Students from Purdue Forestry and Natural Resources took their classroom knowledge to the field for summer internships and paid positions across the country, gaining valuable experience, hands-on training and career guidance. The FNR Field Reports series will offer updates from those individuals as summer positions draw to a close.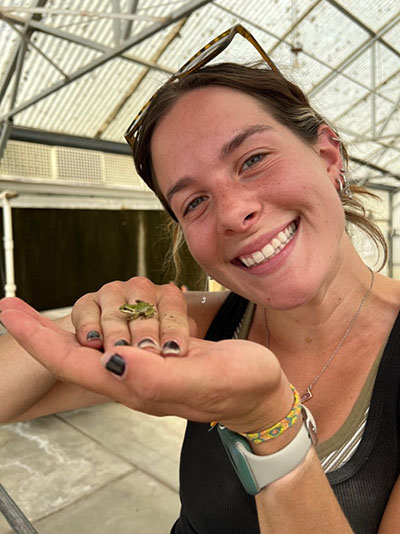
Kadian Brown, a senior forestry major with a forest management concentration, worked as a forest nursery intern at the Franklin H. Pitkin Forest Nursery in Moscow, Idaho.
Brown found the internship in Idaho thanks to Dr. Doug Jacobs.
“I approached Dr. Jacobs after a forest nursery tour during Summer Practicum and asked how I could get involved in nursery work,” Brown recalled. “He put me in touch with the director at Pitkin Forest Nursery. I reached out and was offered an interview and got a job as a summer intern! Having connections through FNR professors has been extremely beneficial in my job searches.”
This summer at the nursery, Brown’s job duties included sowing seeds, mixing fertilizer, irrigation, pruning, and general maintenance of the property.
Brown’s position had her managing the ups and downs of working in a nursery setting.
“My favorite part of the of the job was mixing fertilizer, which was determined by what nutrients each species needed and measured out carefully depending on how many trees were in the lot,” the Clinton, Indiana, native, said. “It was also very cool to see the trees grow over the summer from seeds to foot-tall trees in just a few months!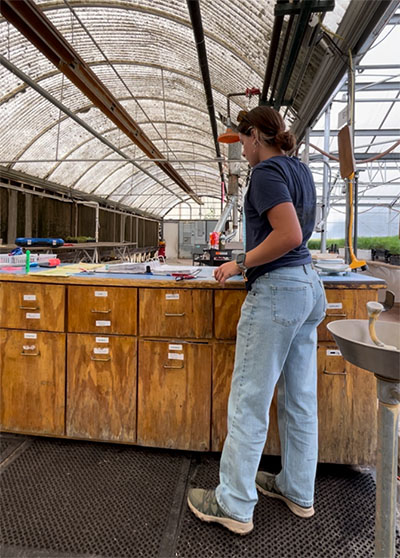 
“The most challenging part was pest management in the greenhouses. Pests include rabbits, fungus, and insects. To mitigate these problems, we set rabbit traps and applied pesticide twice a week. Weeds are another “pest” that we reduced by hand pulling, which was a never-ending task. The Idaho heat sometimes got the best of our hardwoods. It was sometimes very difficult to get everything watered in a day to prevent wilt and sun damage.”
Brown said she was able to see her coursework come to life through the position.
“Through my education in the FNR department at Purdue I have learned how trees grow from a cellular to physiological level; seeing these processes in a real-life setting was very cool to experience,” Brown noted. “I was able to identify nutrient deficiencies by observing foliage changes and my dendrology skills also came in handy when seeing trees that we don’t have in Indiana.”
Working in the forest nursery setting has given Brown new insight into her possible career path.
“It was interesting to learn that many forest nurseries are closing around the country because managers are retiring and the younger generation is not stepping up,” Brown shared. “With major reforestation goals persisting, I wish more people knew about the forest nursery industry so they could learn to appreciate the work that goes into growing trees! Before this internship, I was unsure if this career path was right for me, but being surrounded by supportive professionals in the forest nursery field, I am very excited to pursue this field of work and possibly even start my own forest nursery!”
but being surrounded by supportive professionals in the forest nursery field, I am very excited to pursue this field of work and possibly even start my own forest nursery!”
Brown is set to graduate in May 2024. She is currently involved with the Purdue student chapter of the Society of American Foresters, and is serving as its vice president after spending a year as secretary. She was a member of the Purdue Student Chapter of Environmental Education for two years and was part of the FNR Student Council last year. She also has been an FNR Ambassador since 2021.
In addition to her internship in Idaho this summer, Brown has gained career experience as a camp counselor for the Lilly Nature Camp in the summer of 2022, providing nature related education, and also as a teaching assistant for dendrology this fall.
