Purdue scientist develops method to identify thousands of protein complexes and their location, in one shot
Identifying proteins, the machinery responsible for most of the tasks done in cells, and how they interact with each other is key to improving plants. Using traditional methods, scientists can identify a single protein, which may be one of thousands they want to learn about.
Purdue University research has led to a method for getting at harder-to-reach proteins and identifying thousands of them at one time. The discovery may speed up the ability to understand complex protein interactions and how they control functions such as growth, tolerance to heat and drought, and yield.
Quantitative proteomics is a method to analyze thousands of protein complexes in a single profiling experiment. This has been done only with soluble proteins in the cell that are not attached to a membrane surface.
“About 70 percent of proteins in a plant are associated with membranes. That’s an insoluble pool of proteins with important transport and signaling functions in the cell” said Dan Szymanski, a Purdue professor of Botany and Plant Pathology, whose research was published in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
Szymanski and his graduate student Zach McBride used detergents to solubilize those proteins. The method makes them identifiable and quantifiable without degrading their protein structures.
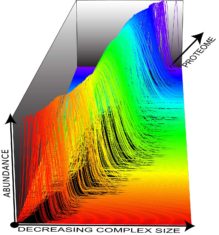
The researchers were able to identify hundreds of large protein complexes — through a process called label-free proteomics. The approach measures native proteins from the cell using mass spectrometry and does not require antibodies to quantify the amount of a protein.
Identifying hundreds or thousands of protein complexes in parallel is key to understanding how complex functions in the plant are controlled. The location of a protein in the plant cell, as well as the proteins that it binds to, will alter that protein’s function.
“In cells, thousands of protein complexes work in a coordinated way to allow the plant to grow and adapt to changing environmental conditions. This method will allow us to analyze how protein complexes function as part of an adaptable network. ” Szymanski said.
Szymanski said he plans to study how protein complexes and plant growth change in response to challenging environmental conditions.