Intro to Trees of Indiana: Northern Catalpa
The classic and trusted book "Fifty Common Trees of Indiana" by T.E. Shaw was published in 1956 as a user-friendly guide to local species. Nearly 70 years later, the publication has been updated through a joint effort by the Purdue Department of Forestry and Natural Resources, Indiana 4-H, and the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, and reintroduced as "An Introduction to Trees of Indiana."
A printed copy of the full publication is available for purchase for $7 in the Purdue Extension Education Store. The field guide helps identify common Indiana woodlot trees.
Each week, the Intro to Trees of Indiana web series will offer a sneak peek at one species from the book, paired with an ID That Tree video from Purdue Extension forester Lenny Farlee to help visualize each species as it stands in the woods. Threats to species health as well as also insight into the wood provided by the species, will be provided through additional resources as well as the Hardwoods of the Central Midwest exhibit of the Purdue Arboretum, if available.
 This week, we introduce the Northern catalpa or Catalpa speciose.
This week, we introduce the Northern catalpa or Catalpa speciose.
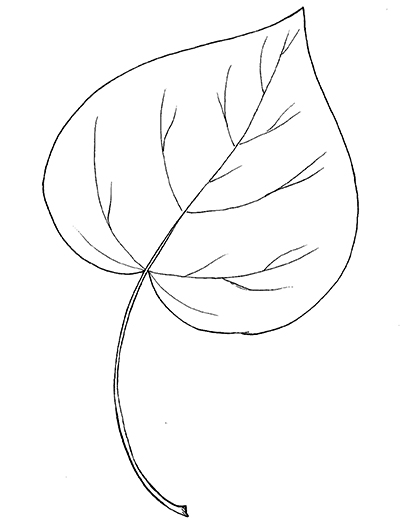
This species, which provides rot resistant wood great for outdoor usage such as fence posts, is native to southern Indiana along the Ohio River bottoms. It features huge heart-shaped leaves in whorled formation, long bean-like fruit pods and beautiful, large clusters of white tubular flower clusters in early summer.
The heart-shaped leaves may be held in either opposite or more commonly in whorled arrangement, meaning three leaves originate at the same point on the twig. The bean-like fruit pods, which contain papery winged seeds, can sometimes be more than two feet in length.
According to the Morton Arboretum, Northern Catalpa can grow 40 to 60 feet tall and between 20 and 40 feet wide. It is native from the lower Midwest into the southern states and from southern Illinois south to Arkansas.
According to the Wood Database, catalpa is rated as durable regarding decay resistance, and is more suited to outdoor carving than other domestic species. It is generally easy to work with hand and machine tools, and common uses are fence posts, utility wood, cabinetry and carving.
Other Resources:
Purdue Plant Doctor
Native Trees of the Midwest
Shrubs and Woody Vines of Indiana and the Midwest
ID That Tree YouTube playlist
Woodland Management Moment YouTube playlist
Investing in Indiana Woodlands
Forest Improvement Handbook