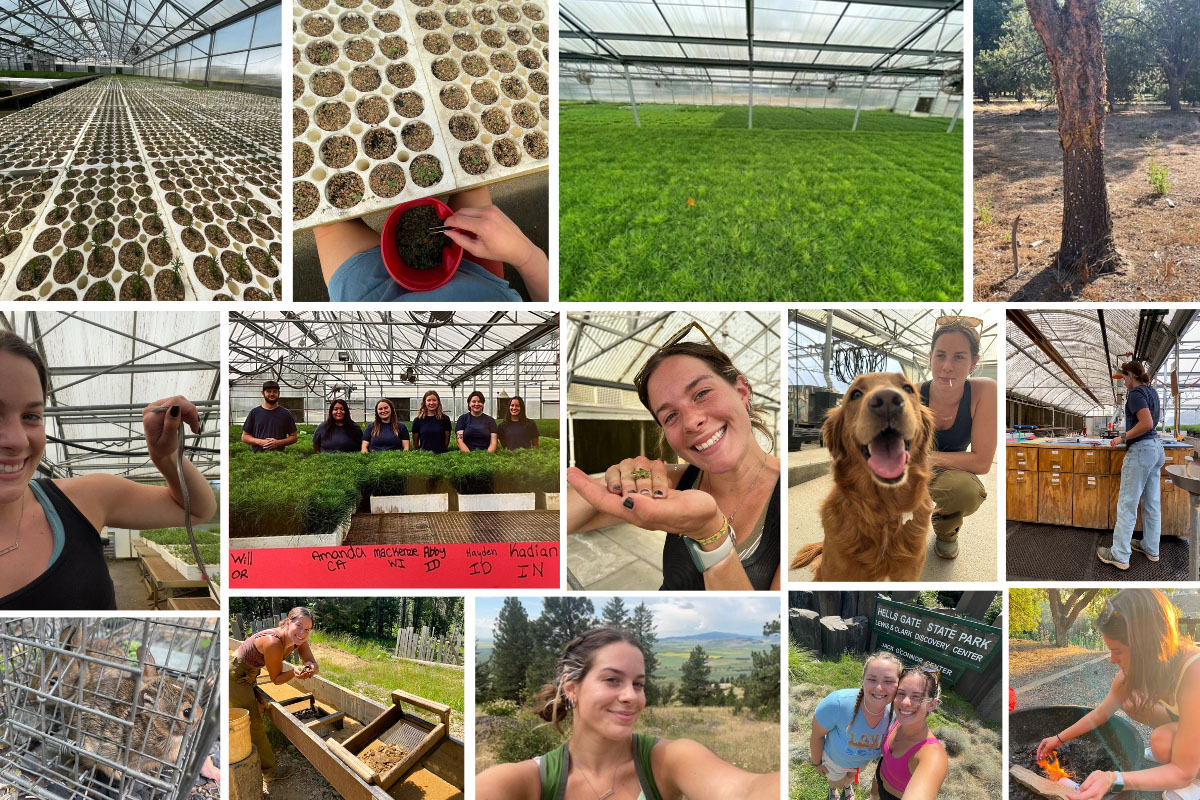 Top row (Left to Right): The greenhouse during Week 1 of Kadian's internship; Thinning and more thinning. Kadian explains "We don’t always know what the germination rate of a seed will be, so you may plant 10 seeds and they all pop up or maybe only two survive. For this reason, we thin each cell down to one seedling once they have had the time to emerge."; The greenhouse during Week 9 of Kadian's internship; A grafted tree fully grown. Trees are grafted in the forest nursery and seed orchard industry to produce offspring that is genetically identical to the mother plant. If the seeds have a high success rate, a grower wants to keep those genetics for future seeds. Row 2: Kadian with a snake found in the greenhouse; Kadian with her fellow interns; Kadian holds a frog found in the greenhouse. She explains that frogs are actually beneficial in the greenhouse because they eat fungus gnats which can damage roots of seedlings.; Kadian with a canine friend in the greenhouse; Kadian mixes fertilizer. She says "it is like making a potion for the plants. We look at what nutrients the plant needs, and include a specifically weighed out amount to the fertilizer. The main nutrients we used were boron, iron, magnesium, and phosphoric acid. Then depending on the state of growth, the plants will receive starter, grower, or finisher. Each species receives a different mixture of fertilizer catered to their needs." Row 3: Some baby bunnies that were caught in the outdoor section of the nursery. Although they are very cute, bunnies will eat the foliage of our plants and severely stunt their growth; Kadian star garnet mining in the Idaho panhandle; Kadian hiking the Palouse in Washington; Kadian camping with a friend at Hell's Gate State Park; Kadian starting a campfire at Hell's Gate State Park.
Top row (Left to Right): The greenhouse during Week 1 of Kadian's internship; Thinning and more thinning. Kadian explains "We don’t always know what the germination rate of a seed will be, so you may plant 10 seeds and they all pop up or maybe only two survive. For this reason, we thin each cell down to one seedling once they have had the time to emerge."; The greenhouse during Week 9 of Kadian's internship; A grafted tree fully grown. Trees are grafted in the forest nursery and seed orchard industry to produce offspring that is genetically identical to the mother plant. If the seeds have a high success rate, a grower wants to keep those genetics for future seeds. Row 2: Kadian with a snake found in the greenhouse; Kadian with her fellow interns; Kadian holds a frog found in the greenhouse. She explains that frogs are actually beneficial in the greenhouse because they eat fungus gnats which can damage roots of seedlings.; Kadian with a canine friend in the greenhouse; Kadian mixes fertilizer. She says "it is like making a potion for the plants. We look at what nutrients the plant needs, and include a specifically weighed out amount to the fertilizer. The main nutrients we used were boron, iron, magnesium, and phosphoric acid. Then depending on the state of growth, the plants will receive starter, grower, or finisher. Each species receives a different mixture of fertilizer catered to their needs." Row 3: Some baby bunnies that were caught in the outdoor section of the nursery. Although they are very cute, bunnies will eat the foliage of our plants and severely stunt their growth; Kadian star garnet mining in the Idaho panhandle; Kadian hiking the Palouse in Washington; Kadian camping with a friend at Hell's Gate State Park; Kadian starting a campfire at Hell's Gate State Park.