Purdue researcher develops fast, accurate and affordable COVID-19 paper-based test
When the COVID-19 pandemic began and the technologies necessary to combat it came into focus, testing was immediately identified as being top on the list.
Mohit Verma, assistant professor of agricultural and biological engineering (ABE), had been working for years on developing a diagnostic tool to detect Bovine Respiratory Disease (BRD) in cattle using nasal swabs. Verma and his colleagues identified nucleic acids specific to different pathogens that cause the disease and developed a paper-based testing device that was cheap to manufacture, accessible and accurate.
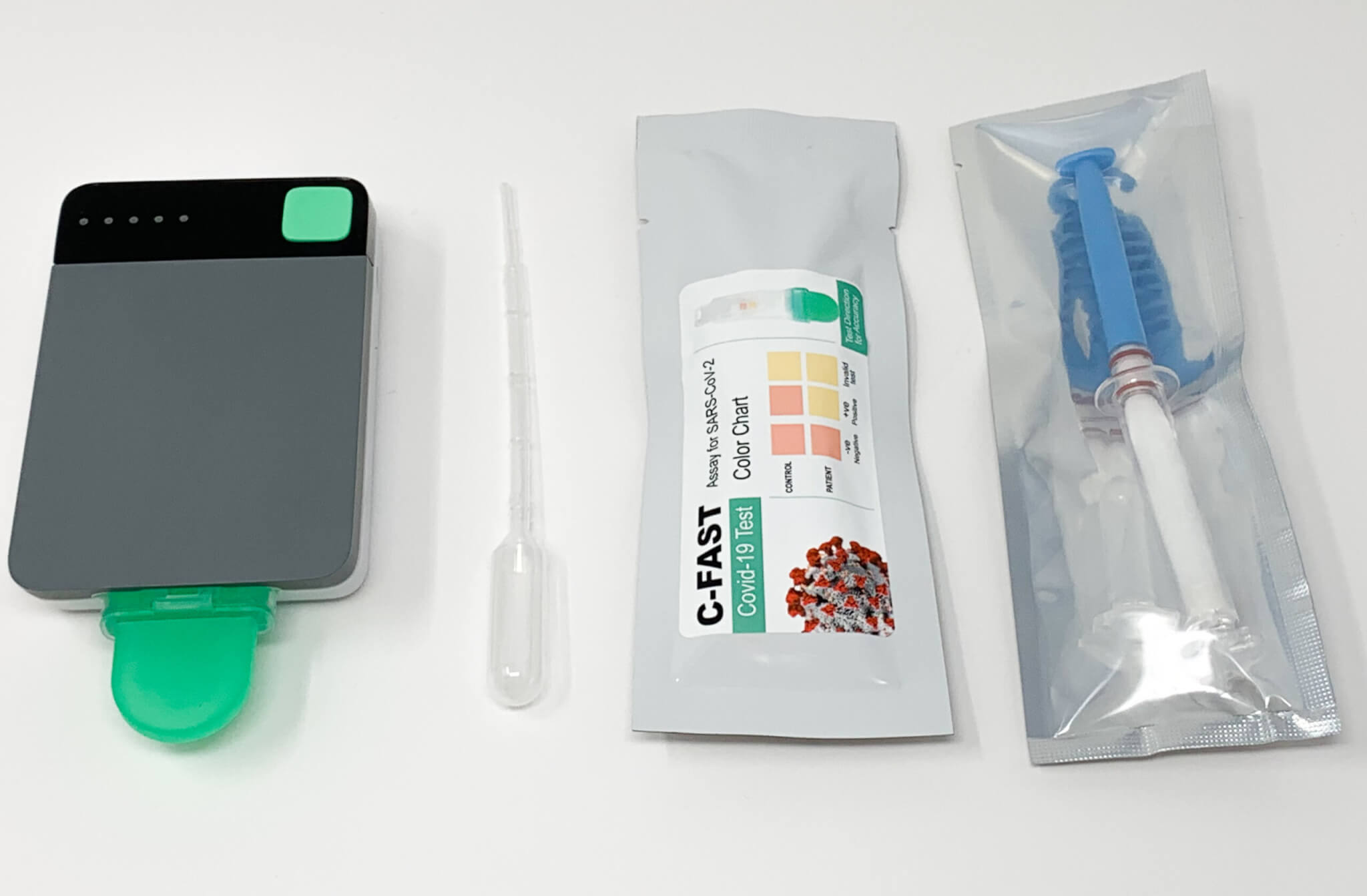
developed by Verma and his lab.
“When COVID-19 hit, that’s exactly the type of testing technologies we needed,” Verma said, and he quickly pivoted his research to developing a scalable testing technology for COVID-19.
Verma’s efforts proved successful with the help of external partners Raytheon BBN, PortaScience, LaDuca RCA and Cortex Design. Verma and his collaborators recently published a paper in the journal Biosensors and Bioelectronics: X that demonstrates the effectiveness of this device in combatting public health crises like COVID-19. The test takes only 60 minutes to deliver a response and has an analytical specificity of 100 percent. Using only saliva, the device has the potential to test for various strains of COVID-19 at the same time.
“Paper based diagnostics like this have great potential to scale-up and be used in a variety of circumstances for humans and animals,” Verma added.
Before this scale-up can happen for the COVID-19 tests, clinical trials must be performed, which Verma said would be a hurdle getting these tests into the marketplace. Due to biosafety restrictions at Purdue and his lab, he can’t conduct these trials, but the technology can be handed to a third party for this process.
“As the virus behind COVID continues to evolve and mutate, our paper-based technology, which could quickly test for multiple pathogens, could become extremely relevant in our ongoing fight against the virus,” Verma added.






