October 12, 2023
Impact of Lower Corn Prices On Feeding Cost of Gain for Cattle Finishing
by Michael Langemeier
Cash corn prices in Kansas were over $7 per bushel in the first 4 months of 2023, peaking in February at $7.35 per bushel. The average corn price in August, the latest month for which data is available from USDA-NASS, was $5.70 or 22% lower than the average corn price in February. Corn futures prices for 2024 currently range from $5.00 to $5.20 per bushel. Thus, corn prices are expected to remain below the levels experienced in the last couple of years for the foreseeable future. This article examines the impact of lower corn prices on feeding cost of gain for cattle finishing.
Feeding Cost of Gain
Feeding cost of gain is sensitive to changes in feed conversions, corn prices, and alfalfa prices. Information on these items are available from monthly issues of the Focus on Feedlots newsletter. Figure 1 illustrates feeding cost of gain from January 2013 to August 2023. In August 2023, corn and alfalfa inventory prices were $7.04 per bushel and $273 per ton, respectively. After averaging $125 per cwt. in 2022, feeding cost of gain averaged $147 and $145 per cwt. for the first and second quarters of 2023. Feeding cost of gain in August was $141.83. It is important to note that since this estimate was made corn prices have continued to decline.
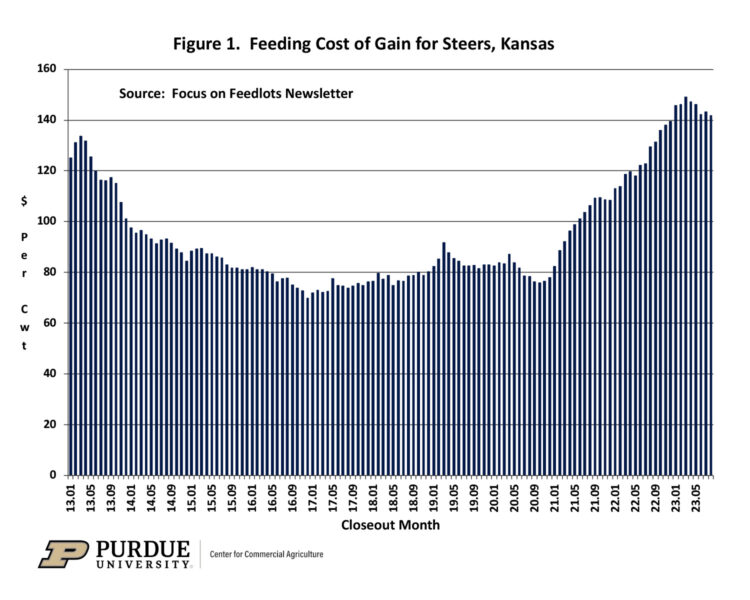
Figure 1. Feeding Cost of Gain for Steers, Kansas
Feeding of gain for the rest of 2023 was estimated using early October projections of corn and alfalfa prices, and seasonal average feed conversions. Because feeding cost of gain is computed using corn prices from the time cattle are placed to the time they are sold, corn prices experienced earlier this year will impact feeding cost of gain for the next several months. With this in mind, feeding cost of gain for the third quarter of 2023 is expected to range from $134 to $143 per cwt., with the highest cost occurring in July. For the fourth quarter, feeding cost of gain is expected to range from $115 to $130 per cwt. Feeding cost of gain for the first six months of 2024 is expected to range from $103 to $112 per cwt. Is it possible for feeding cost of gain to drop below $100 per cwt.? The answer is yes, but this is not likely to occur unless corn price this fall and winter drops below $4.50 per bushel.
Sensitivity of Feeding Cost of Gain to Changes in Corn Prices
To determine the sensitivity of feeding cost of gain to changes in corn prices, alfalfa prices, and feed conversion, a regression using data for the last ten years was estimated. Results are as follows: each 0.10 increase in feed conversion increases feeding cost of gain by $1.33 per cwt., each $0.10 per bushel increase in corn prices increases feeding cost of gain by $0.96 per cwt., and each $5 per ton increase in alfalfa prices increases feeding cost of gain by $0.53 per cwt. To more fully understand the impact of feed conversion, corn price, and alfalfa price on feeding cost of gain, we computed coefficients of separate determination (Langemeier et al., 1992). These coefficients can be used to measure the influence of each independent variable upon the dependent variable. The sum of the coefficients of separate determination for each variable equals the R-square goodness of fit measure, which was 0.959 for the feeding cost of gain regression. This goodness of fit statistic indicates that 95.9 percent of the variation in feeding cost of gain was explained by fluctuations in feed conversions, corn prices, and alfalfa prices. Computed coefficients of separate determination indicated that corn price explained approximately 76 percent of the variation in feeding cost of gain.
To further examine the sensitivity of feeding cost of gain to changes in the corn price, let’s use the farmdoc Price Distribution Tool and the March 2024 corn futures contract. The mid-point price is currently about $5 per bushel. The 25% and 75% percentile prices are approximately $4.60 and $5.40, respectively. Feeding cost of gain at the mid-point price is $107 per cwt. At the 25% and 75% percentile corn prices, feeding cost of gain would be $103 and $111 per cwt., respectively. This analysis strengthens the argument made above that corn price would need to drop below $4.50 for feeding cost of gain to fall below $100 per cwt.
Summary and Conclusions
Corn prices have declined substantially since the first half of this year. This article examined the impact of higher corn prices on feeding cost of gain for cattle finishing. Using projected corn prices, feeding cost of gain is expected to decline from $142 per cwt. in August to $114 in December, and then remain in the $103 to $112 per cwt. range for the first 6 months of 2024. However, it is important to note than each $0.10 change in corn price results in a change feeding cost of gain of $0.96 per cwt. Thus, it would not take a particularly wide swing in corn prices to change our projections.
References
Focus on Feedlots, Animal Sciences and Industry, Kansas State University, www.asi.k-state.edu/about/newsletters/focus-on-feedlots , accessed October 11, 2023.
Langemeier, M., T. Schroeder, and J. Mintert. “Determinants of Cattle Finishing Profitability.” Southern Journal of Agricultural Economics. 24(December 1992):41-47.
TAGS:
TEAM LINKS:
RELATED RESOURCES
UPCOMING EVENTS
We are taking a short break, but please plan to join us at one of our future programs that is a little farther in the future.
