Your perfect lawn could be killing pollinators, researchers say
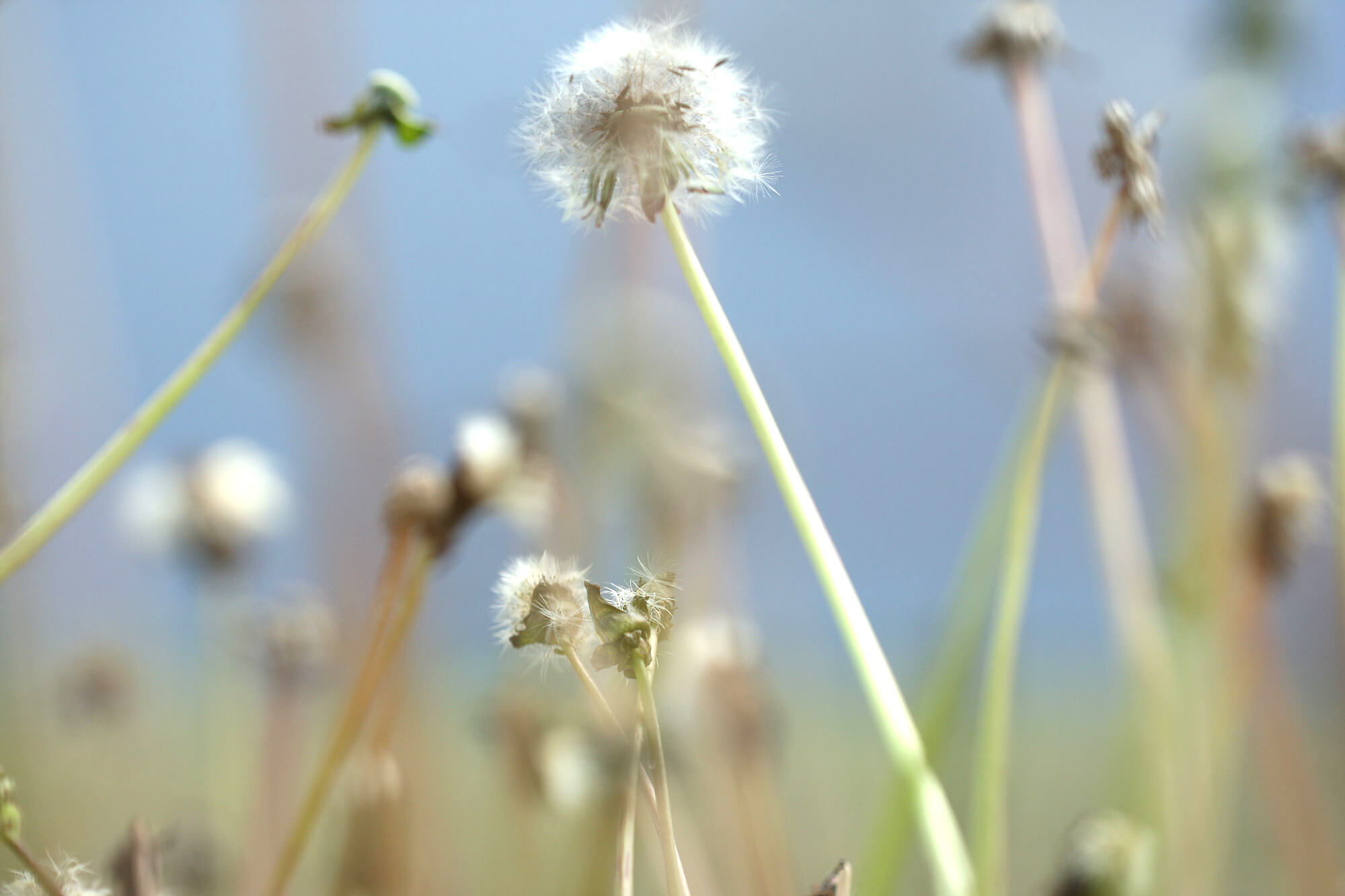
If dandelions, clovers or other perennial weeds seem to be overtaking your lawn, be cautious about using insecticides. That’s one of the recommendations offered by a group of researchers who studied the impact urban lawn care practices have on pollinators.
