January 25, 2013
Alternative Futures for Agriculture: A Scenario Analysis Exercise
This paper describes the results of a scenario analysis exercise conducted at the Center for Commercial Agriculture Advisory Council meeting January 23-24, 2013. The description is provided as a way to illustrate the process of scenario analysis. It was also conducted to provide insights as to the factors that commercial farmers and agribusinesses consider when evaluating scenarios and how management strategies might evolve in these scenarios.
Description of the Scenario Analysis Exercise
The point of scenario analysis is not to predict how the future will unfold, but rather to consider different scenarios that might occur and what the economic environment might look like in these scenarios. Participants then use these situations to consider what strategies their businesses might use were these situations to occur. In doing so, the hope is that participants begin to form a view for how they might alter their strategies were the economic situation to change, and what strategies they would want to employ regardless of the economic environment.
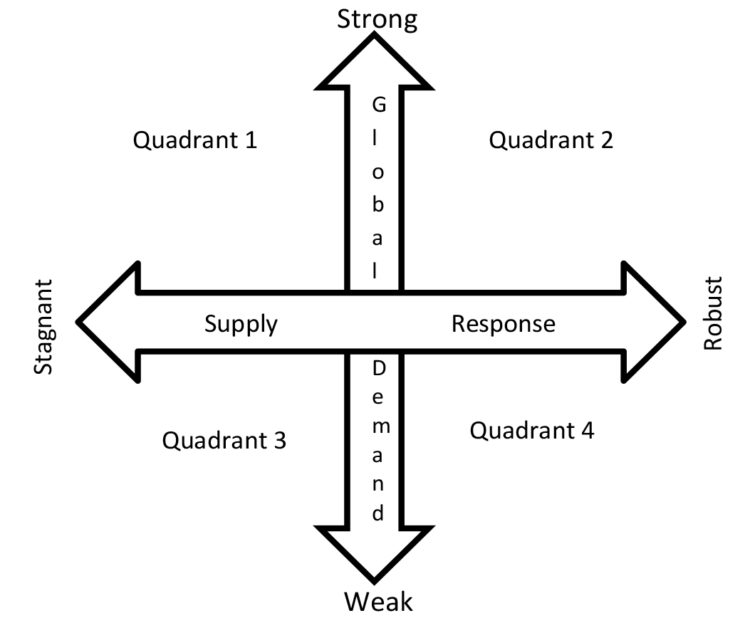
While any number of initial conditions might be considered in a scenario analysis exercise, this exercise focused on two dimensions of economic conditions, global agricultural demand and supply response. These two factors were chosen for analysis because it is expected that both will play a key role in determining farm level economic conditions. Both of these conditions were ranged from strong to weak, resulting in the four-quadrant matrix depicted in Figure 1. In this diagram, supply response is shown on the horizontal axis and global demand on the vertical axis. For example, quadrant 1 consists of strong global demand and stagnant or slow supply agricultural supply response.
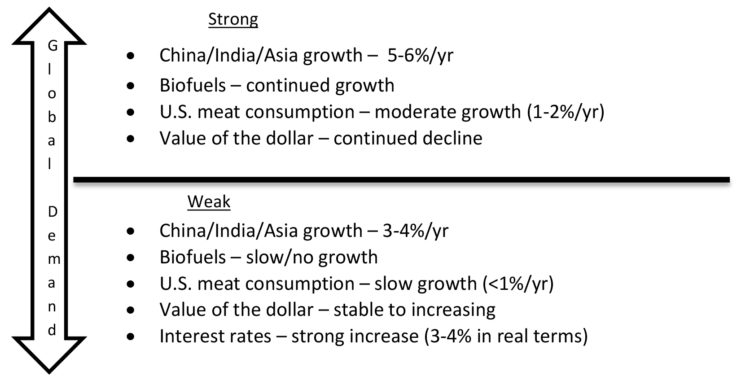
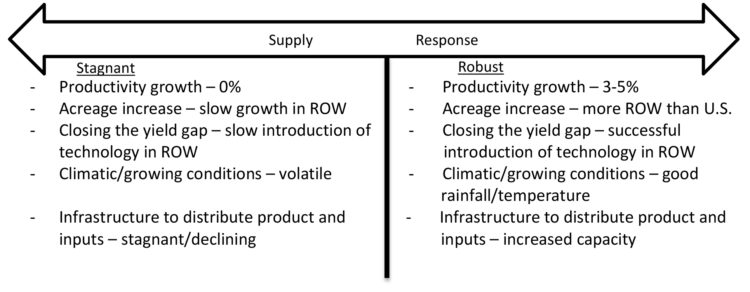
Before proceeding participants were given some guidelines as to what might characterize the economic conditions. This was done to level the field and make sure that all participants were considering different conditions in the various quadrants — otherwise one group might characterize strong global demand the same way that another characterizes weak demand. Figure 2 shows the conditions that were assumed to characterize the global demand scenarios and Figure 3 the agricultural supply response scenarios.
Developing the Scenario Matrix
Next participants were assigned to one of the four quadrants and asked to more definitively describe the business climate in their quadrant. Specifically, they were asked to describe the events that would cause their quadrant to materialize. For example, what would cause China to grow at the assumed amount per year, or what might cause interest rates to change by the assumed amount? Participants were asked to consider factors that might not have been identified in the stage setting that would be important in causing their quadrant to materialize. They were also asked to identify how the realization of these factors would impact output prices, input costs, margins, volatility, and asset values. They were then asked to consider the appropriate business strategies in their respective quadrants. Participants were broken into groups to discuss each quadrant and then the group discussed each quadrant in succession.
