny and white. The bark peels revealing patches of white, gray and green.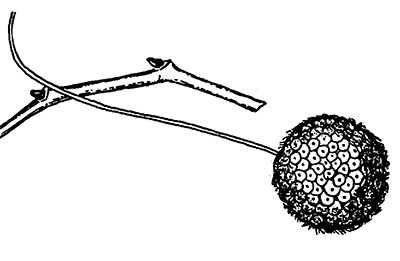
The fruit of the Sycamore is a soft, one-inch brown ball-like seed head, which hangs on a long stem. The seeds shatter during winter months.
Sycamore trees, which grow 75 to 100 feet tall, are among Indiana’s largest deciduous trees. They are often found on stream or creek bottoms and other moist soil areas. This species is tolerant of clay soil, occasional flooding and road salt.
The natural range of the sycamore is the central and eastern United States. It extends from eastern Texas and Oklahoma and Kansas west across Iowa Illinois, Indiana, Ohio and up into southern Michigan and parts of New York and Massachusetts. It extends down the Atlantic coast to southern Georgia and across Alabama, Mississippi and Louisiana, but do not reach the Gulf coast.
The Morton Arboretum warns that sycamores are best planted in full sun as it does not tolerate shady sites and should not be grown near septic fields. This species can be affected by anthracnose, leafspots, aphids, plant bugs, scale insects, bagworms and borers and is also susceptible to frost cracks.
According to the Hardwood Lumber and Veneer series, sycamore wood has a 12 percent moisture content and weighs 34 pounds per cubic foot, making it a relatively light weight hardwood. Sycamore lumber is commonly used for drawer sides as well as concealed furniture parts. It can be used for interior millwork and paneling, especially if quartersawn stock is available. Sycamore also can be used to make pallets, crates, boxes and veneer for baskets as well as for tool handles and other turned objects. It was once used to make butcher blocks. Sycamore is rated as non-durable to perishable regarding decay resistance and is susceptible to insect attack.
Other Resources:
ID That Tree: Sycamore
Morton Arboretum: Sassafras
Hardwood Lumber and Veneer Series: Sycamore, The Education Store
Purdue Arboretum Explorer
The Woody Plant Seed Manual, U.S. Forest Service
Purdue Plant Doctor
Native Trees of the Midwest, The Education Store
Shrubs and Woody Vines of Indiana and the Midwest, The Education Store
Investing in Indiana Woodlands, The Education Store
Forest Improvement Handbook, The Education Store
ID That Tree, Purdue Extension-Forestry & Natural Resources (FNR) YouTube playlist
Woodland Management Moment , Purdue Extension-FNR YouTube playlist






