Purdue expert warned of coffee rust threat, part of FFAR project to protect Hawaii's coffee trees
With looming threats of coffee leaf rust to farmers’ yields, Purdue University mycologist Catherine Aime is working to protect this staple of daily lives and the economies of areas throughout the world.
Aime and colleagues warned of the potential threat to the coffee industry in June. She now is part of a team supported by the Foundation for Food & Agriculture Research (FFAR) and led by the Synergistic Hawaii Agriculture Council to investigate the fungus that causes the disease and to develop tactics to counter it.
Aime leads a team of researchers that will sequence the coffee leaf rust genome to inform breeding of coffee cultivars resistant to the fungus or to develop fungicides based on the disease’s genetic weaknesses.
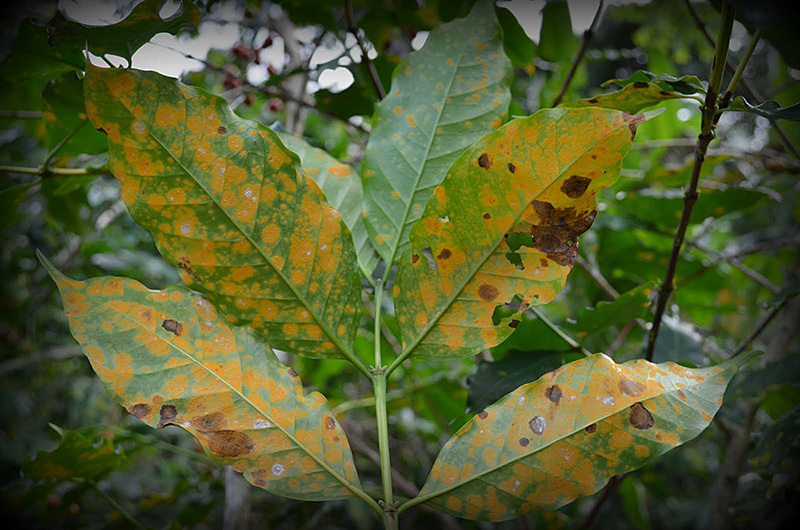
“Coffee rust has already caused a lot of devastation to the small shareholder farmers in Central America and the Caribbean that depend on coffee for their income,” she said. “Along with cacao, it is one of the tropical cropping systems that is really vulnerable to perturbations, such as is expected with changing climates, which has vast socioeconomic implications.”
Coffee leaf rust, which is caused by the fungus Hemileia vastatrix, attacks the leaves of coffee trees, reducing yields and damaging the trees. First discovered in Hawaii in late 2020, it has caused billions of dollars in damage to farms in Central and South America since 2011.
Aime, a professor in the Department of Botany and Plant Pathology, is the only academic mycologist in the nation who broadly specializes on the order of fungi that cause rust diseases. She also is a pioneer in the identification of fungi that cannot be put into culture and is an expert on fungi in tropical ecosystems.