While flowering weeds may be unsightly to you, they’re food to bees and other pollinators. If you must spray, mow the weeds down first to remove the flowers, the researchers recommend in an in-depth guide published in the Journal of Integrated Pest Management (JIPM). The guide also outlines other recommendations to protect pollinators, including preferred times to apply insecticide.
It’s important to consider the consequences of treating your flowers, including flowering weeds, said Doug Richmond, an associate professor of turfgrass entomology and applied ecology for Purdue’s College of Agriculture.
“We must understand that there are some tradeoffs,” Richmond said. “These pollinators live in our urban environment. There are many ways we can expose them to pesticides unintentionally. If you spray your flowers to protect them from pests, you may be increasing the chance that pollinators will be exposed to that same pesticide.”
American homeowners often think of clovers and dandelions as weeds that need to be destroyed - rather than flowers that attract pollinators, said the guide’s lead author Jonathan Larson, an Extension educator for the University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
“If you’re going to treat your lawn for pests, consider the effect on pollinators,” said Larson, who earned degrees in entomology from Purdue University and the University of Kentucky. “A lot of people often forget that weeds like dandelion and clover are flowers; resources for pollinators. We tend to think of roses, lilacs and violets as flowers.”
Richmond and Larson were among the members of a group that was formed during the 2016 National Turfgrass Entomology Workshop. They developed the guide to distribute lawn care best practices to the general public and turf professionals maintaining spaces like golf courses.
Other recommendations listed in the guide include:
- Wait until May or June to apply pesticides. Early-season pollinators and colonies of bees are still recovering from winter stress in March and April.
- Use granular formulations of insecticides, which fall to the ground and avoid direct contamination of flowering portions of blooming plants.
- Select and plant grass breeds that are resistant to pests.
- Maintain a high mowing height for grass to promote deeper root systems and enhance tolerance to stress and injury from pests.
- Introduce biological control agents, such as parasitic nematodes and fungi that attack pest insects but are generally safe for non-target organisms.
- Establish plots of pollinator-friendly plants, which is an increasingly growing practice among golf course managers and homeowners.
More research needed
With Americans spending about $75 billion a year on lawn care expenses, the impact of certain lawn care practices on pollinators could be more far-reaching than scientists realize. Richmond said there has not been extensive research on the effect of urban lawn care practices on pollinators - an increasing source of concern among scientists because of their vulnerability to environmental stressors.
“We have identified some knowledge gaps in terms of our understanding of pollinator diversity and the impacts of pest management practices in urban landscapes,” Richmond said. “With the exception of Jonathan’s work, there have been surprisingly few studies and almost no synthesis”. This guide was developed to improve our management practices.”
For some perspective, Australia spends the next highest amount on lawn care - $3 billion a year, according to the IBISWorld Landscaping Services market research.
Richmond and Larson stressed Americans may need to change their definition of a perfect lawn.
“We have been convinced, over time, that a perfect lawn is nice, green, lush and completely uniform with no other plants,” Richmond said. “But that’s perfect for what? It’s a human construct.”
Richmond said a “perfect” lawn, which includes turfgrass and other plants, should be considered one that is beneficial “for filtration, cutting down on the heat in urban areas and serving as a habitat for pollinators.”
Larson, who said he doesn’t treat his own lawn with pesticides, said many Americans aren’t satisified until their lawn looks like a golf course. “Understand what your lawn is for. If you want it to look nice, there are more sustainable ways of doing it.”
The researchers who compiled the information for the guide consider it a first step in addressing some of the increasing concerns about protecting pollinators in urban neighborhoods.