Intro to Trees of Indiana: Black Willow
The classic and trusted book "Fifty Common Trees of Indiana" by T.E. Shaw was published in 1956 as a user-friendly guide to local species. Nearly 70 years later, the publication has been updated through a joint effort by the Purdue Department of Forestry and Natural Resources, Indiana 4-H, and the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, and reintroduced as "An Introduction to Trees of Indiana."
A printed copy of the full publication is available for purchase for $7 in the Purdue Extension Education Store. The field guide helps identify common Indiana woodlot trees.
Each week, the Intro to Trees of Indiana web series will offer a sneak peek at one species from the book,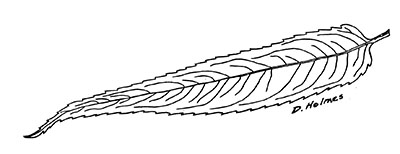 paired with an ID That Tree video from Purdue Extension forester Lenny Farlee to help visualize each species as it stands in the woods. Threats to species health as well as also insight into the wood provided by the species, will be provided through additional resources as well as the Hardwoods of the Central Midwest exhibit of the Purdue Arboretum, if available.
paired with an ID That Tree video from Purdue Extension forester Lenny Farlee to help visualize each species as it stands in the woods. Threats to species health as well as also insight into the wood provided by the species, will be provided through additional resources as well as the Hardwoods of the Central Midwest exhibit of the Purdue Arboretum, if available.
This week, we meet Black willow or Salix nigra. The black willow is one of several species of willow in Indiana, but it is the only tree-sized willow in the state.
This species has long, narrow leaves with short leaf stems, which are held alternately on slender, flexible twigs. Willows have a single scale covering the bud, which helps differentiate them from other species. The finely toothed leaves are medium green in the spring, changing to yellow-green in the fall.
The bark on young trees is smooth, but may be warty or feature some flaking. In old trees, the bark features prominent, light gray vertical flakes.
Black willows, which grow 50 to 70 feet tall, prefer moist or wet soils and often are found growing along streams or in other wetland areas. This species can tolerate alkaline soil, clay soil, occasional flooding and road salt.
The natural range of the black willow is along the Gulf and Atlantic coastal plains northward into the central portion of the Great Lake states, southern Ontario and central Maine.
The Morton Arboretum warns that black willows have excessive sucker growth and may be highly susceptible to ice damage due to its weak wood and branch structure, requiring regular pruning. Its roots are also prone to invading sewer pipes and drainage systems. Canker diseases also can affect this tree.
Wood from willow trees has a 12 percent moisture content and weighs in at 27.1 pounds per cubic foot, making it one of the lightest hardwoods.
It is commonly used to make cabinets, boxes, crates and caskets. It also can be used for pallets and crating that will not be carrying heavy loads. Willow branches can be used in basket weaving or furniture making due to their flexibility.
Other Resources:
ID That Tree: Black willow
Hardwoods of the Central Midwest: Black willow
Hardwood Lumber and Veneer Series: Black willow
Morton Arboretum: Black willow
Purdue Arboretum Explorer
The Woody Plant Seed Manual, U.S. Forest Service
Purdue Plant Doctor
Native Trees of the Midwest, The Education Store
Shrubs and Woody Vines of Indiana and the Midwest, The Education Store
Investing in Indiana Woodlands, The Education Store
Forest Improvement Handbook, The Education Store
ID That Tree, Purdue Extension-Forestry & Natural Resources (FNR) YouTube playlist
Woodland Management Moment , Purdue Extension-FNR YouTube playlist






