Intro to Trees of Indiana: Blue Beech
The classic and trusted book "Fifty Common Trees of Indiana" by T.E. Shaw was published in 1956 as a user-friendly guide to local species. Nearly 70 years later, the publication has been updated through a joint effort by the Purdue Department of Forestry and Natural Resources, Indiana 4-H, and the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, and reintroduced as "An Introduction to Trees of Indiana."
A printed copy of the full publication is available for purchase for $7 in the Purdue Extension Education Store. The field guide helps identify common Indiana woodlot trees.
Each week, the Intro to Trees of Indiana web series will offer a sneak peek at one species from the book, paired with an ID That Tree video from Purdue Extension forester Lenny Farlee to help visualize each species as it stands in the woods. Threats to species health as well as also insight into the wood provided by the species, will be provided through additional resources as well as the Hardwoods of the Central Midwest exhibit of the Purdue Arboretum, if available.
 This week, we introduce the Blue Beech or Carpinus caroliniana.
This week, we introduce the Blue Beech or Carpinus caroliniana.
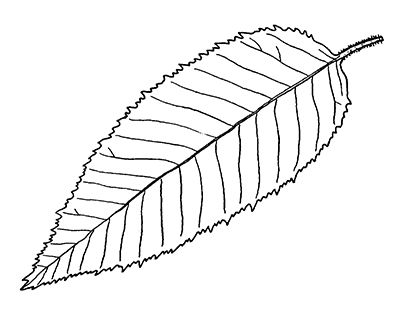
The blue beech, also known as the American hornbeam, musclewood or the water beech, is an understory tree that stands out due to its gray bark and striations that resemble muscles and sinews as well as its doubly toothed leaves.
The small tree, which typically grows to a height of 20 to 35 feet, has oblong leaves with doubly toothed leaf margins, arranged alternately on very fine twigs. Lower leaf veins are seldom forked. The fruit is in clusters, consisting of small, seed-like nuts on small, three-lobed leaves. It's bark and fruit help differentiate blue beech from its close relative, the ironwood.
Blue beech's natural range is the majority of the midwestern and eastern United States, reaching as far south as Texas.
Blue beech can be used an ornamental tree in urban parks and large backyards. According to the University of Minnesota's Extension, the wood can be used for tool handles, although due to the small statue of the tree it is not practical for commercial harvesting.
Beech - Hardwood Lumber and Veneer Series
Purdue Plant Doctor
Native Trees of the Midwest
Shrubs and Woody Vines of Indiana and the Midwest
ID That Tree YouTube playlist
Woodland Management Moment YouTube playlist
Investing in Indiana Woodlands
Forest Improvement Handbook






