Study identifies interaction that promotes cancerous state in cells
When the machinery that guides the transition of stem cells to somatic cells doesn’t shut down properly, cells can become cancerous. Identifying the mechanisms that impede those processes would offer scientists a target for cancer research.
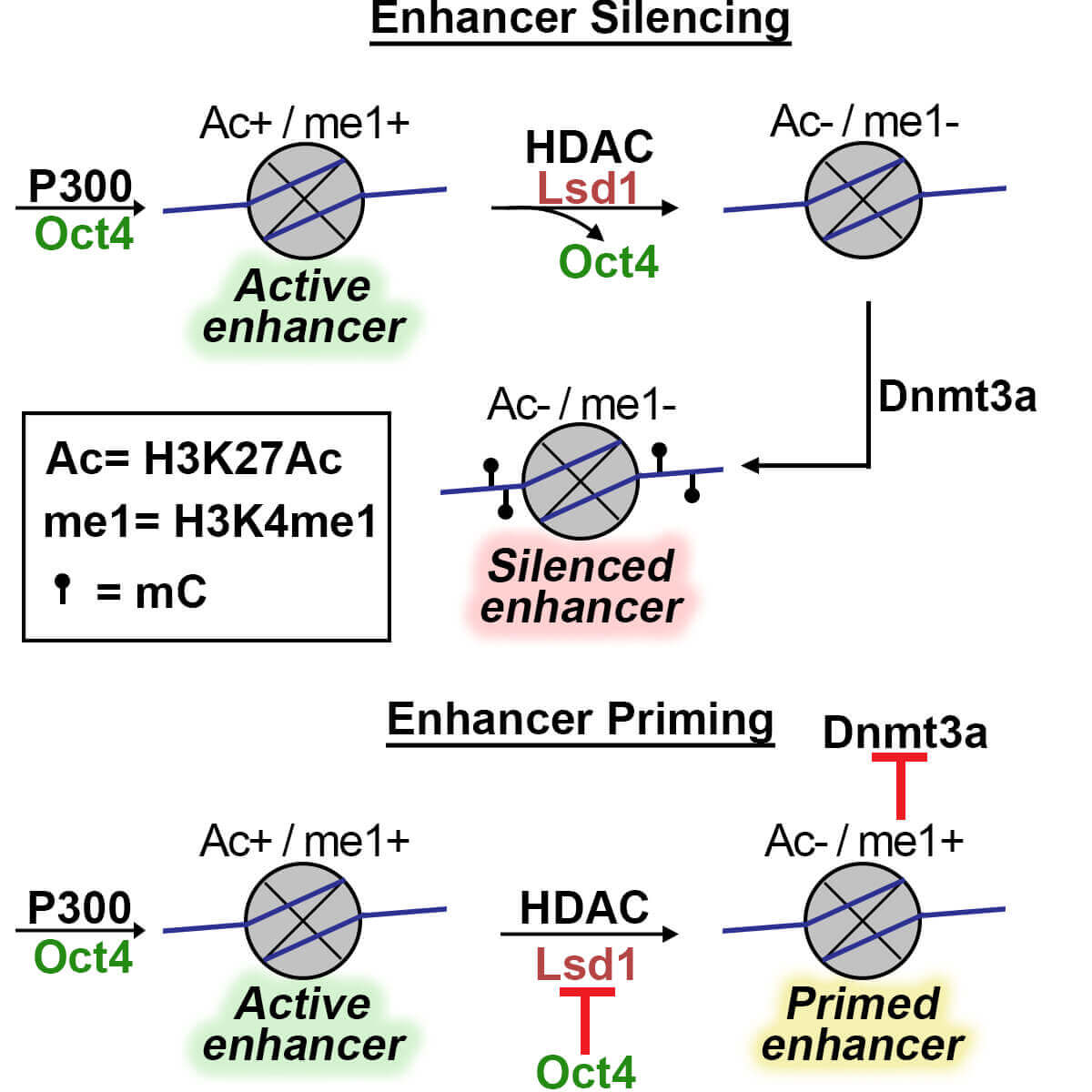
Purdue University scientists, led by Humaira Gowher, an associate professor in the Department of Biochemistry, have discovered the epigenetic process that keeps stem cell enhancers in active, primed or repressed states. In particular, her team has identified a protein-protein interaction that blocks proper formation of these states.
The findings, published in the journal Cell Reports, show that the OCT4 protein interferes with a sequence of events that shut down a cell’s “stemness” when cells differentiate and should no longer be able to duplicate themselves. Removing that interference could stop cancer cells from proliferating.

Cancers can be difficult to eradicate because they maintain this stemness that allows them to continue proliferating. Scientists have shown that only some cancer cells can be forced into terminal differentiation with treatment by retinoic acid. The embryonic carcinoma cells Gowher’s team works can be used as a model to study the resistant cancer cells.
Gowher’s lab had previously discovered that as normal embryonic stem cells differentiate, they repress their stemness genes by epigenetically silencing specific control elements called enhancers through DNA methylation, which is the addition of methyl groups to a segment of DNA that changes the DNA’s activity. The group also discovered that an enzyme, Lsd1, assists in the acquisition of DNA methylation.
But these stemness genes are incompletely repressed in some carcinoma cells leading to only partial differentiation.
“If you differentiate normal stem cells, they should silence their pluripotency gene enhancers, but these cells are not doing that. They’re leaving the enhancer program partially open,” Gowher said. “We’ve uncovered the issue that shelves these cells in some kind of intermediate, rather than in terminally differentiated, state.”
The primed enhancers are susceptible to reactivation that can lead to renewed cell multiplication. It’s likely why the cancer stem cells resist differentiation therapy.
“What people have seen in some cancers is that enhancers exist in a primed state,” Gowher said. “It can potentially help the cancer stem cells survive and propagate. It’s a pro-survival mechanism.”
Gowher and colleagues showed that this was because the activity of Lsd1 is inhibited by stem cell transcription factor OCT4 in these cells.
“Because of this aberrant presence of OCT4, cells aren’t completely differentiating,” Gowher said. “If you could inhibit the OCT4-Lsd1 interaction, or target degradation of OCT4, that should allow the cells to differentiate. That could be a target for a cancer therapy.”
Going forward, Gowher plans to determine the interface of Lsd1-OCT4 interaction and identify other transcription factors that may inhibit Lsd1 activity.