 The classic and trusted book "Fifty Common Trees of Indiana" by T.E. Shaw was published in 1956 as a user-friendly guide to local species. Nearly 70 years later, the publication has been updated through a joint effort by the Purdue Department of Forestry and Natural Resources, Indiana 4-H, and the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, and reintroduced as "An Introduction to Trees of Indiana."
The classic and trusted book "Fifty Common Trees of Indiana" by T.E. Shaw was published in 1956 as a user-friendly guide to local species. Nearly 70 years later, the publication has been updated through a joint effort by the Purdue Department of Forestry and Natural Resources, Indiana 4-H, and the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, and reintroduced as "An Introduction to Trees of Indiana."
A printed copy of the full publication is available for purchase for $7 in the Purdue Extension Education Store. The field guide helps identify common Indiana woodlot trees.
Each week, the Intro to Trees of Indiana web series will offer a sneak peek at one species from the book, paired with an ID That Tree video from Purdue Extension forester Lenny Farlee to help visualize each species as it stands in the woods. Threats to species health as well as also insight into the wood provided by the species, will be provided through additional resources as well as the Hardwoods of the Central Midwest exhibit of the Purdue Arboretum, if available.
 This week, we introduce the Kentucky Coffeetree or Gymnocladus dioicus.
This week, we introduce the Kentucky Coffeetree or Gymnocladus dioicus.
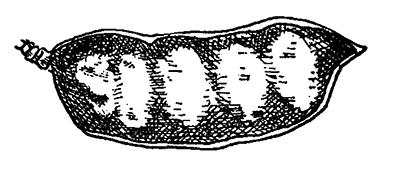
This native species, which is part of the broad legume family, historically provided a substitute for coffee, care of the dark bean like seeds held within its fruit, which is in the form of a wide, thick-shelled pod.
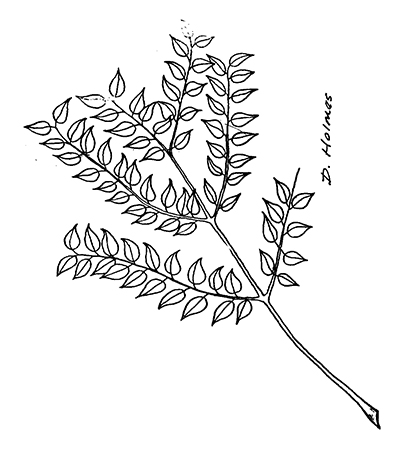
It is easily identifiable by its large seed pods, long doubly-compound leaves and textured, flaking/peeling bark with vertical ridges. Its compound leaves, sometimes two feet or more in length, are arranged alternately on very thick twigs that have a mottled color and a distinct, salmon-colored pith.
This tree is found in many parts of the state, but it is never a common tree and is usually widely scattered. According to the Morton Arboretum, Kentucky coffeetree is tolerant to pollution and a wide range of soils making it a suitable tree for urban environments.
This species can grow to up to 100 feet in height and as large as five and a half feet in diameter at breast height.
The wood of Kentucky Coffeetree has a very coarse grain pattern and ranges from reddish brown to reddish orange. Its growth rings tend to undulate or weave throughout the board. The wood of this species is often confused with honey locust.
Kentucky coffee tree wood weighs 42 pounds per cubic foot, nearly as much as oak. It is mainly used for posts and railroad ties as it is moderately resistant to decay. It is also used for small runs of furniture, millwork or paneling.
Other Resources:
Kentucky Coffeetree - Hardwoods of the Central Midwest
Top 5 List for Tree Selection and Planting
Fifty Trees of the Midwest app for the iPhone
Native Trees of the Midwest
Shrubs and Woody Vines of Indiana and the Midwest
ID That Tree YouTube playlist
Woodland Management Moment YouTube playlist
Investing in Indiana Woodlands
Forest Improvement Handbook