Quadrant 1: Strong Demand and Stagnant Agricultural Supply Response
The group felt that this scenario described the situation that has been prevalent the last 5 years. Some of the factors that might cause this situation to continue included the following:
- Strong global economic growth
- Strong China demand with China fiscal/monetary policy that stimulates growth
- Weaker dollar
- Agricultural R&D continues at current pace
- Weather cyclicality continues
- Trade policy encourages growth
- No U.S. supply chain/transportation disruptions
- Environmental concerns increase limiting production increases
- Slow biotech adoption in the rest of the world
- Capital for supply expansion in rest of world restricted/limited
- Continuing biofuel development
- Disruptive weather events in major agricultural regions
- Economic recovery in Europe strengthens
The group also considered some of the outcomes that might occur in their businesses. The consensus was for the following:
- Corn prices in the range of $5-7 and perhaps $6-10
- Costs remain high – higher spikes
- Margins up
- Volatility up
- Asset values up
In terms of business strategies the group felt the following would be appropriate:
- Strong growth – 10% per year
- Increase access to debt and equity
- Buy assets
- Careful with liquidity, but can be aggressive in debt use
- Rapid adoption of technology – embrace cutting edge technology
- Less aggressive risk management because margins are high
- More specialization
- Control more land (rent preferred)
Quadrant 2: Strong Demand and Robust Agricultural Supply Response
The group felt that there was a possibility that the current situation was moving toward quadrant 2. In this scenario agricultural supply response is strong as is demand. The group expected the following conditions might give rise to this situation.
- China ties their currency to the dollar
- Strong domestic China demand
- Strong oil demand
- Strong exports
- Biofuel demand strong
- Higher GMO acceptance/adoption
- U.S. inflation moderate
- Reductions in unemployment
- Livestock sector adjusts (downsizes to reduced demand)
- U.S. economic recovery
- Supply stays ahead of corn demand but only slightly
The group felt that the following would best characterize prices, costs, margins, volatility, and asset values in this quadrant:
- Lower corn prices perhaps in the range of $4.5 – 6 per bushel
- Costs up
- Margins down/squeezed
- Volatility down
- Asset values flat
Were this scenario to arrive they felt that the most prudent business strategies would include the following:
- Growth – moderate 2-3% per year
- Less leverage
- Aggressive technology adoption
- Rent land
- Lock in positive margins
- Diversify
Quadrant 3: Weak Demand and Stagnant Agricultural Supply Response
In this scenario the economic environment for agricultural producers is less desirable than the current situation. Some of the factors that might cause this to happen include the following:
- Stronger economic growth in U.S. but not enough to pull the rest of the world forward and a strengthening U.S. dollar
- Volatility in rest of the world
- Dollar value up because of volatility of rest of the world
- Weakening of oil prices
- Flat biofuel demand
- China exports weak and internal Chinese financial issues
- Risk premiums increase due to poor business climate
In terms of agricultural outcomes the group saw the following as possible in this quadrant:
- Lower agricultural prices perhaps corn prices in the $4-4.5 per bushel range
- Costs down
- Margins negative
- Volume down
- Asset values down (and trade stops)
- Farmer exits
As for strategies that might be appropriate:
- Limited growth, must be strategic, “wait for opportunity”
- More cost control/debt reduction
- Adopt proven technology; less acceptance of cutting edge innovations
- Strategic land control/acquisition/liquidation
- Reduce exposure to risk
- Lock margins when available
- Focus on core for expansion
- Strong initial financial position good for growth
- Partnerships to spread risk and manage cost margin
Quadrant 4: Weak Demand and Robust Agricultural Supply Response
This scenario is the least attractive situation considered. Some of the factors that might give rise to this situation would include:
- Economic struggles in the developed world
- Loss of confidence in developed world debt
- Flat oil prices
- Less aggressive biofuel policy expansion
- Weak China growth
- Weak policy safety net/emergency legislation
- Strong dollar
- Strong GMO/tech adoption in rest of world
- Emerging economies continue towards self sufficiency
- Emerging market producers expand
The agricultural outcomes in this situation were seen as unfavorable to most farmers. They might include:
- Significantly lower crop prices for example corn at $3 per bushel
- Costs down but not immediately
- Margins down on everything
- Volatility perhaps lower but generally resulting in undesirable prices
- Asset values 20 – 40% down
- Lower oil prices
The strategies that might be appropriate in this scenario included the following:
- Pause and hunker down to make it through the lower cycle
- Look for opportunities for expansion when they become available
- Conservative financial strategy
- Deleverage
- Adopt technology if it lowers cost but has to show clear benefit
- Risk management to protect cash positions even at economic losses
- Less risky crop mix
- Focus on lowering costs
- Realistic downsizing if necessary
Summary of the Scenario Analysis Exercise
Overall, the scenario analysis exercise was useful in helping us think about the factors that are likely to drive the economic future and to prepare for different possibilities. One outcome of the exercise was the development of a list of factors that constitute things to watch in the economic environment. These included factors such as weather, environmental and political issues in South America, biofuel policy, European economic outcomes, China economic conditions, and trade/geopolitical risk. The group felt that paying attention to these factors might help them identify when conditions are changing and when business strategies might require alteration. Further, the exercise allowed participants to ask themselves what they might do were economic conditions to change. It is unlikely that conditions will evolve exactly as in this exercise, but it is hoped that the mental preparations associated with this exercise will put farmers in a better position to react when conditions begin to change.
TAGS:
TEAM LINKS:
RELATED RESOURCES
UPCOMING EVENTS
We are taking a short break, but please plan to join us at one of our future programs that is a little farther in the future.